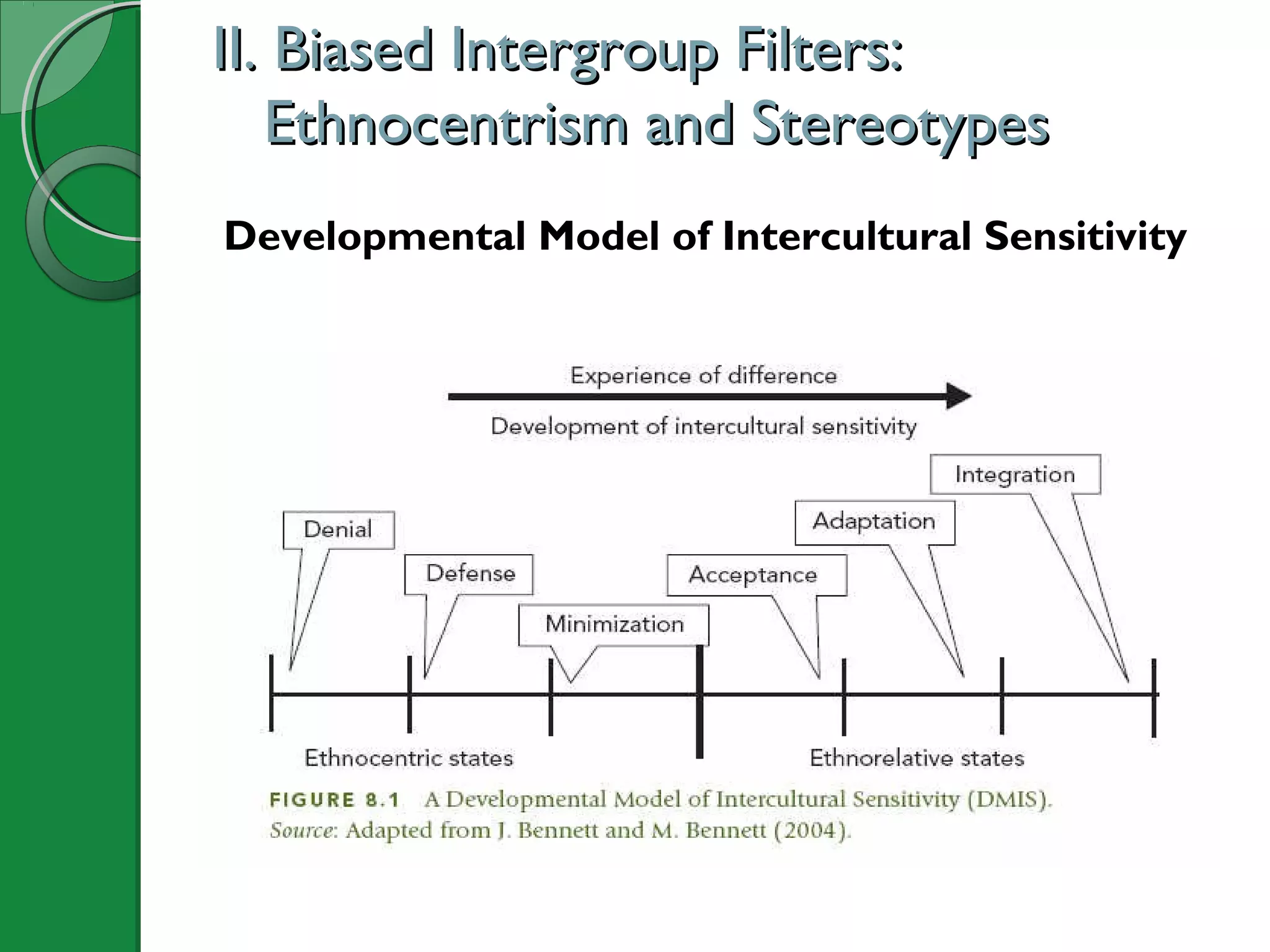
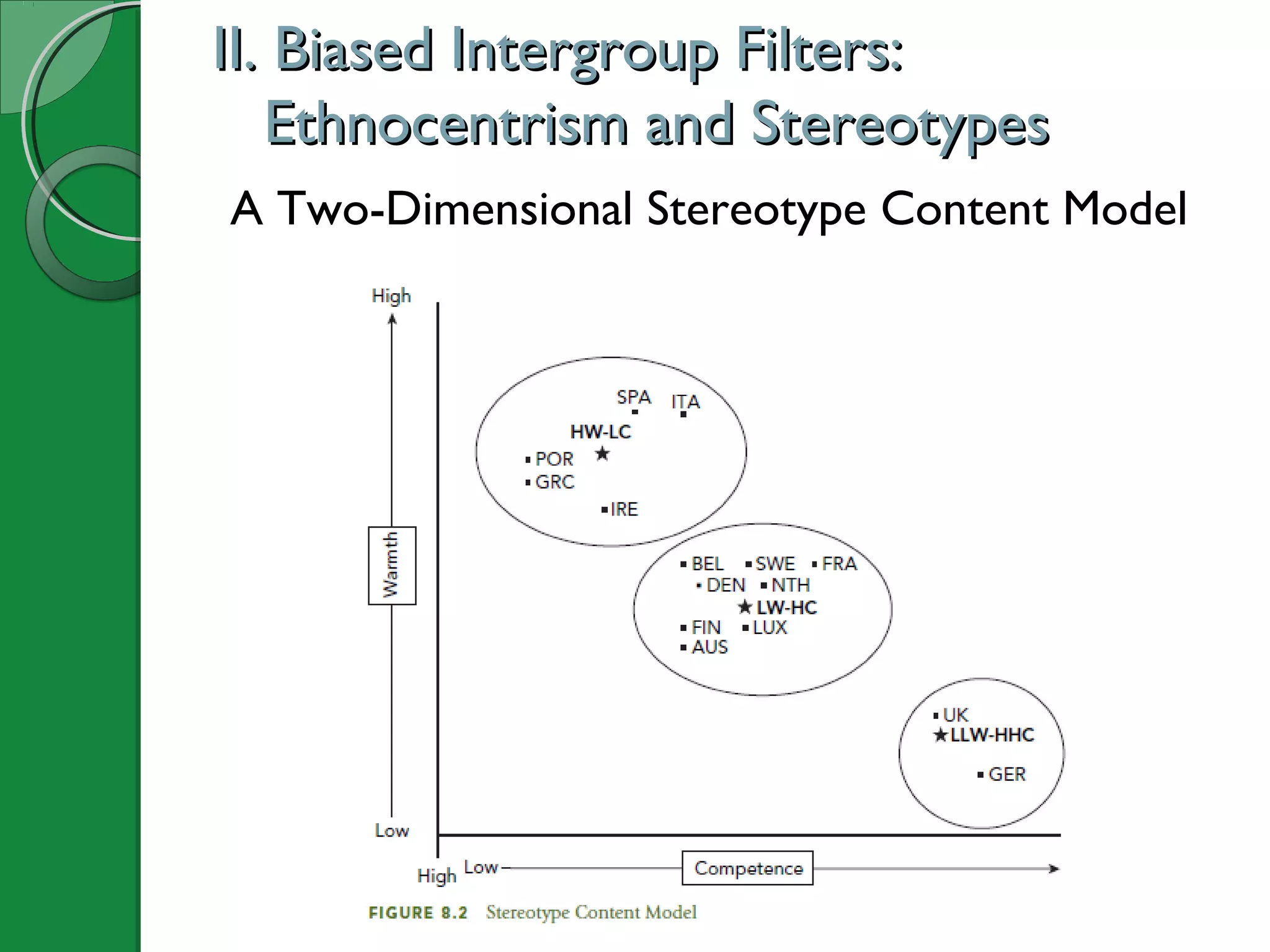
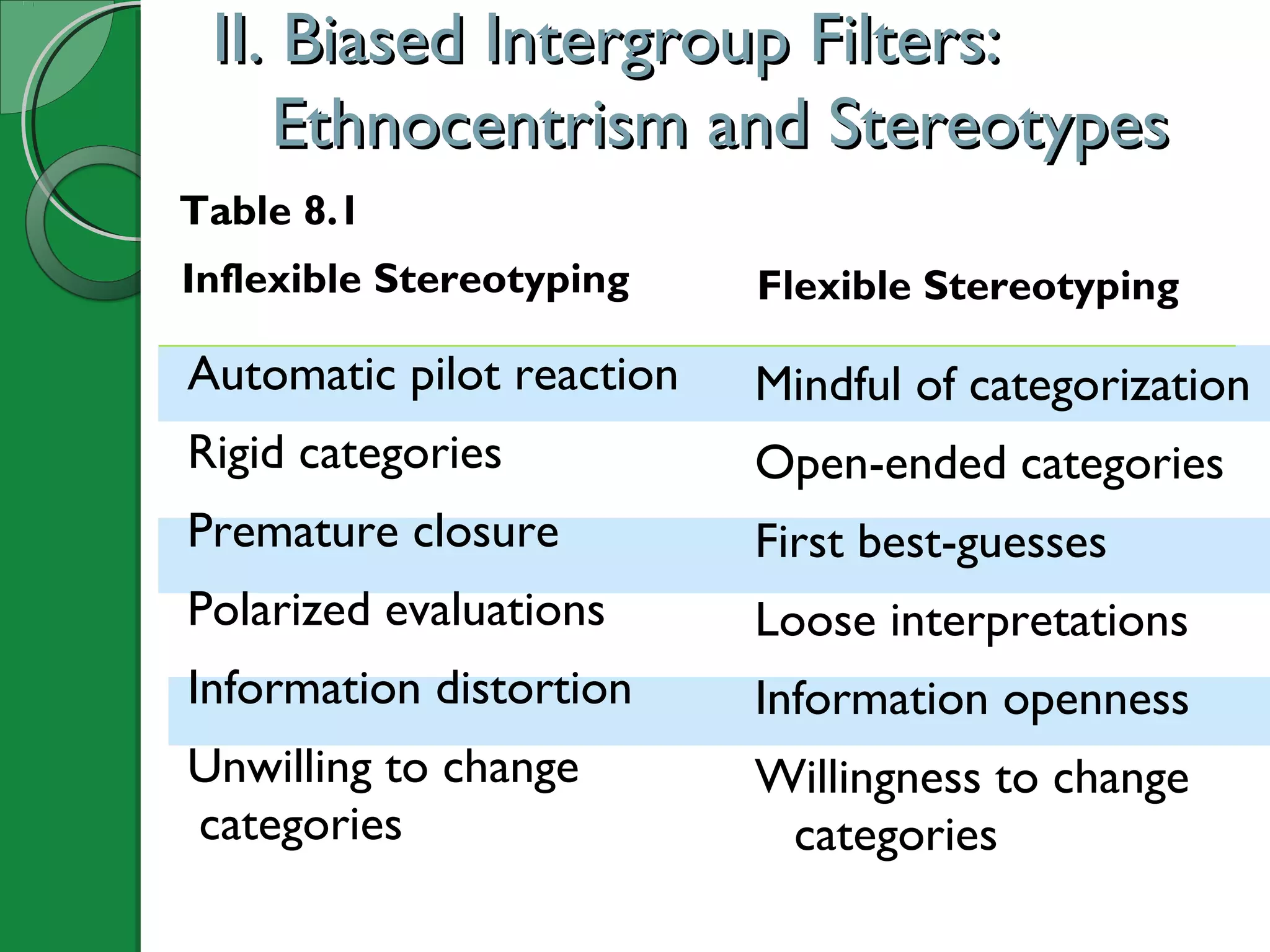
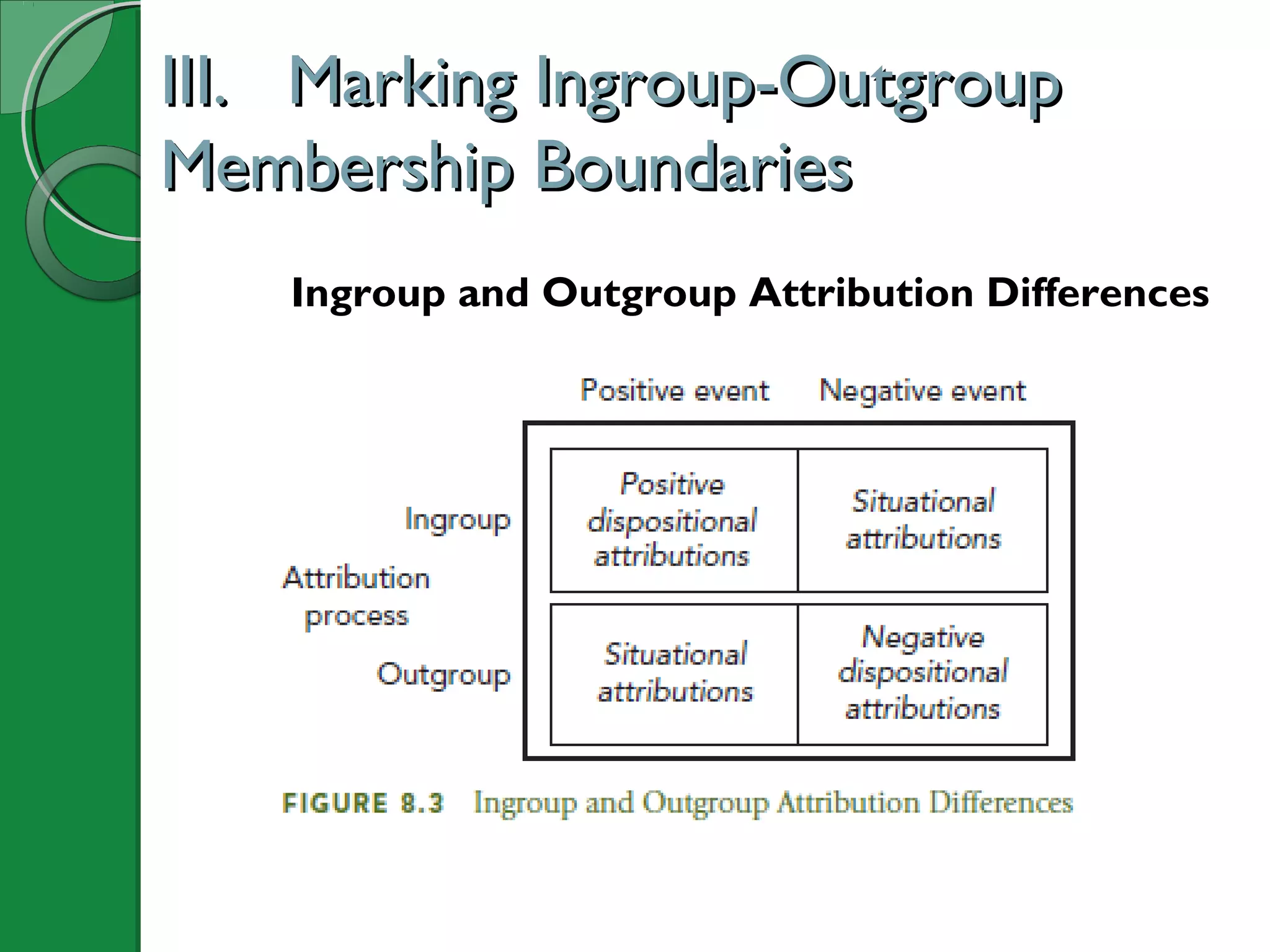
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 8 of the textbook "Understanding Intercultural Communication". It discusses how human perception tendencies can lead to biases against outgroups through selective attention, organization, and interpretation. Specifically, it examines ethnocentrism and the development of stereotypes along dimensions of warmth and competence. The chapter also explores how ingroup and outgroup membership boundaries are formed through social identity and attribution biases. Prejudice, discrimination, and different types of racism are then defined and explained. Finally, recommendations are provided for reducing biases through self-reflection, seeking accurate knowledge of other groups, and cultivating intergroup contact and cooperation.