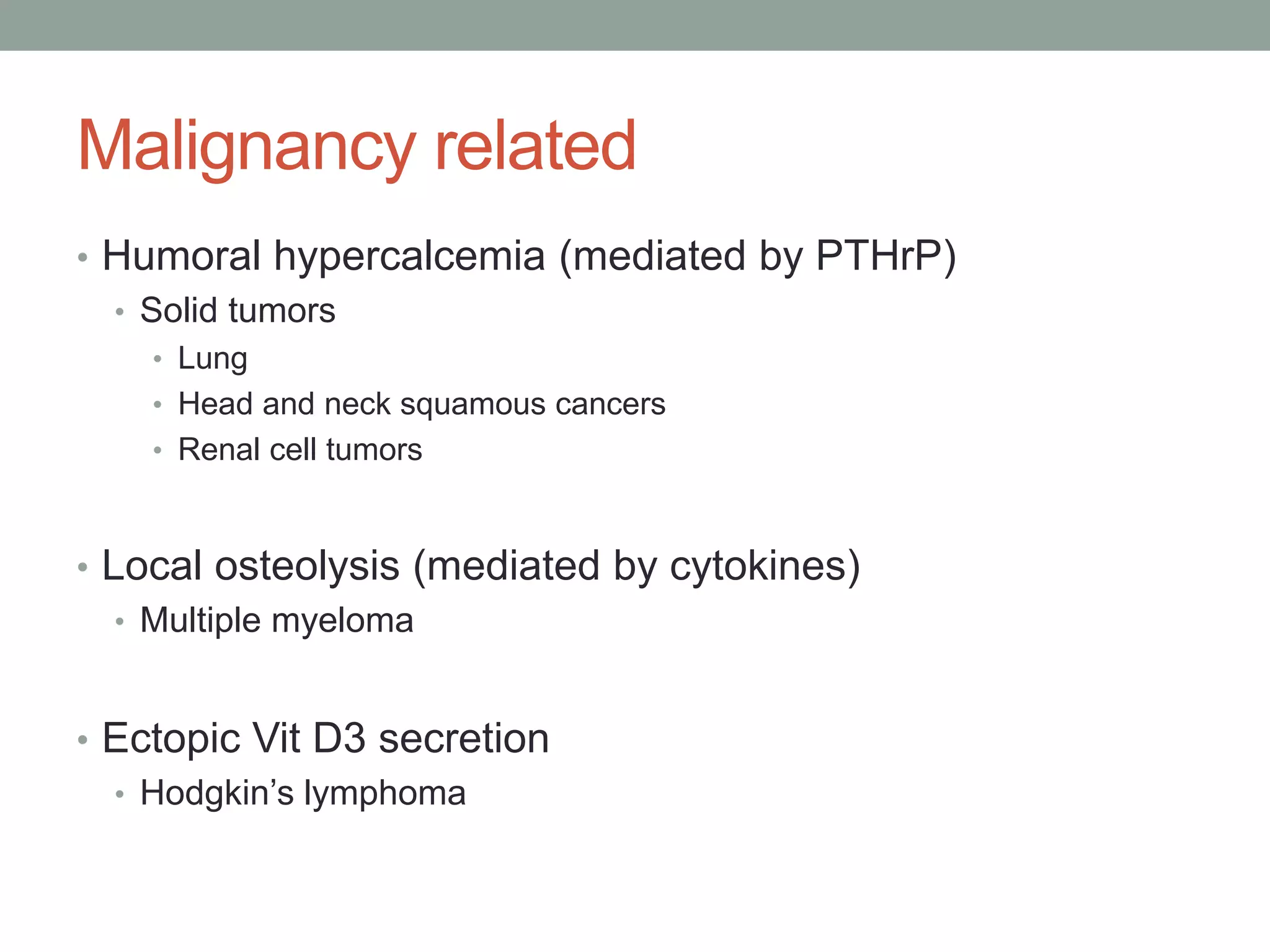
This document discusses hypercalcemia, defined as a serum calcium level above 10.3 mg/dl. It lists the main causes as primary hyperparathyroidism, malignancy like multiple myeloma and breast cancer, and excess vitamin D. Symptoms involve the renal, musculoskeletal, gastrointestinal and neurological systems and include nephrolithiasis, bone pain, nausea and confusion. Emergency treatment involves rehydration with IV saline and bisphosphonates while medical management focuses on fluid intake, diet modification and exercise. Specific treatments address the underlying cause such as surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism or treating the malignancy.