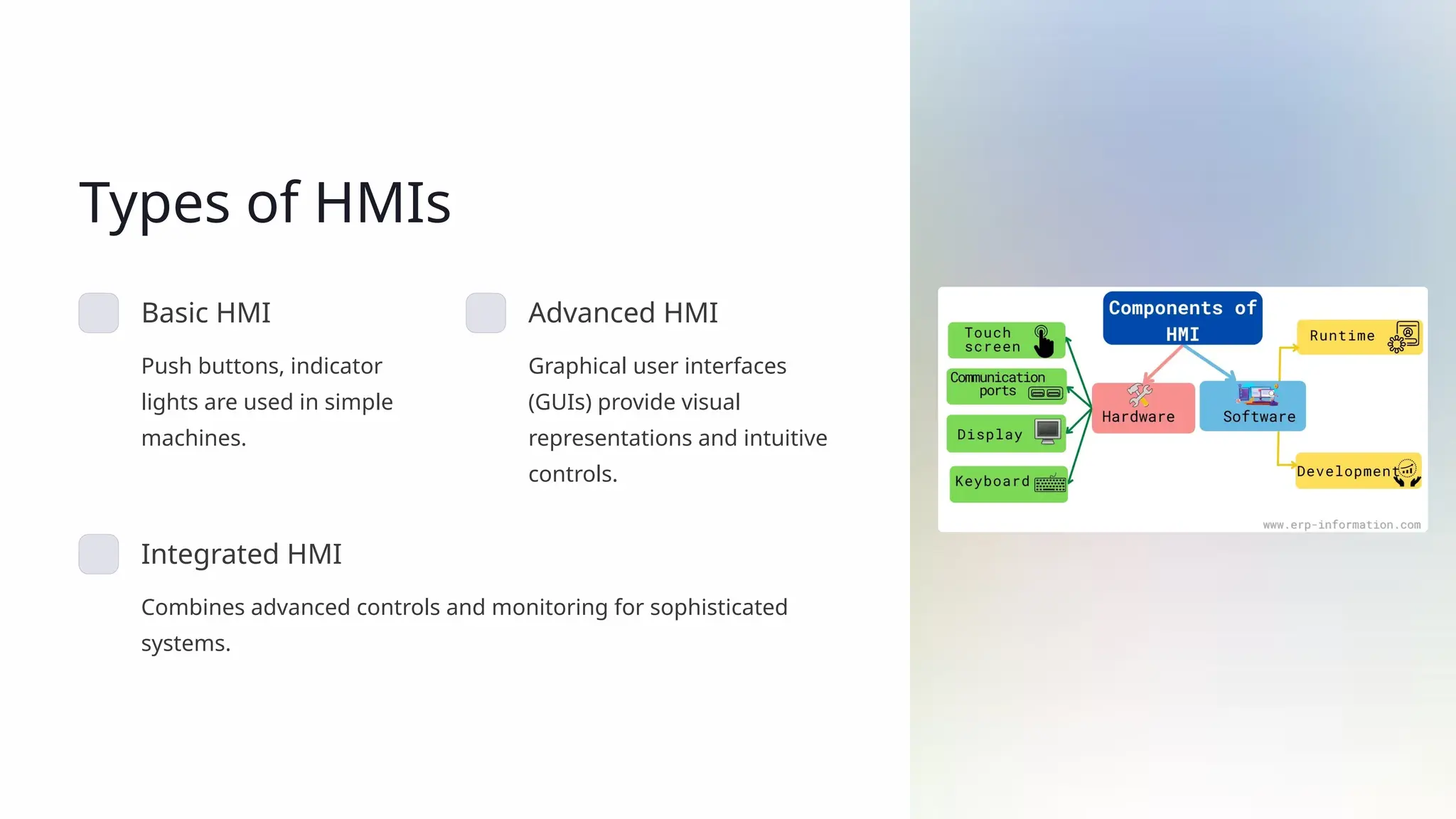
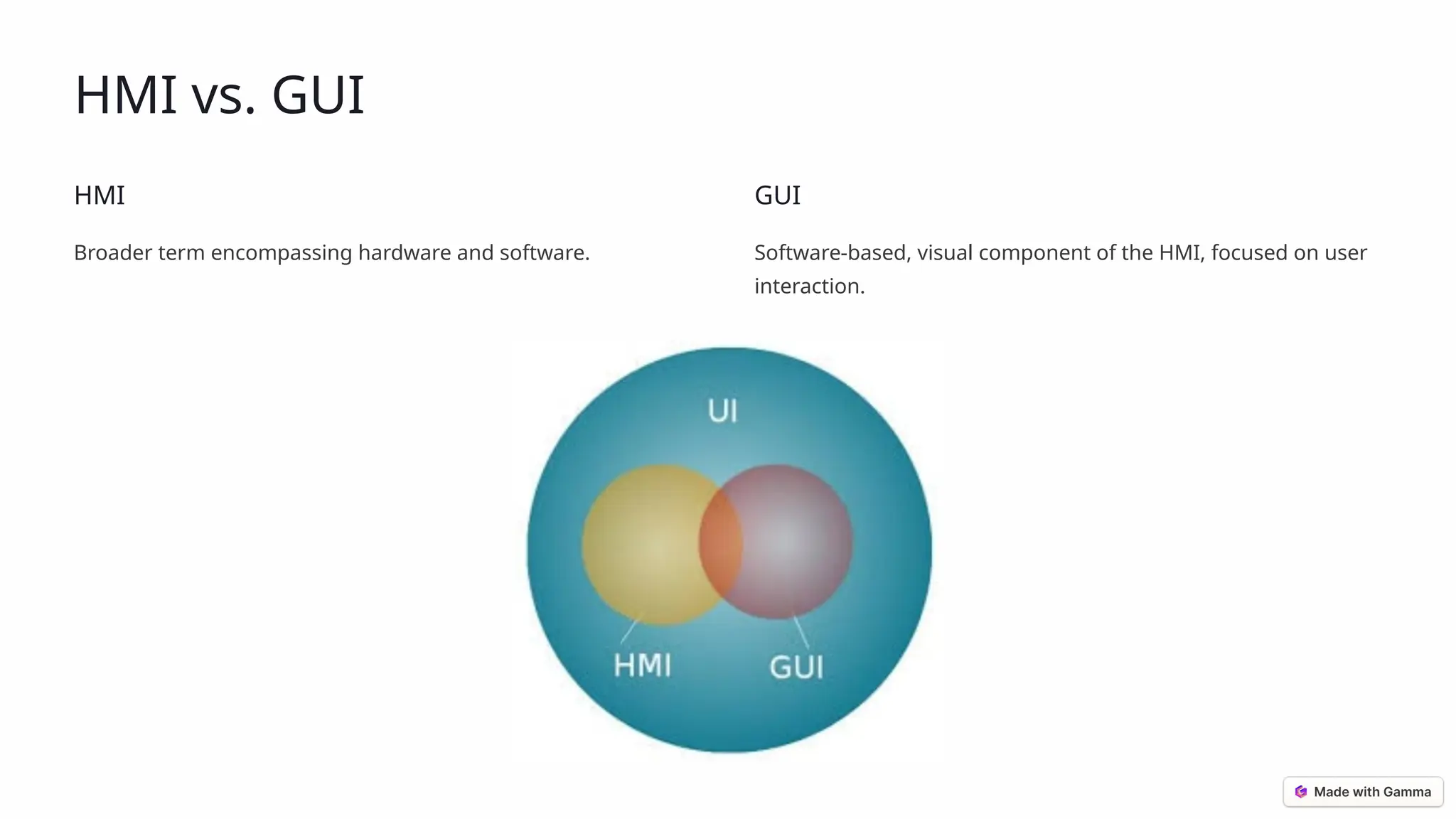
The document presents an overview of human-machine interfaces (HMIs), detailing their definition, significance, components, and various applications across sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and automotive. It highlights the features of effective HMIs, the benefits they provide, and the challenges faced in their design, emphasizing the importance of simplicity, user training, and cybersecurity. Furthermore, it addresses future innovations such as AI-driven interfaces, augmented reality, and voice control that are shaping the evolution of HMIs.