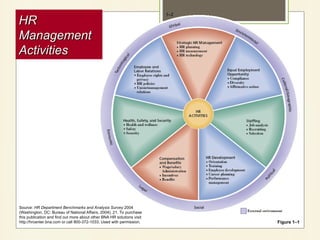
The document outlines the nature and functions of human resource management (HRM), highlighting its role in effectively utilizing human talent to achieve organizational goals. It discusses the challenges faced by HRM, including globalization, workforce demographics, and ethical considerations, and emphasizes the importance of strategic HR practices for organizational performance. Additionally, it explores the integration of technology in HRM, such as Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS), and the essential role of HR in maintaining ethical standards within organizations.