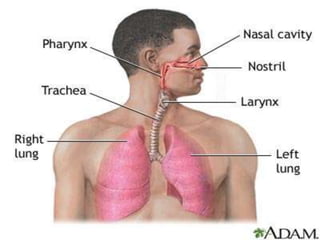
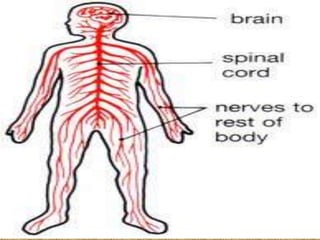
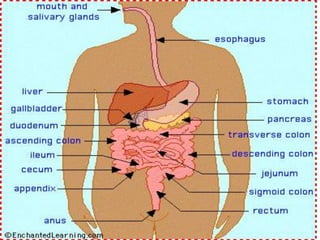
The document describes several body systems - respiratory, nervous, skeletal, and digestive. It provides details on key parts of each system and their functions. The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide. It includes the lungs, trachea, bronchi, and diaphragm. The nervous system controls and coordinates the body using neurons, brain, and spinal cord. The skeletal system provides structure with bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. The digestive system breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and used, moving food through the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.