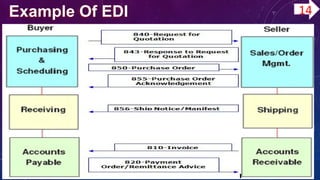
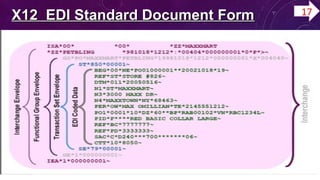
This document discusses IBM and its business-to-business (B2B) integration tool called Sterling Integrator. Sterling Integrator is a transaction engine that supports high-volume electronic message exchange and integration between internal systems and external business partners. It allows modeling and managing of business processes through a web-based interface. The document also provides an overview of electronic data interchange (EDI) standards, including the X12 standard format which defines three envelope levels for EDI documents: interchange, functional group, and transaction. Sterling Integrator can be used to map between different data formats and automate business processes using EDI.