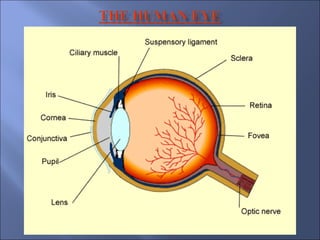
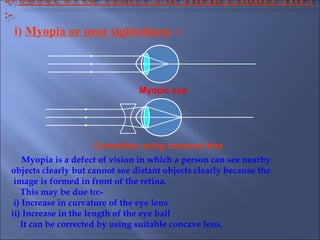
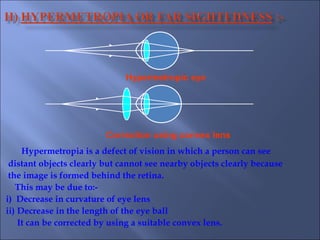
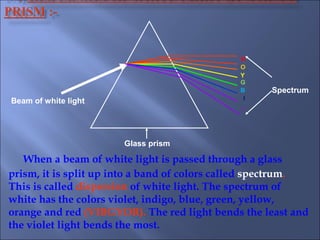
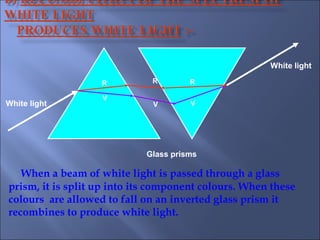
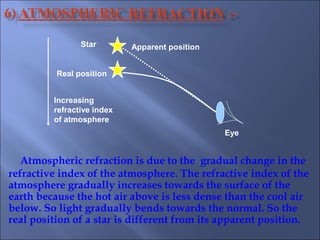
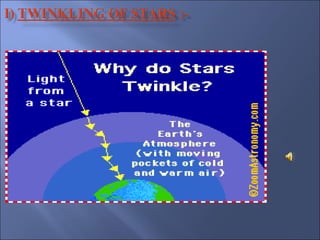
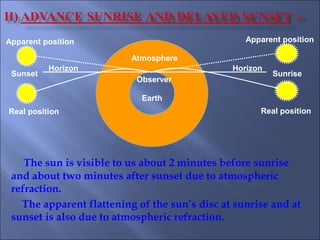
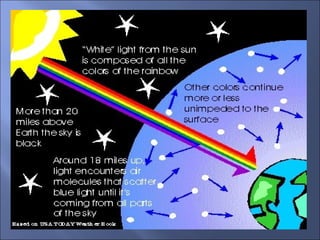
The document provides an overview of the human eye's structure, its function, and the optical phenomena associated with it, including vision defects like myopia and hypermetropia, along with their corrections. It also explains concepts like light refraction, dispersion, atmospheric refraction, and the scattering of light, which result in phenomena such as rainbows and the blue sky. Additionally, the document describes the eye's ability to adjust focus, termed accommodation, and outlines various visual optics principles and common refractive errors.