This document provides a summary of various valvular heart lesions including:
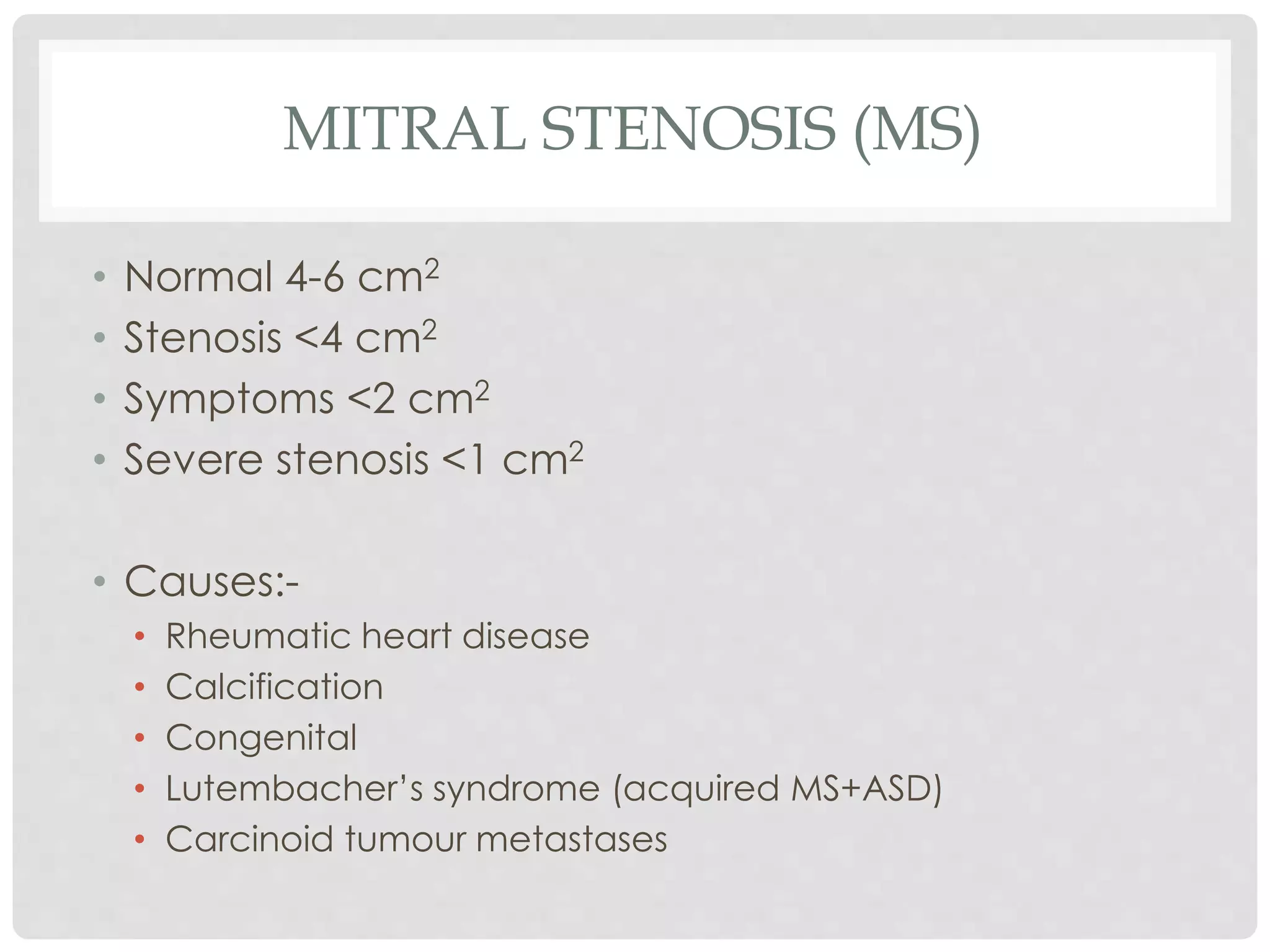
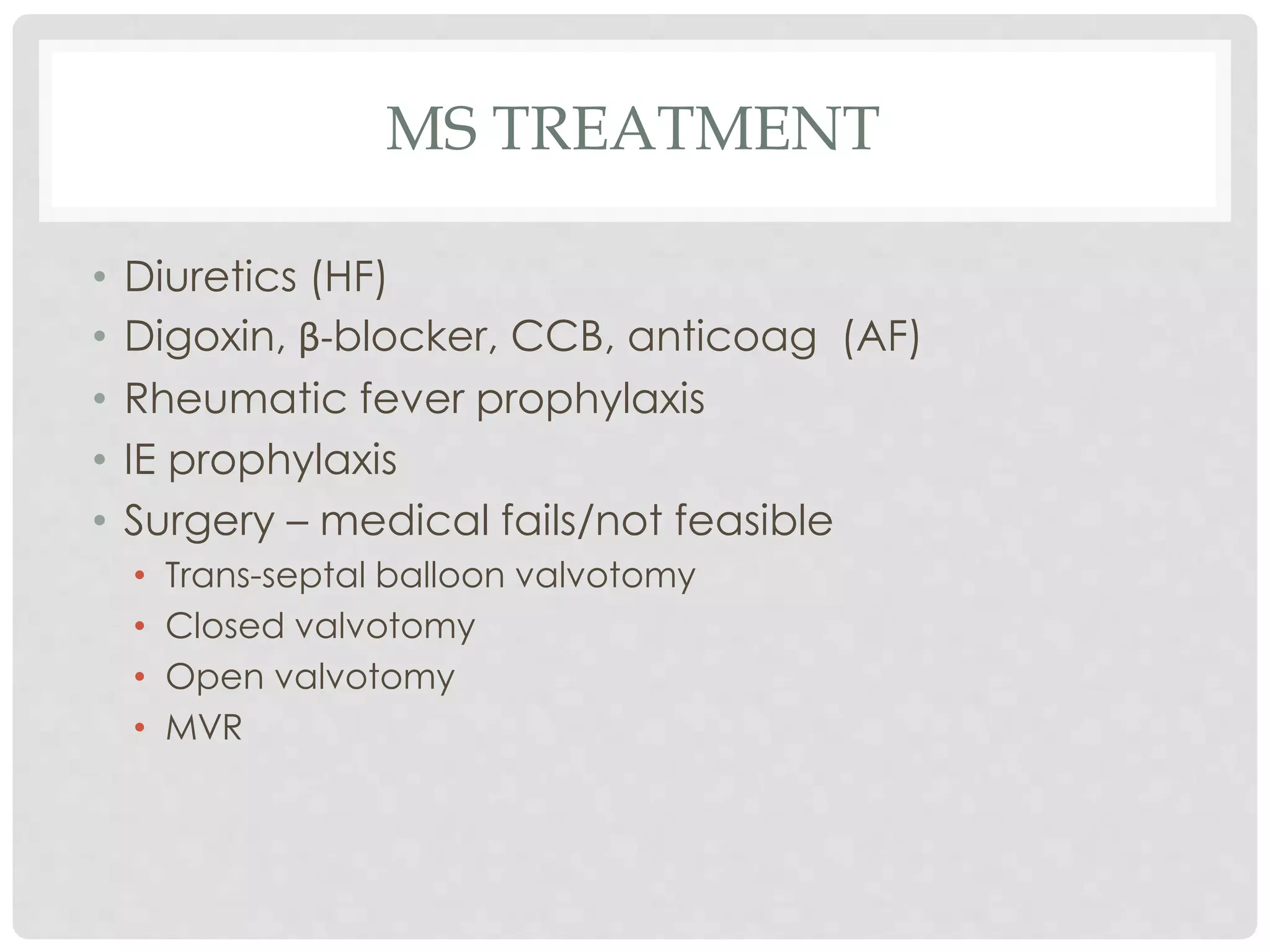
1. Mitral stenosis causes narrowing of the mitral valve and leads to left atrial and pulmonary hypertension. Symptoms include dyspnea and right heart failure.
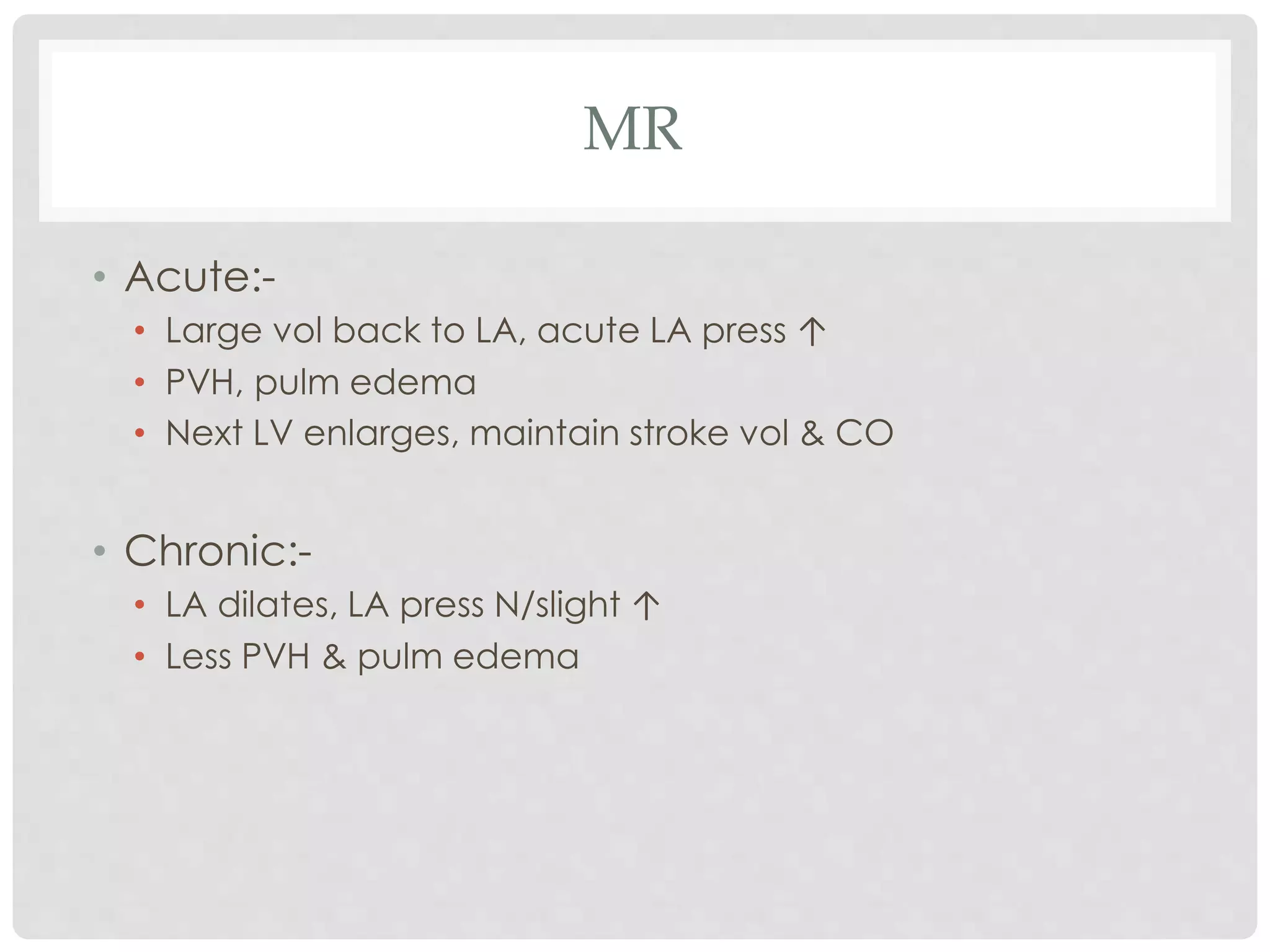
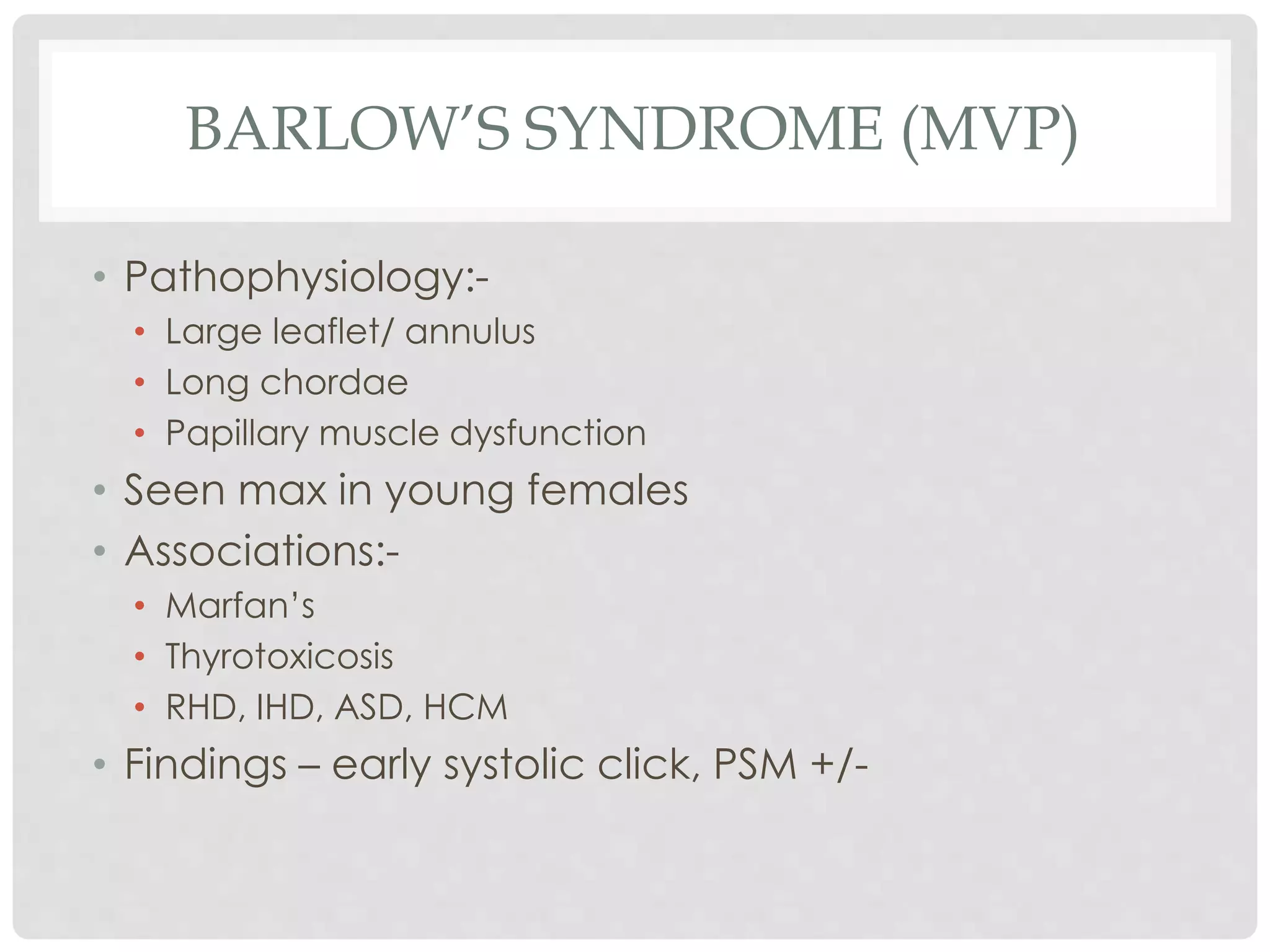
2. Mitral regurgitation results in blood flowing back to the left atrium, causing left atrial and ventricular enlargement. Symptoms develop later and include fatigue and cardiac cachexia.
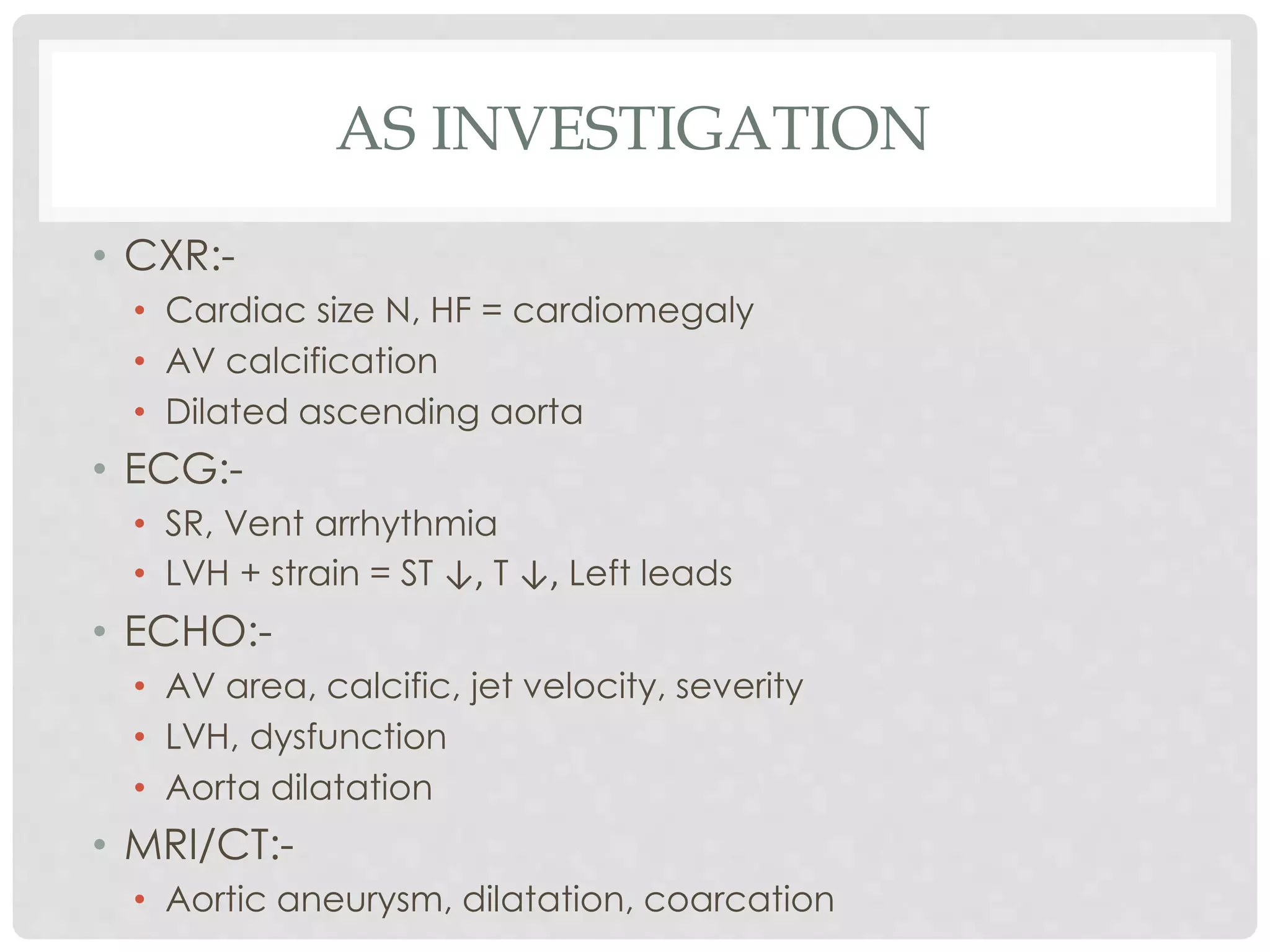
3. Aortic stenosis narrows the aortic valve and increases left ventricular pressures, causing hypertrophy and later heart failure. Symptoms include exertional dyspnea and angina.