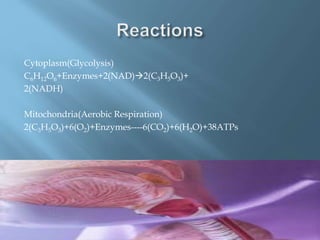
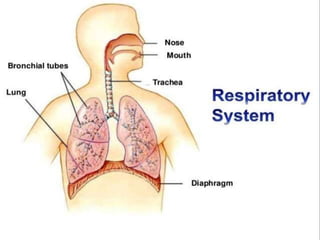
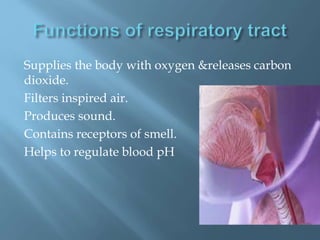
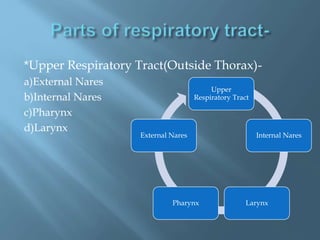
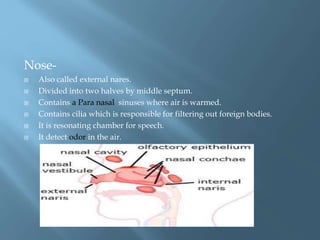
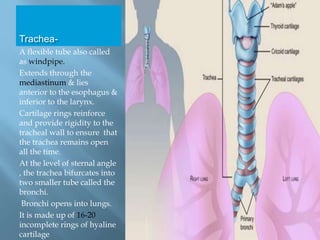
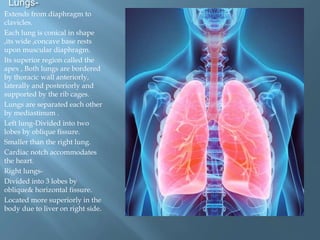
The document provides an overview of the human respiratory system, detailing its components such as the lungs, trachea, and bronchi, as well as the biochemical processes of aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It explains the functions of different respiratory structures and emphasizes the roles of oxygen and carbon dioxide in energy production and waste elimination. Additionally, it outlines the anatomical features of the upper and lower respiratory tracts.