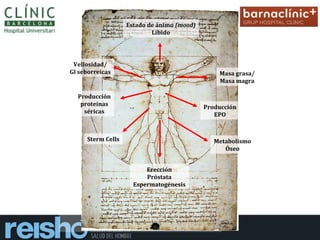
This document discusses testosterone deficiency syndrome (TDS) and its relationship to prostate cancer. It begins by providing background on testosterone physiology and the prevalence of TDS, which increases with age. It then reports on a study of 705 men who underwent prostate biopsies. The study found that testosterone levels were not related to prostate cancer diagnosis in men with normal testosterone, but were related in men with low testosterone. Specifically, men with testosterone levels below 346 ng/dL who were diagnosed with prostate cancer had even lower testosterone levels on average of 272 ng/dL. The study suggests testosterone levels may be a risk factor for prostate cancer diagnosis only in hypogonadal men.









































































![“Mean body weight decreased more in patients in the intervention group (−4.0 [1.1]
kg) than in those in the control group (−1.2 [0.6] kg) . Compared with patients
consuming the control diet, patients consuming the intervention diet had
significantly reduced serum concentrations of hs-CRP.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tdsfulltalk-130528032524-phpapp02/85/Hypogonadism-75-320.jpg)











