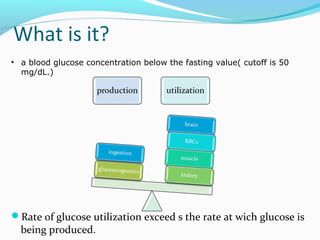
This document provides an overview of hypoglycemia, including its definition as low blood glucose below 50 mg/dL, importance due to the brain's reliance on constant glucose supply, and symptoms ranging from adrenergic to neuroglycopenic effects. It describes the body's glucoregulatory systems that work to prevent and correct low blood sugar, including the release of glucagon, epinephrine, cortisol and growth hormone. Various causes of hypoglycemia are outlined, from insulin-induced in diabetes to other drug-related, critical illness, hormonal deficiency, tumor and genetic causes. The diagnosis involves considering history, symptoms and confirming a low blood glucose level, while treatment focuses on oral or IV glucose administration and


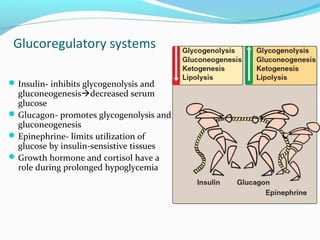
![Glucoregulatory systems
Two overlapping glucose-regulating
systems are activated by
hypoglycemia:
1) the islets of Langerhans, which
release glucagon
2) receptors in the hypothalamus,
which respond to abnormally low
concentrations of blood glucose.
The hypothalamic glucoreceptors can
trigger both the secretion of
epinephrine and release of ACTH
and GH by the anterior pituitary.
[ACTH increases cortisol synthesis
and secretion in the adrenal cortex]
Glucagon, epinephrine, cortisol, and
GH are each opposes the action of
insulin on glucose use.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypoglycemia-171130061746/85/Hypoglycemia-5-320.jpg)