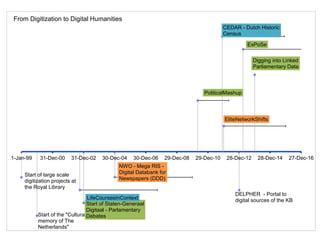
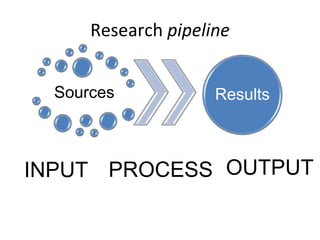
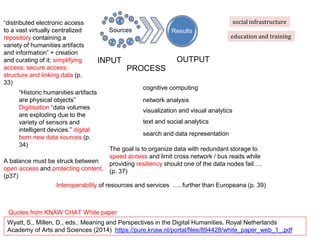
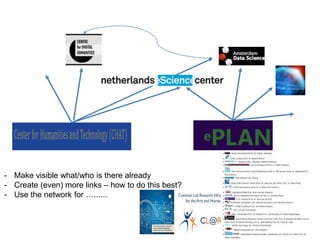
The document discusses the intersection of humanities and information and communication technology (ICT), particularly during a workshop focused on national infrastructure in social sciences and humanities. It explores various large-scale digitization projects, the importance of ICT infrastructure for research, and the challenges in credit allocation between technical and scientific staff. Key points include the explosion of data, the need for interoperability, and the balance between open access and content protection.