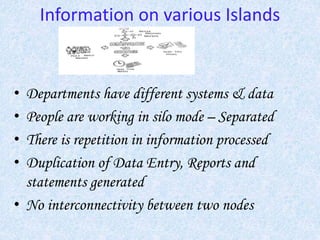
This document provides an overview of enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions. It defines ERP as a solution that integrates a company's information systems across all functional areas to perform core activities and focus on customer satisfaction and service. The document then discusses the current scenario of isolated information systems, outlines why ERP is needed to improve management and reduce costs, and provides a brief history of ERP systems. It also summarizes the expectations of ERP, describes Reflex IRP as a generalized off-the-shelf application, and outlines the typical project life cycle for an ERP implementation project.