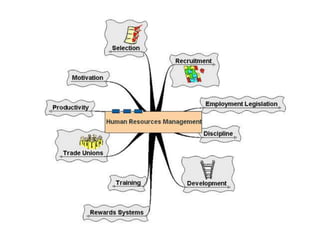
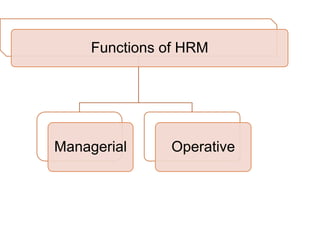
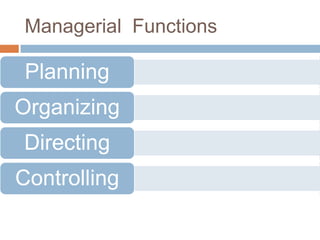
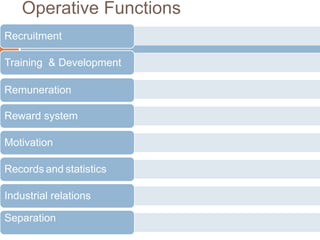
This document discusses the functions of human resource management. It outlines the managerial functions of HRM which include planning, organizing, directing, and controlling. It also describes the operative functions, which are recruitment, training and development, remuneration, reward systems, motivation, records and statistics, industrial relations, and separation. For each function, it provides a brief definition or description.