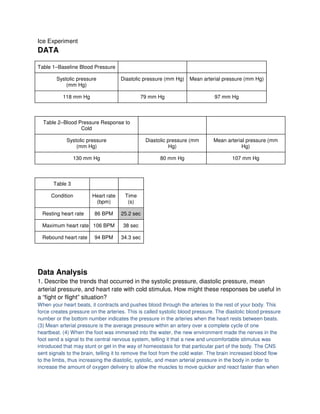
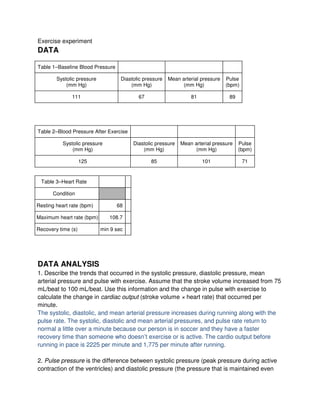
1. The data tables show the subject's baseline blood pressure and heart rate measurements, as well as measurements taken after exercising. Systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressures all increased after exercise, as did heart rate.
2. Cardiac output increased from 2225 mL/min at baseline to 2775 mL/min after exercise due to an increase in stroke volume from 75 mL to 100 mL and a decrease in heart rate from 89 bpm to 71 bpm.
3. Pulse pressure, the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure, increased after exercise primarily due to an increase in stroke volume ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat.