Embed presentation
Download to read offline

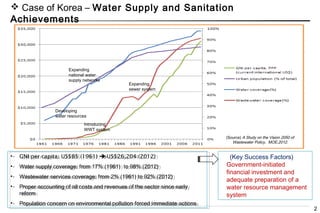

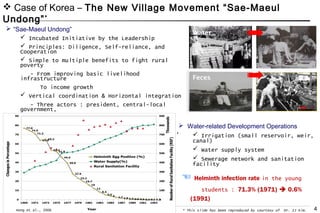
The document discusses Korea's substantial advancements in water supply and sanitation from 1961 to 2012, highlighting improvements in coverage and investments driven by government initiatives and foreign aid. Key success factors include effective planning, financial investment, and community engagement through the 'New Village Movement' which emphasized local cooperation and infrastructure development. Lessons learned underscore the importance of integrating water sector development into economic growth strategies and the role of comprehensive monitoring and regulatory frameworks.



