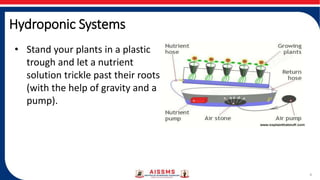
Hydroponics farming is a technique for growing plants without soil by using a nutrient-rich water solution. Some key points:
- Plants' roots absorb balanced nutrients dissolved in water to meet developmental needs without soil. Various materials besides soil can support plant growth.
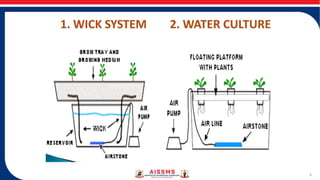
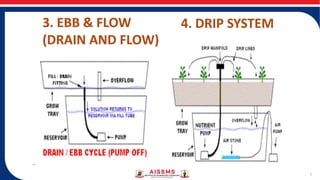
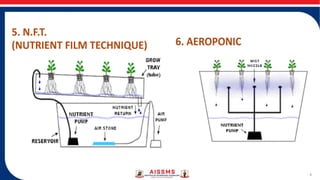
- Hydroponic systems include methods like nutrient film technique (NFT), drip system, and ebb and flow systems which circulate nutrient solutions. Nutrient and environmental factors like pH, EC, temperature must be carefully controlled.
- Hydroponics allows growing many crop types like lettuce, tomatoes, herbs indoors with precise nutrient delivery and without soil-borne pests. It has higher yields but also higher costs than traditional agriculture