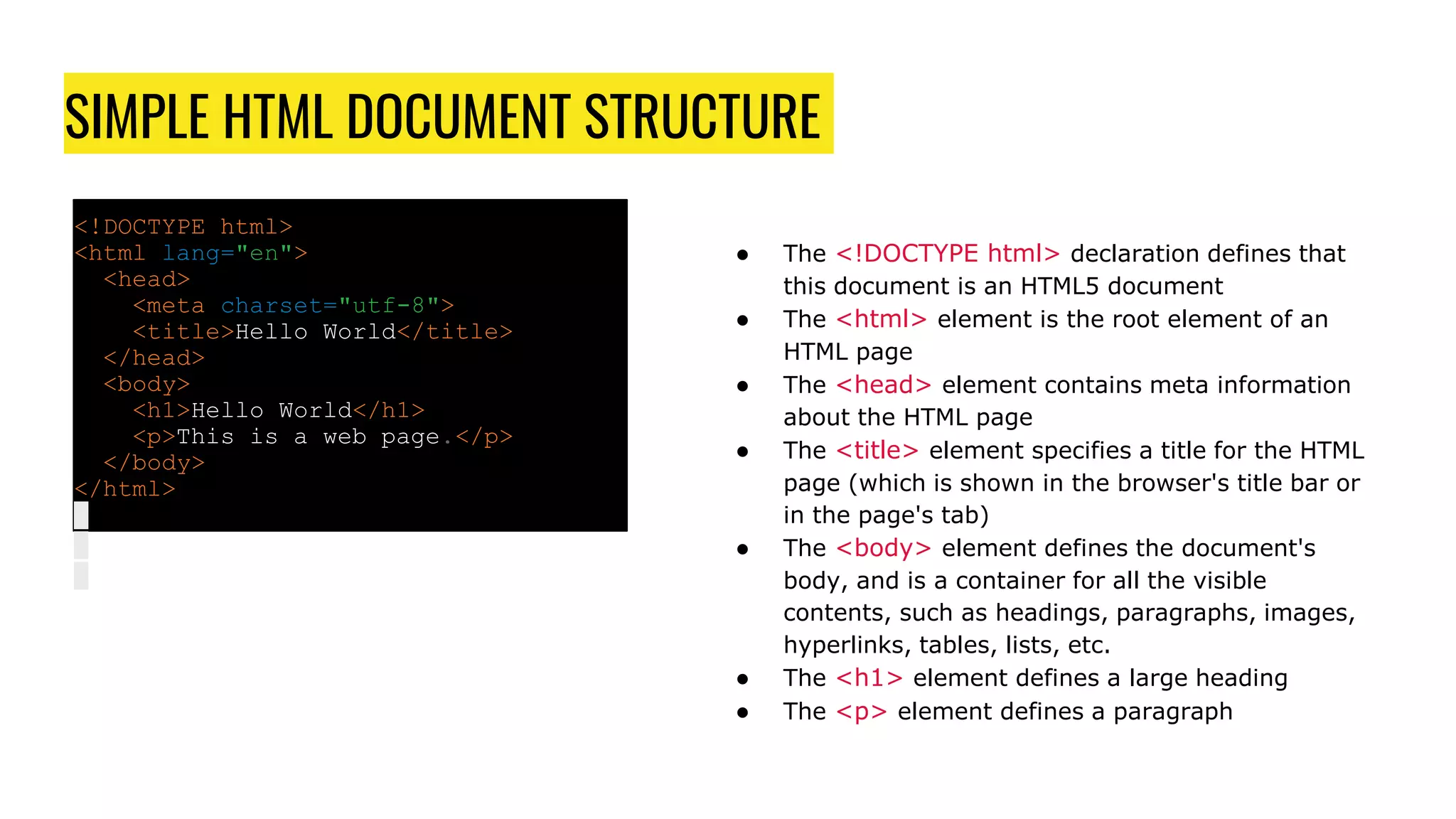
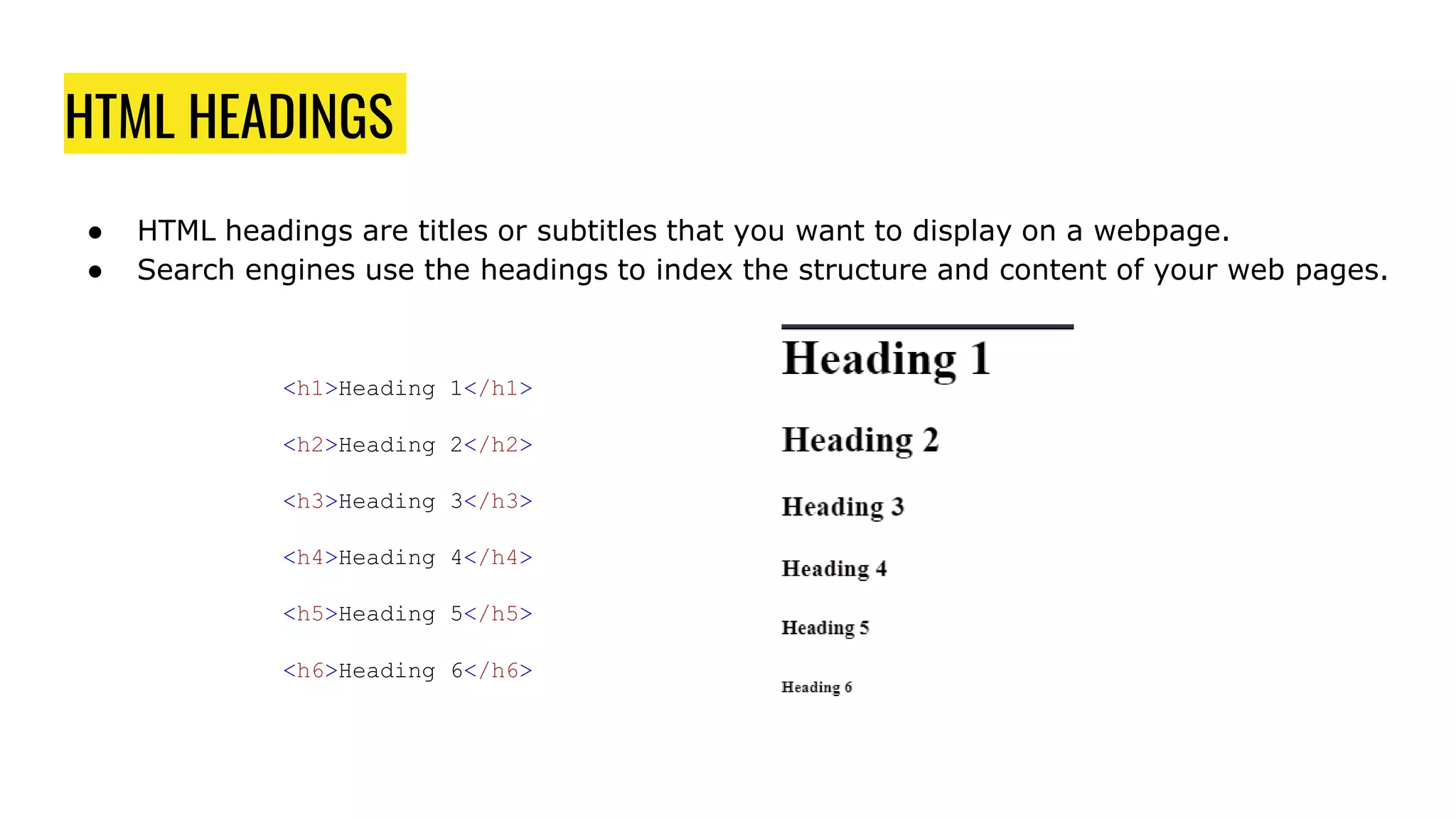
This document serves as an introduction to HTML, explaining its purpose as a markup language for web pages and outlining the basic structure of HTML documents. It covers key elements such as the doctype declaration, the main elements like <html>, <head>, and <body>, and the usage of tags and attributes. The document also provides examples of HTML headings, paragraphs, and the <pre> element for preformatted text.