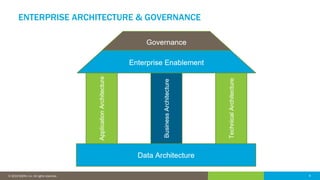
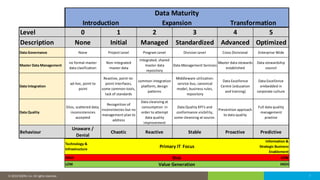
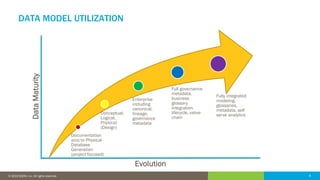
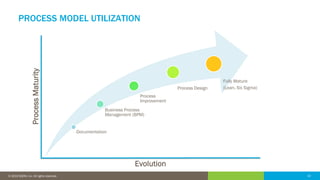
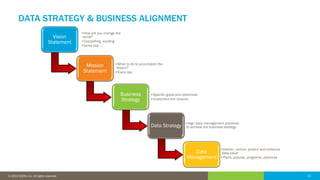
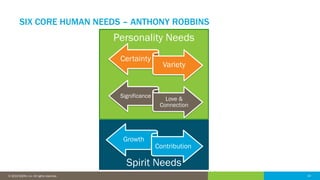
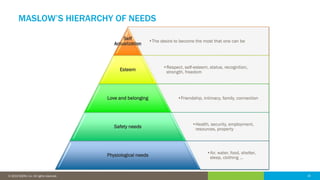
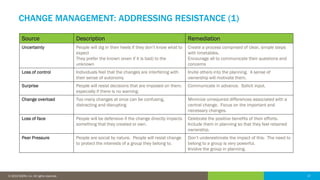
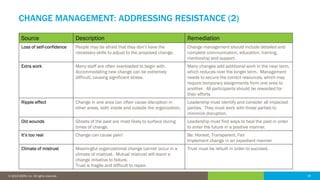
The document discusses the critical role of human factors in data governance and highlights the decline in organizations becoming data-driven due to cultural resistance and lack of alignment. It emphasizes that successful data governance requires strong leadership, effective communication, and a deep understanding of human motivation to overcome resistance to change. The importance of organizational change management is reiterated, advocating for clear strategies, education, and continuous improvement to implement lasting change.