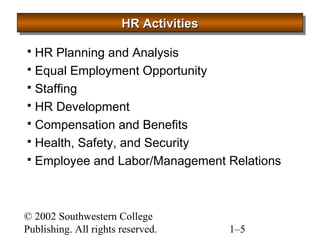
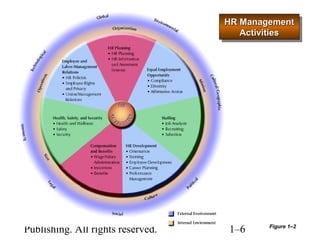
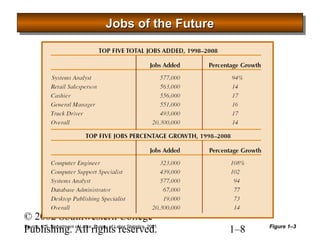
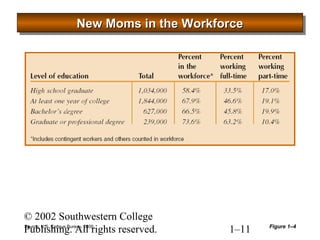
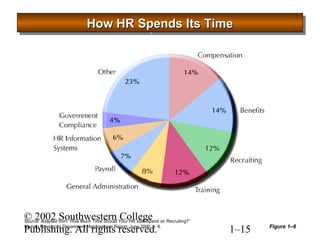
This document provides an overview of human resource management. It defines HR management and discusses the changing nature of the field. It also outlines seven categories of HR activities, identifies challenges facing HR today, and describes the four common roles of HR management, which include administrative, employee advocate, operational, and strategic roles. Finally, it discusses the importance of ethics in HR management.