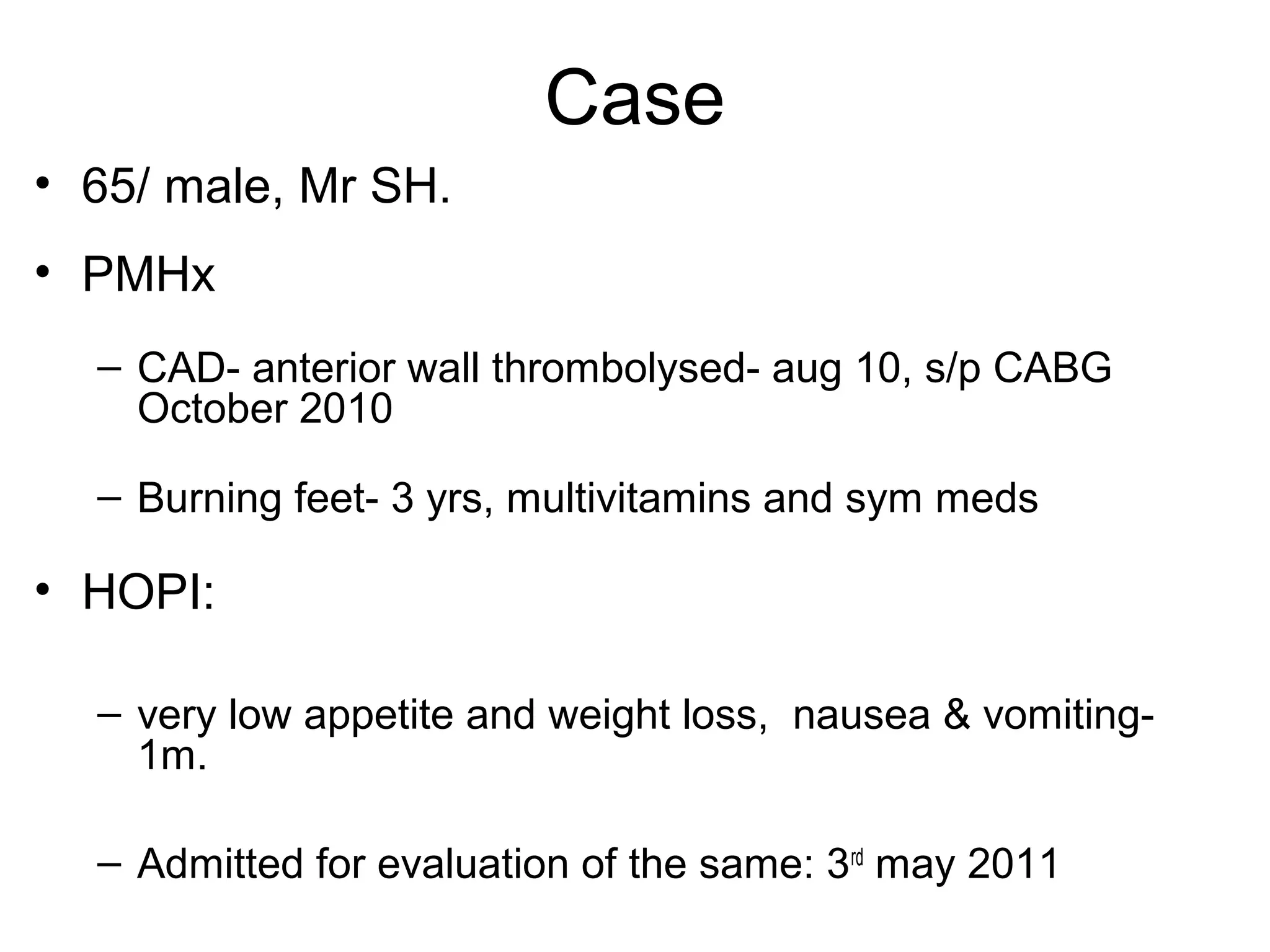
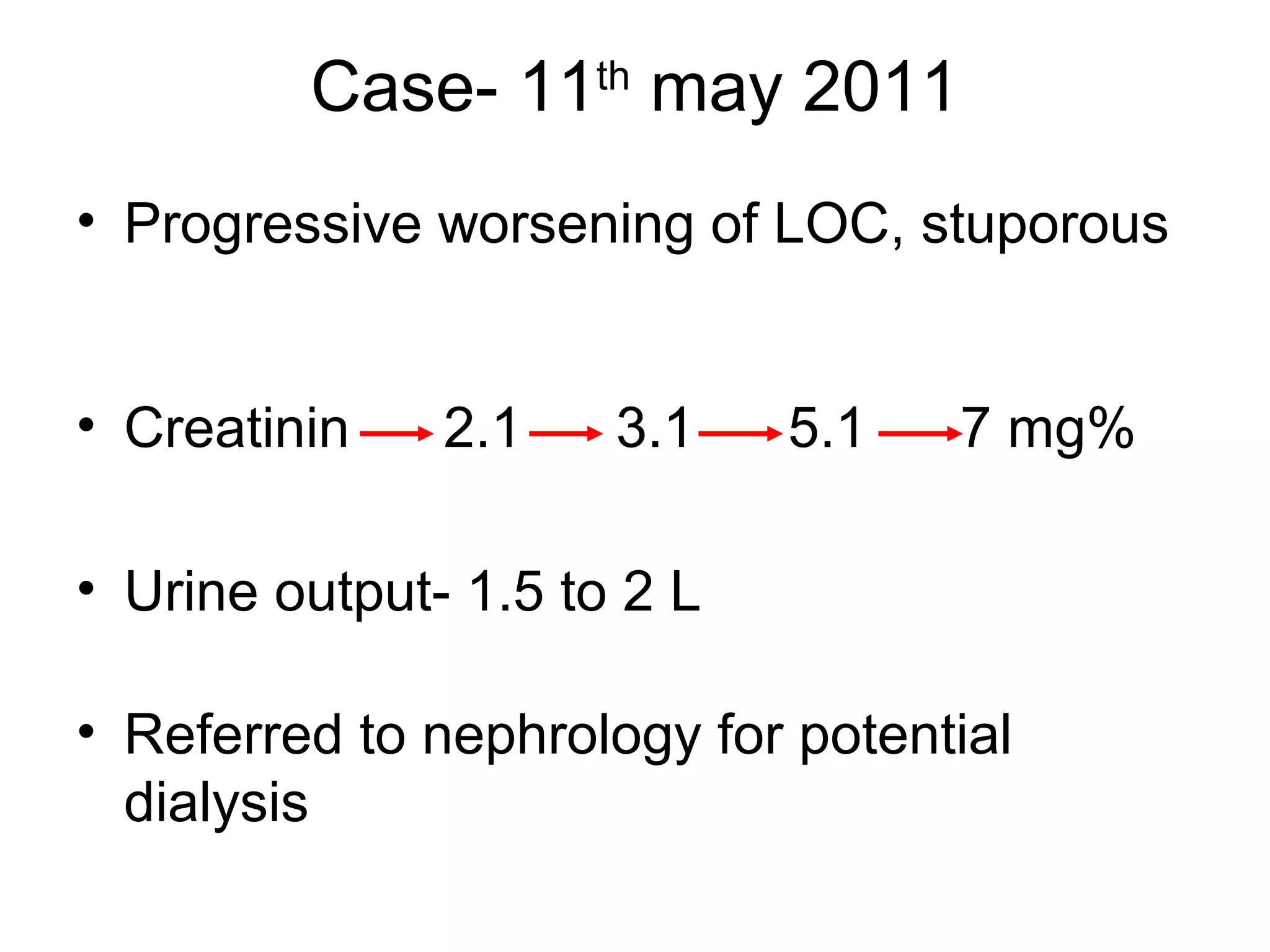
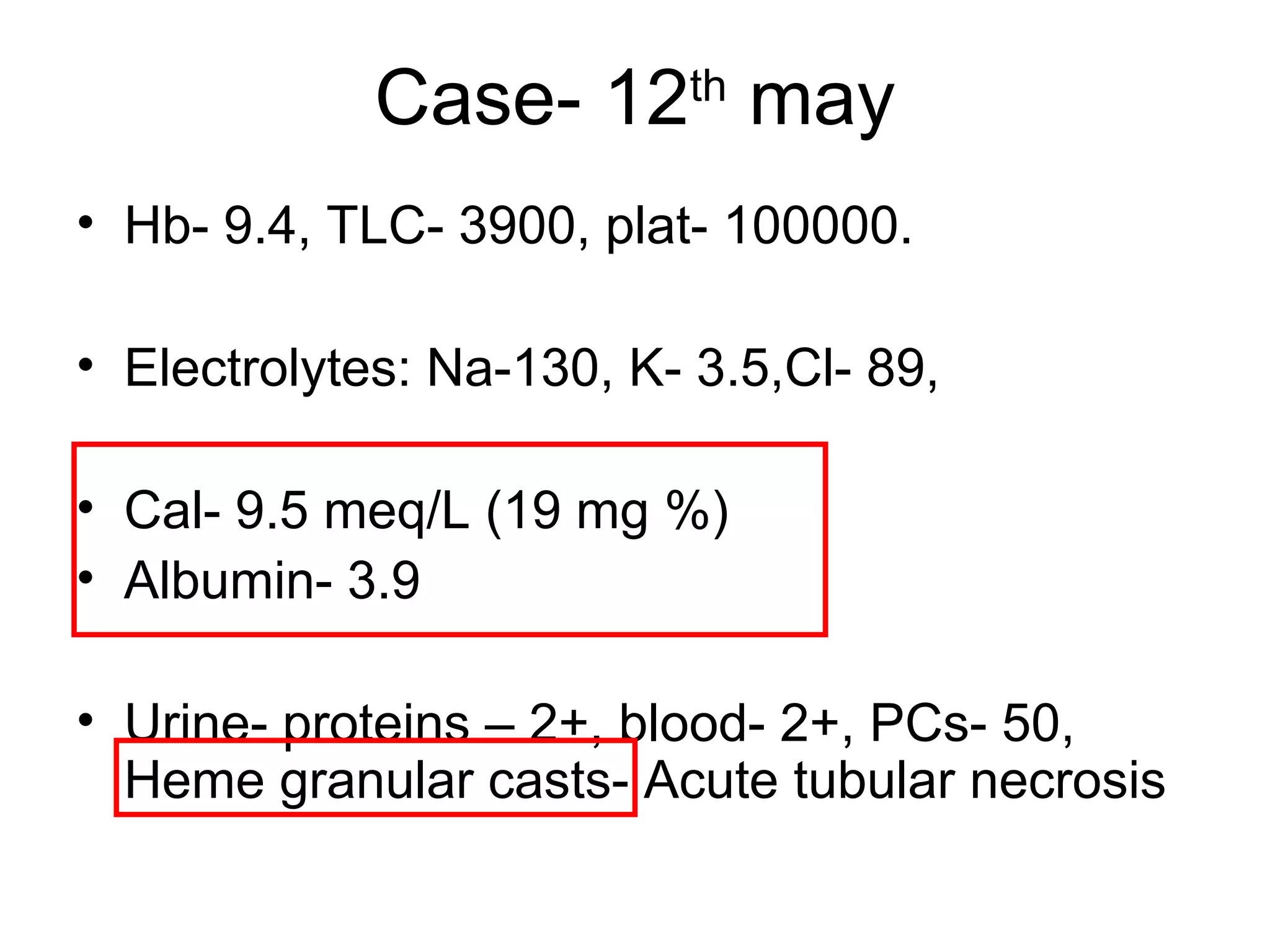
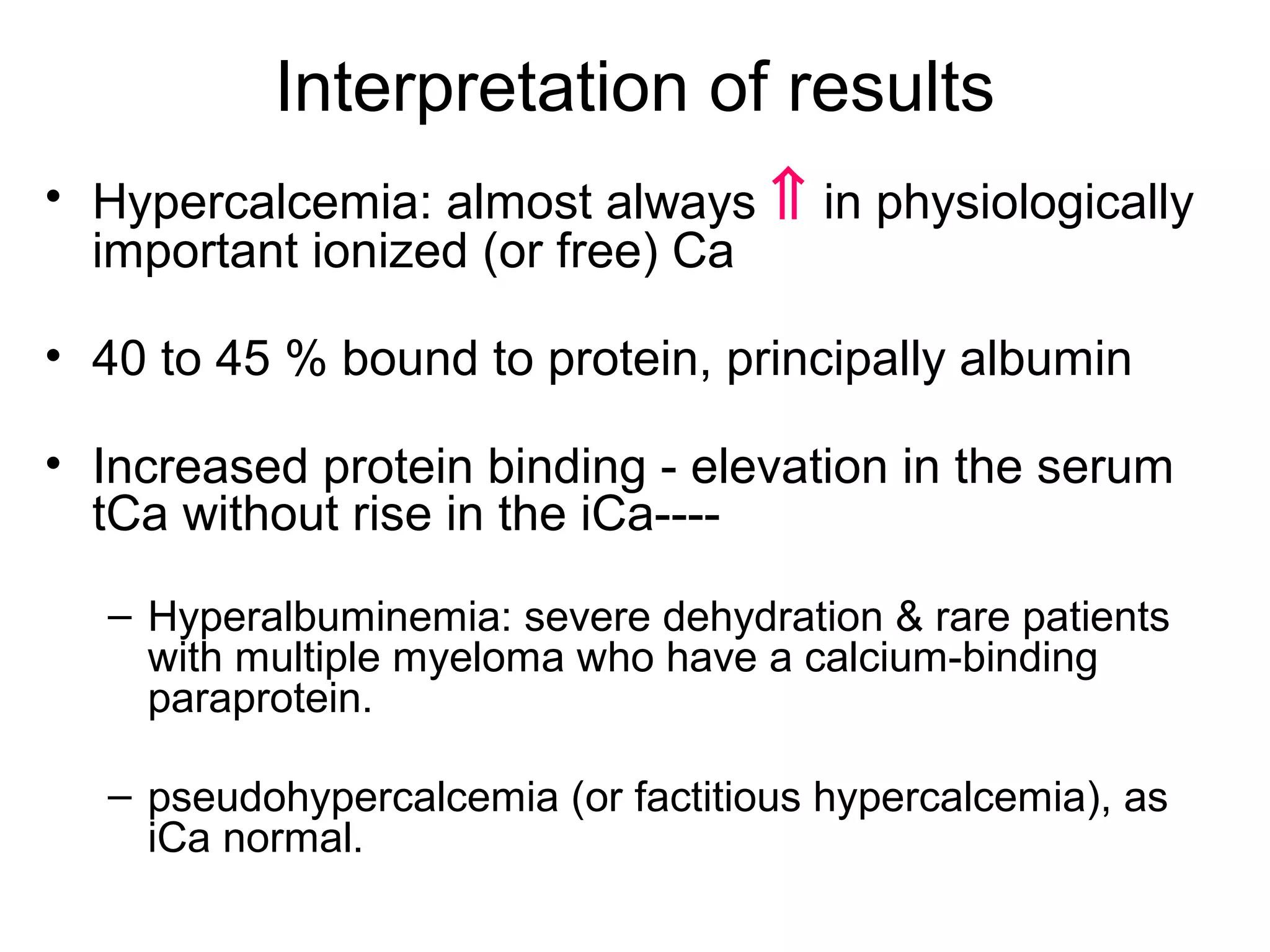
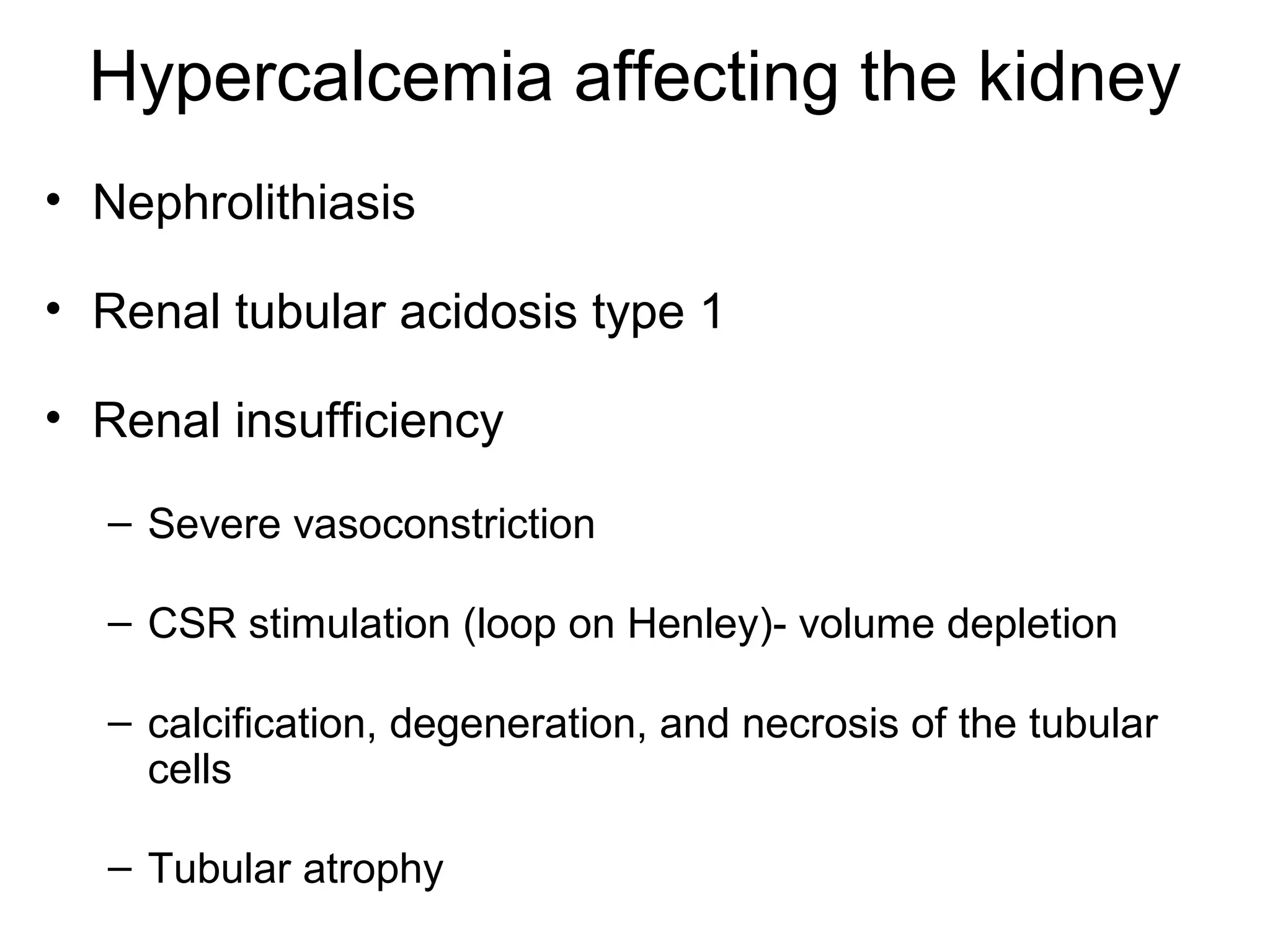
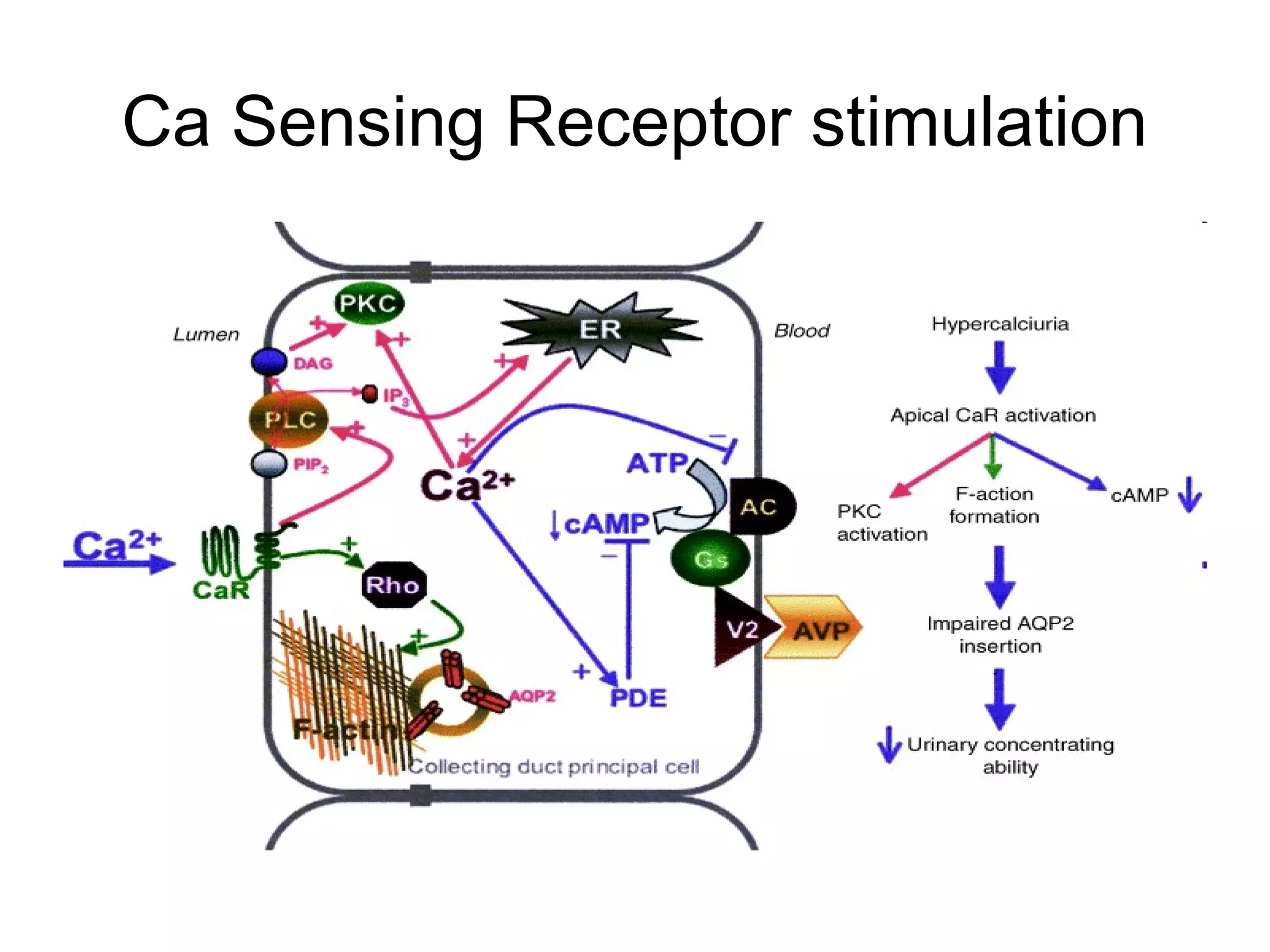
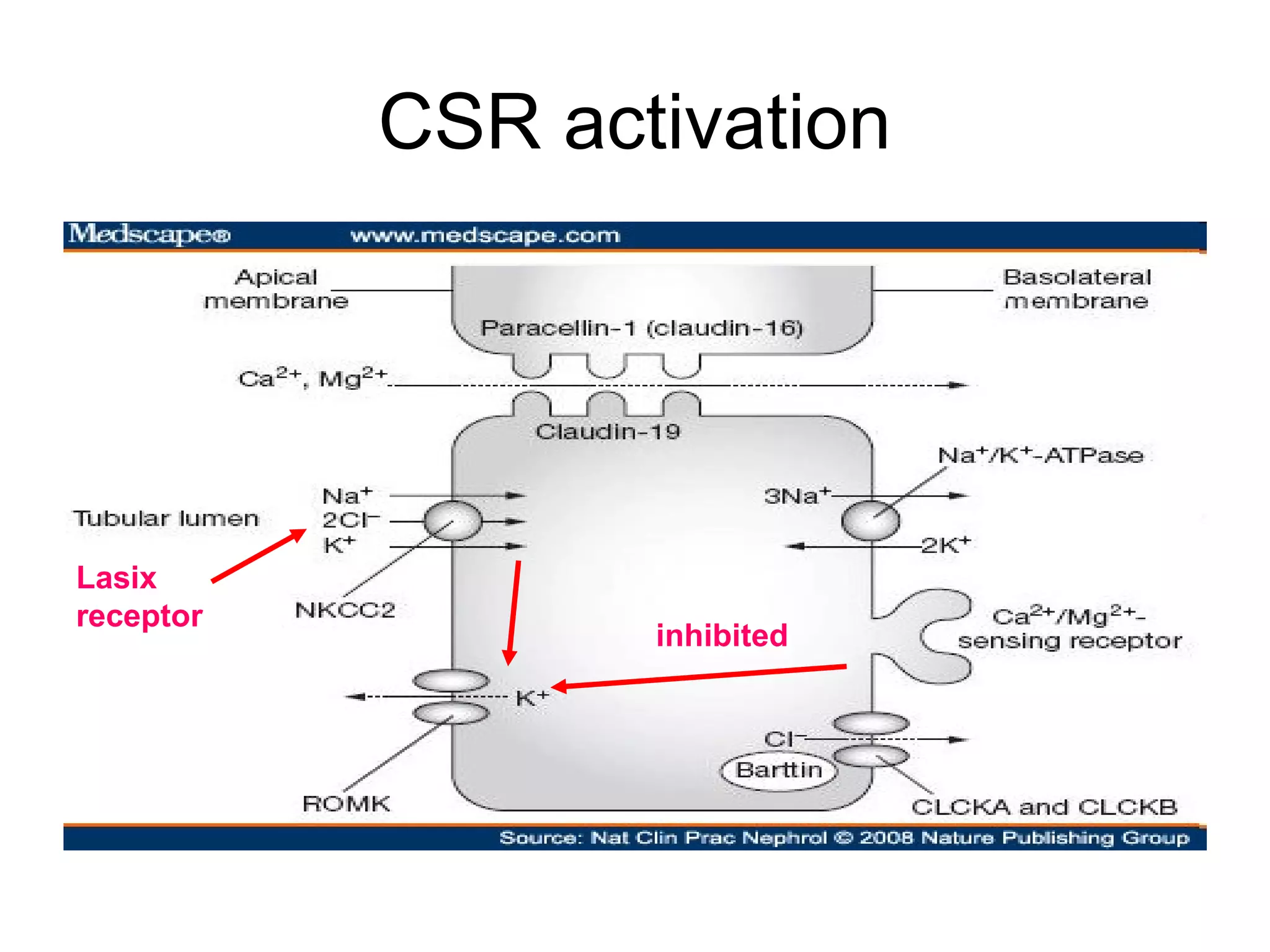
Hypercalcemia was causing the patient's acute renal failure. Treatment for hypercalcemia included intravenous fluids, furosemide, steroids, bisphosphonates, and dialysis which lowered the calcium levels and improved renal function. The underlying cause of hypercalcemia could not be determined after extensive testing, but was likely a malignancy given the persistent pancytopenia. Hypercalcemia can directly damage the kidneys by decreasing medullary osmolality and inducing nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, nephrolithiasis, and renal tubular acidosis. It also causes vasoconstriction and activation of the calcium-sensing receptor which stimulates renin release and worsens volume