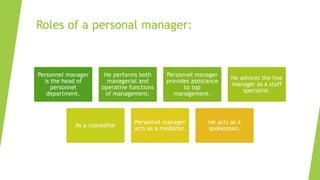
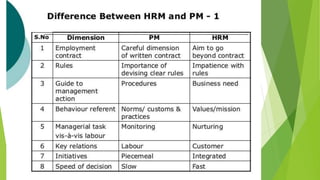
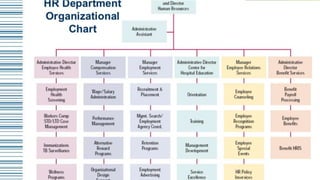
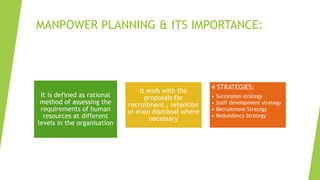
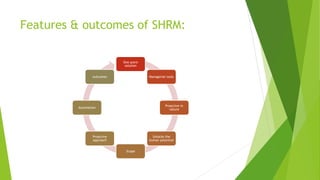
This document provides an overview of key concepts in human resource management (HRM). It begins by explaining that humans are the fundamental resource behind all products and services. It then defines HRM and discusses why organizations invest in human resource development and talent management. The document outlines various HRM functions like selection, training, performance appraisal, compensation, and strategic HRM. It emphasizes that HRM involves attracting, developing and retaining skilled employees to help organizations achieve their goals.