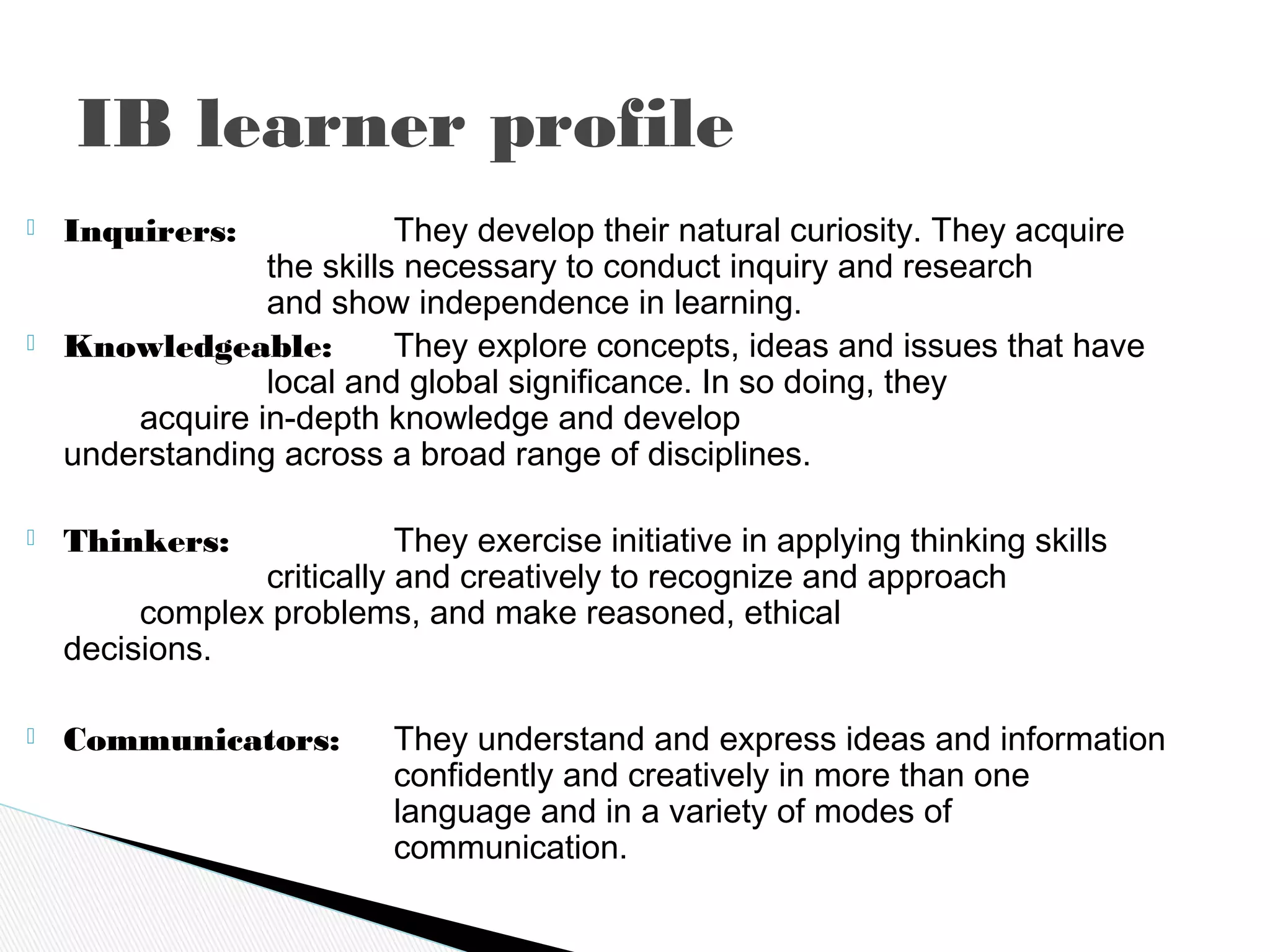
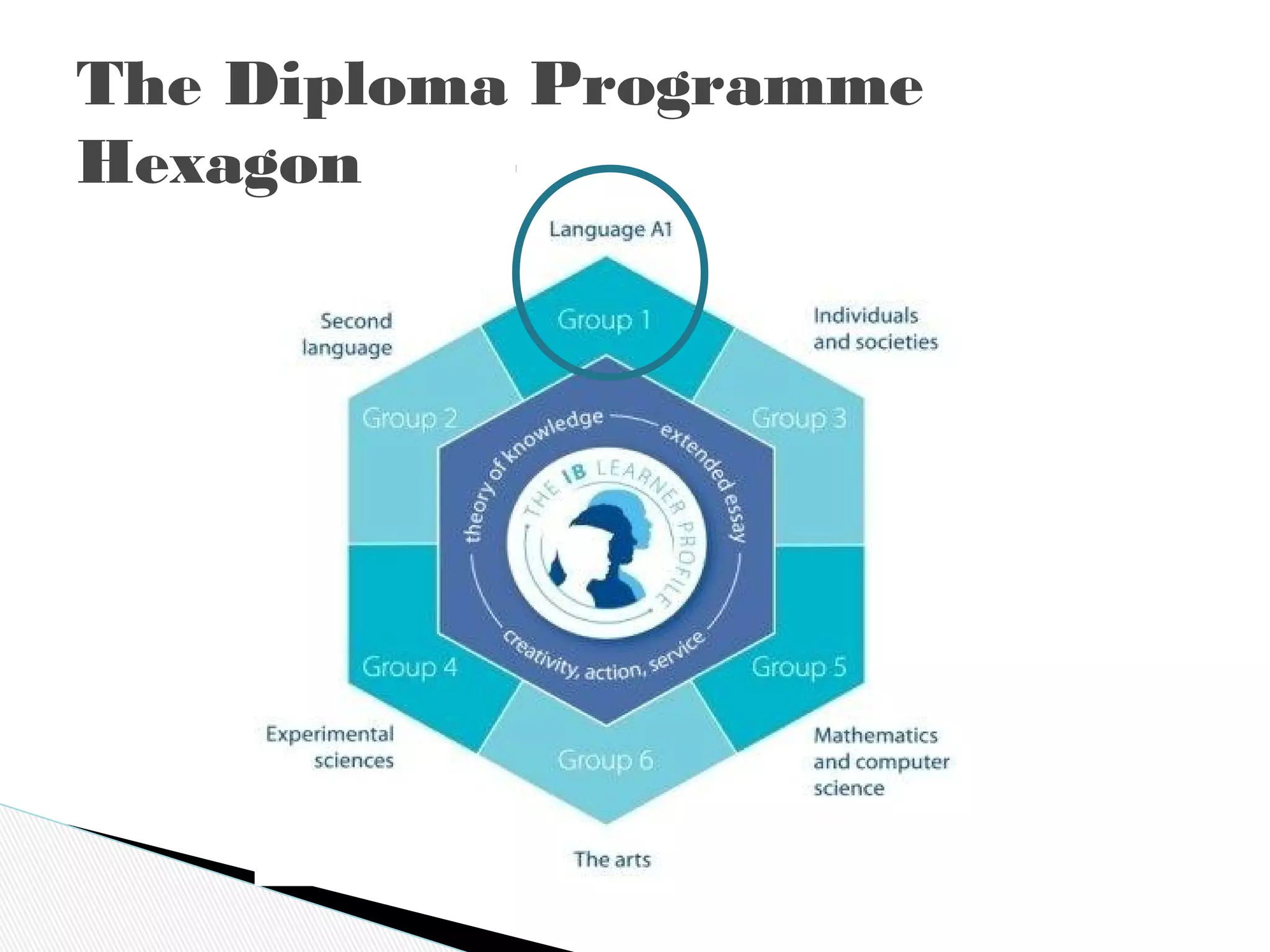
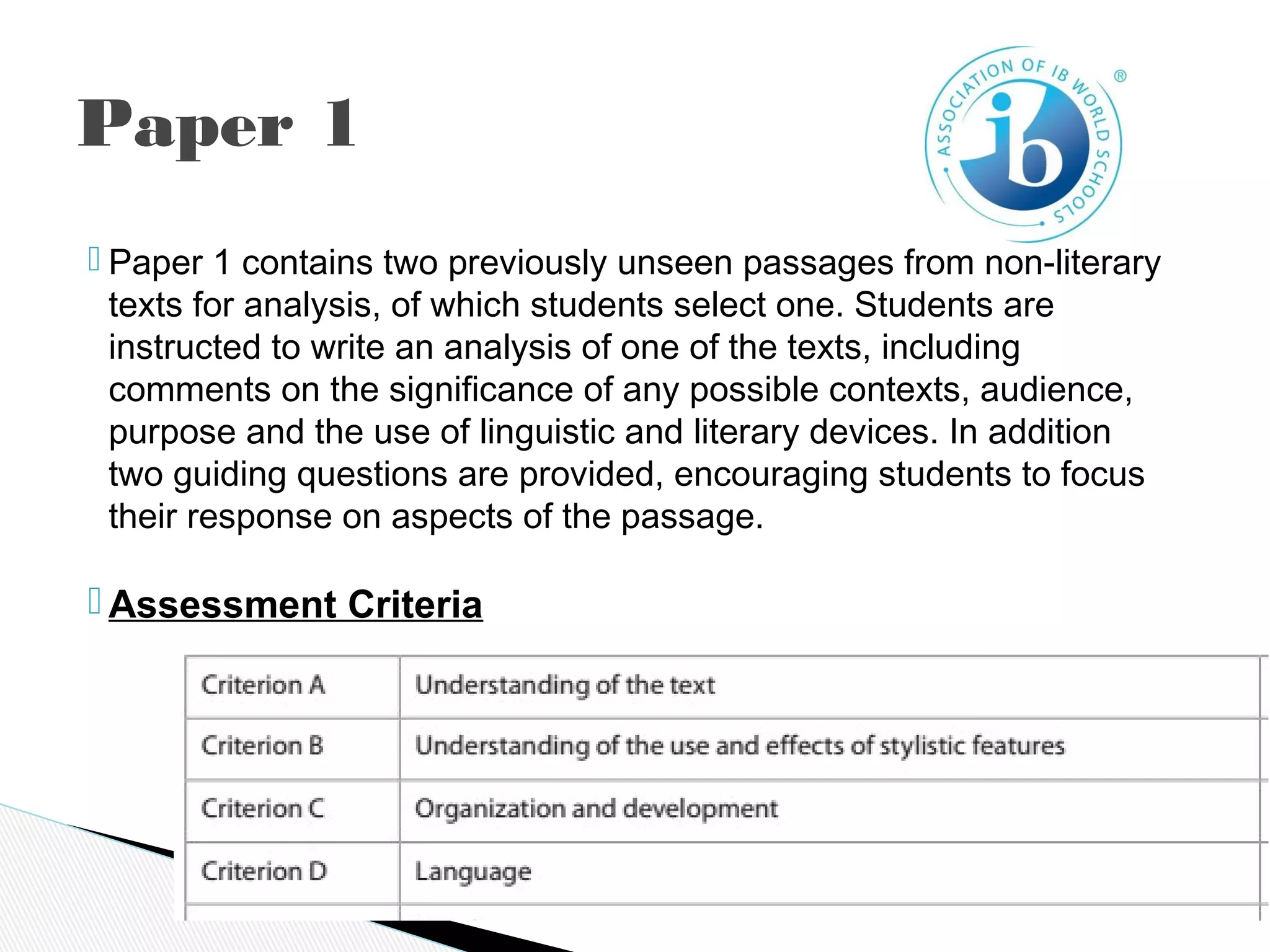
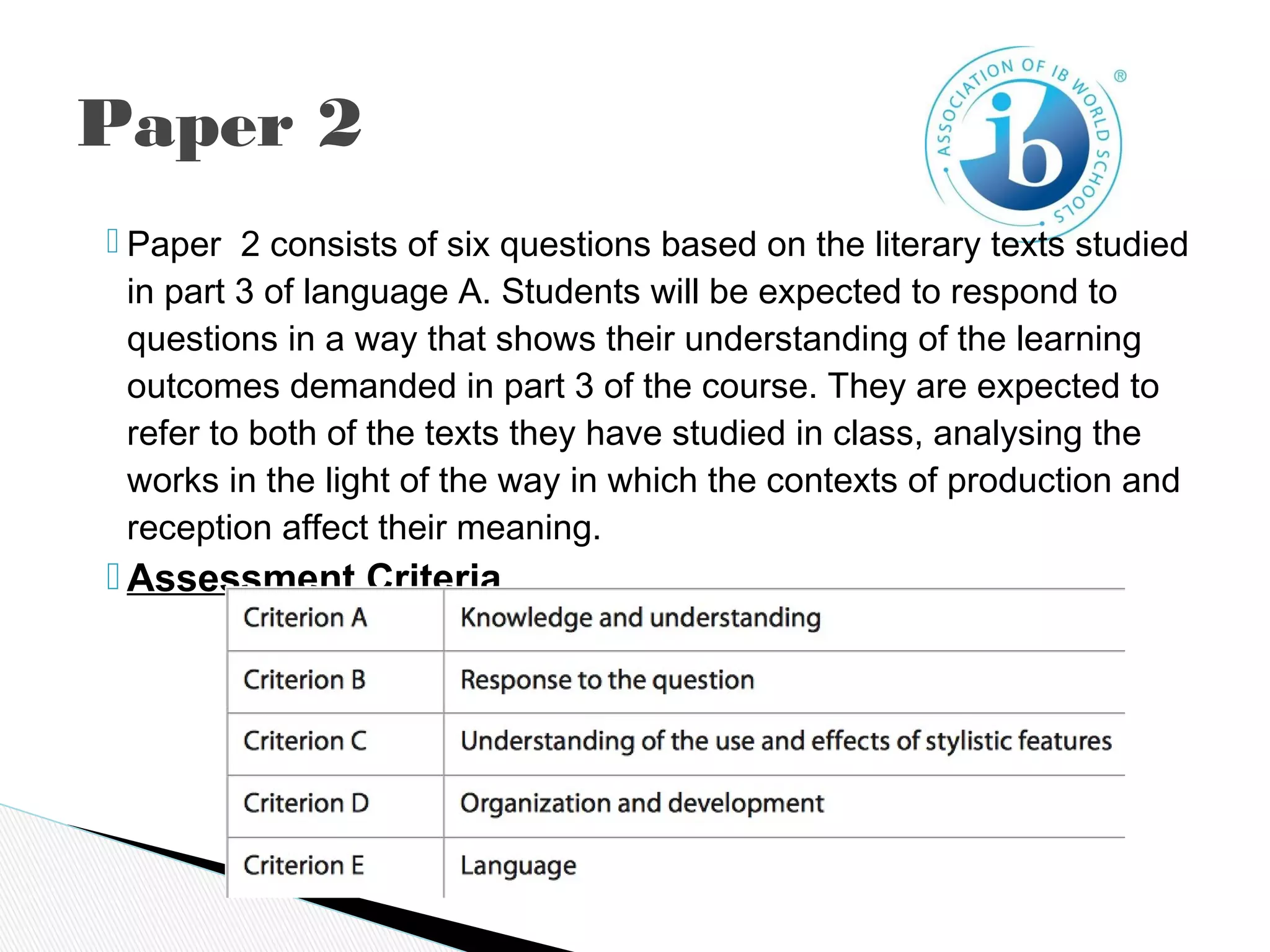
The International Baccalaureate Language A program focuses on developing students' skills in textual analysis and understanding how cultural contexts influence meaning. The two-year program encourages open-mindedness and critical thinking. It examines topics like language and mass communication, literature and contexts, and how formal elements create meaning. Students are assessed through written tasks, oral commentaries, and exams analyzing passages and literary works with consideration of production and reception contexts. The goal is to promote intercultural understanding by reflecting on different cultural practices and perspectives.