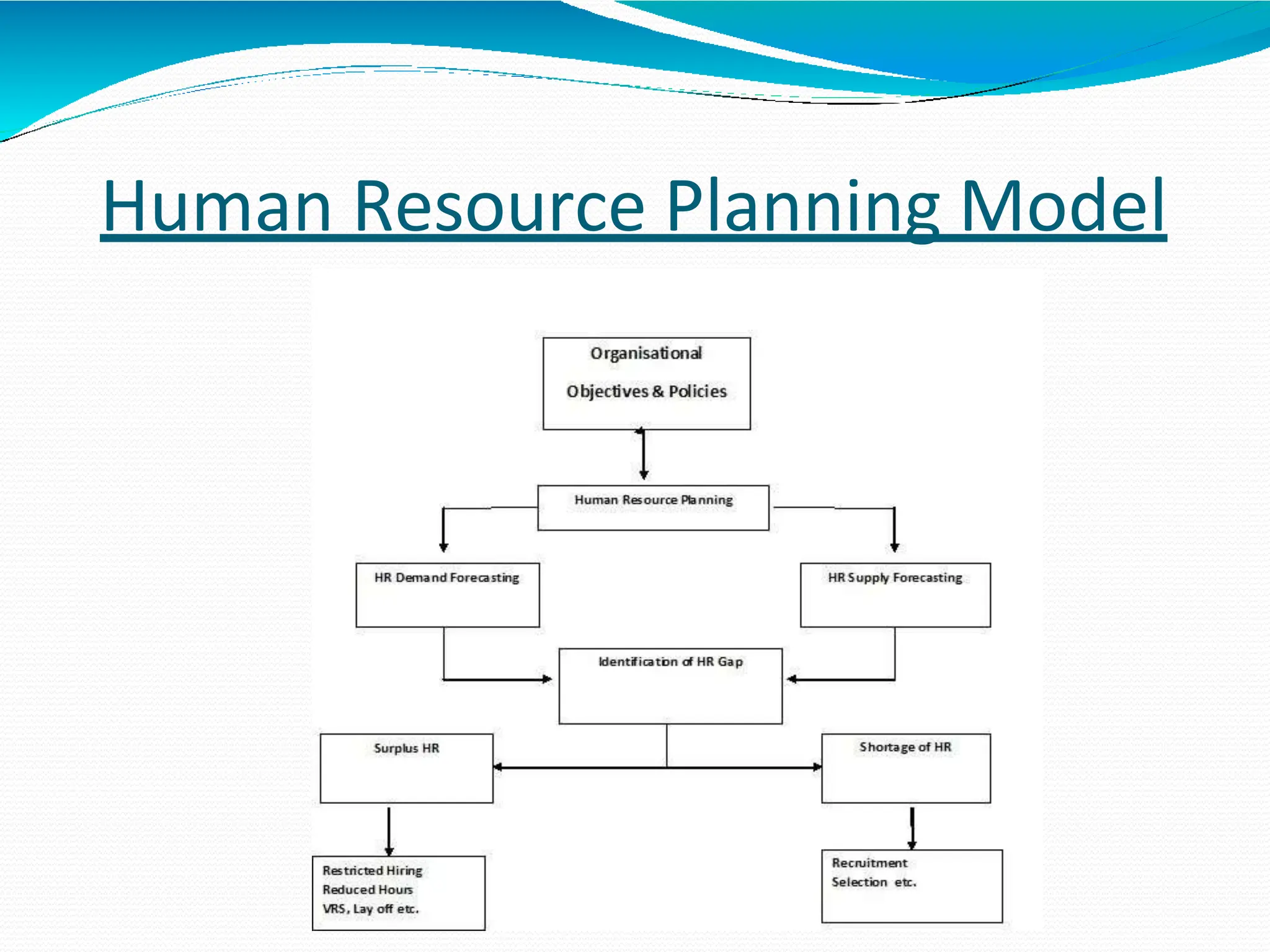
The document outlines the human resource planning (HRP) model, emphasizing the importance of aligning HR objectives with organizational goals. It details the processes of HR demand and supply forecasting to identify gaps between required and available human resources and suggests action plans to address these gaps. Additionally, it distinguishes between short-term and long-term HR planning based on immediate needs and future projections.