Embed presentation
Download to read offline











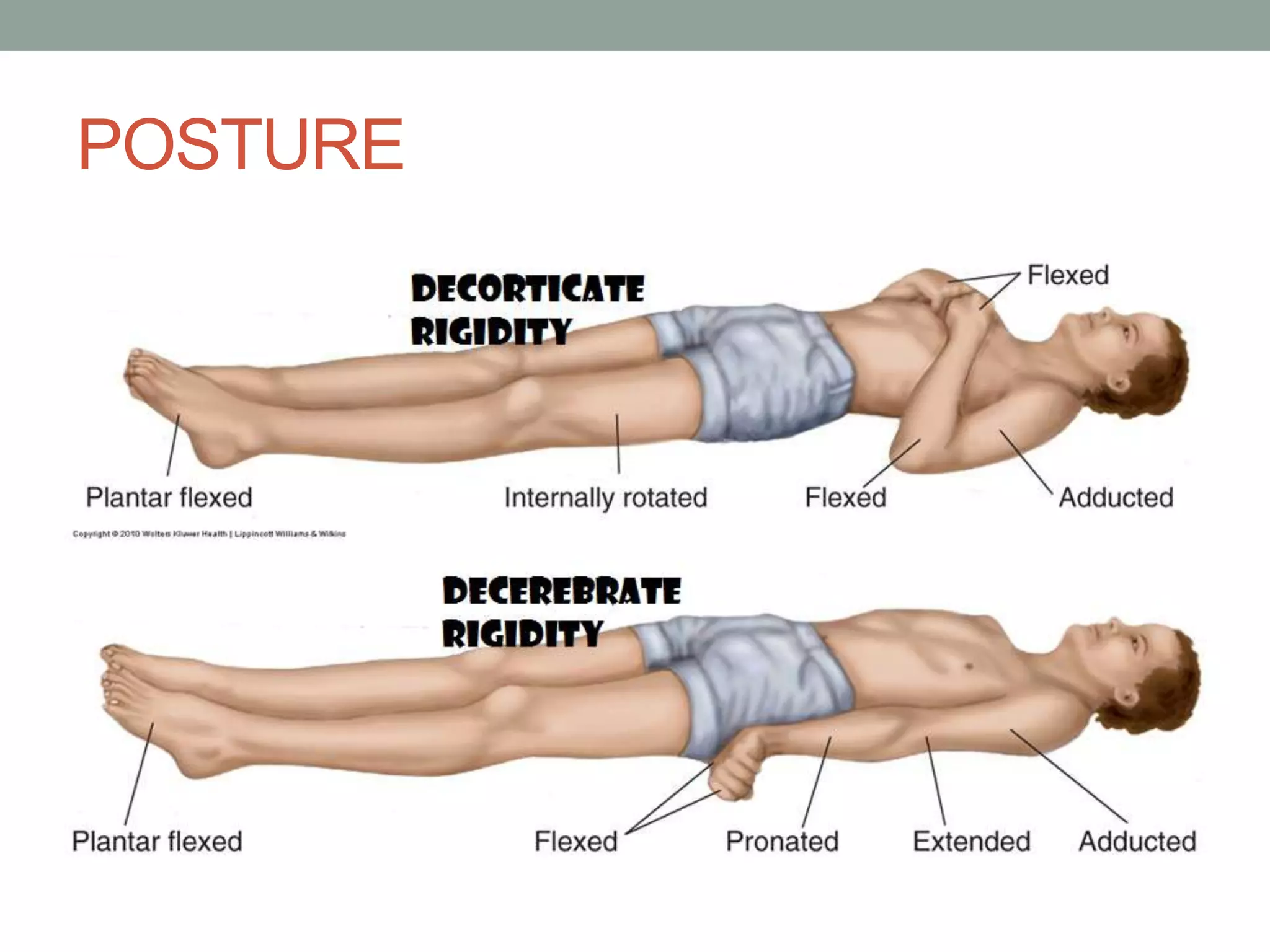






The document outlines the evaluation of unconsciousness, focusing on the assessment of consciousness through arousal and cognition. It discusses coma as a state of total unresponsiveness with reference to the Glasgow Coma Scale and initial assessment protocols for medical responders. Key areas of examination include pupil response, breathing patterns, motor and sensory functions, and reflexes, as well as signs of injury and vital signs.
















