This document discusses various aspects of teaching listening skills to language learners. It begins by defining listening as the ability to understand what others are saying, including pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, and meaning. Several key points are then made: listening is important for communication; it helps students acquire language subconsciously; and it is a receptive skill. Common problems students face with listening are also outlined.
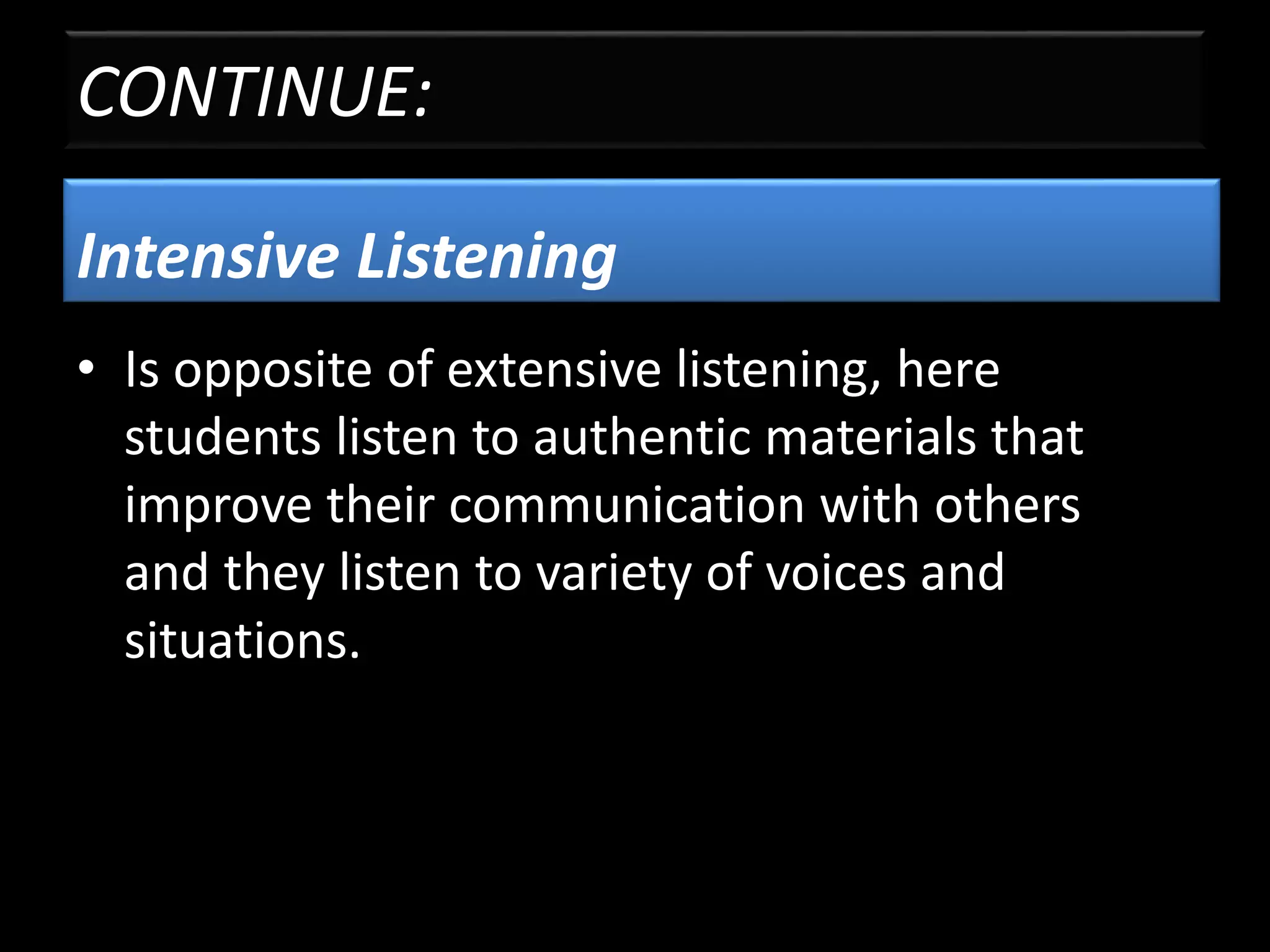
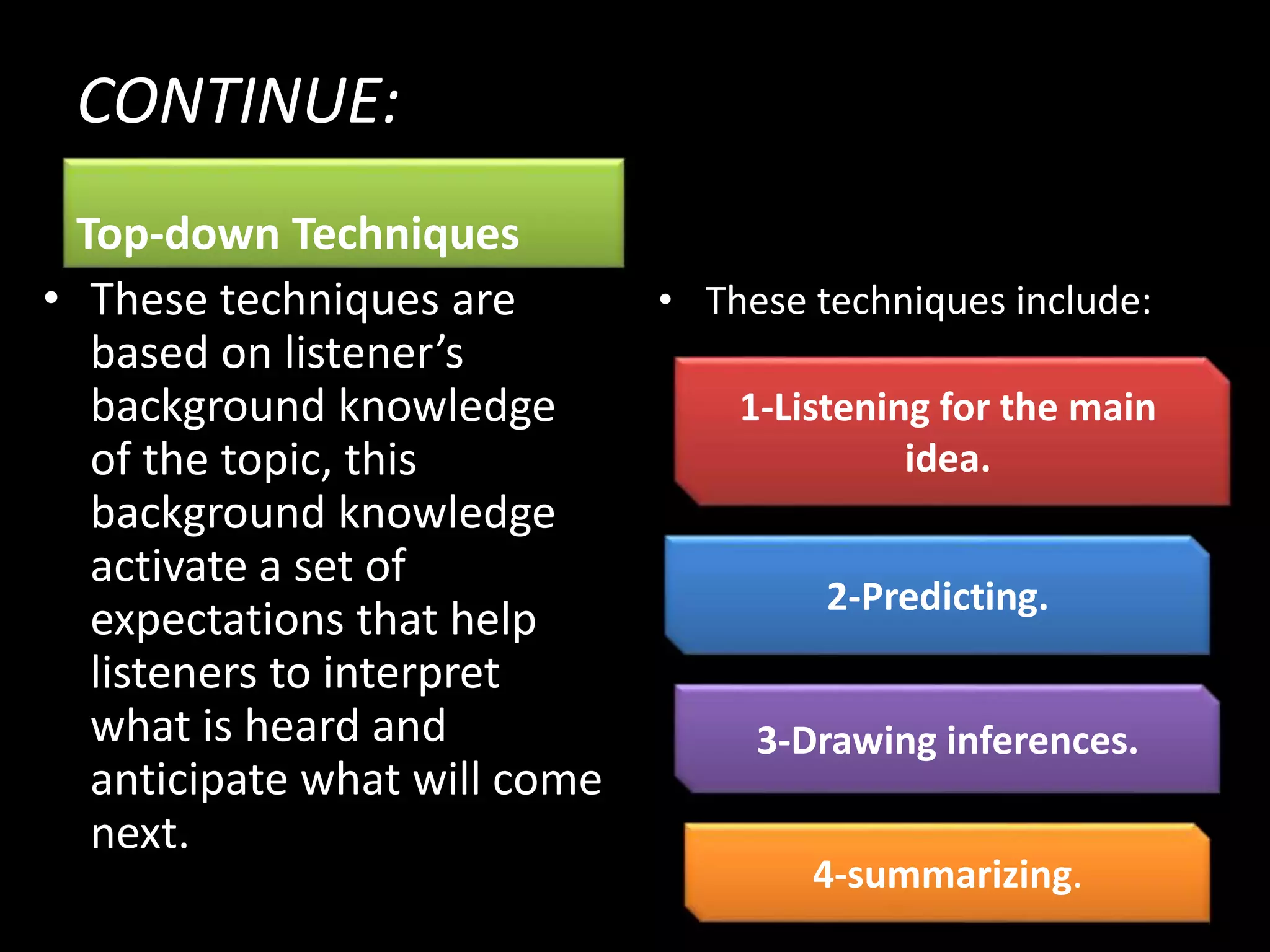
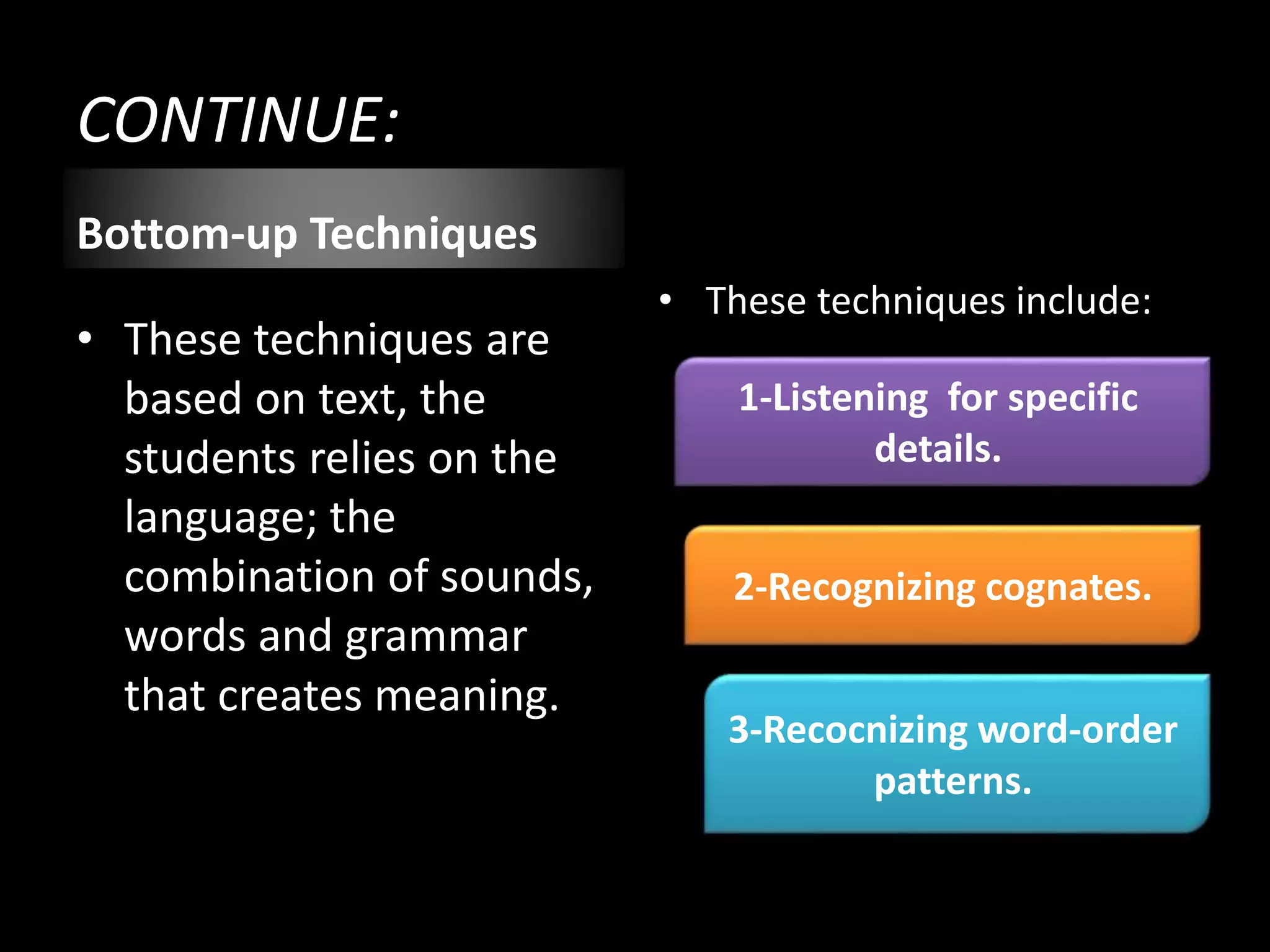
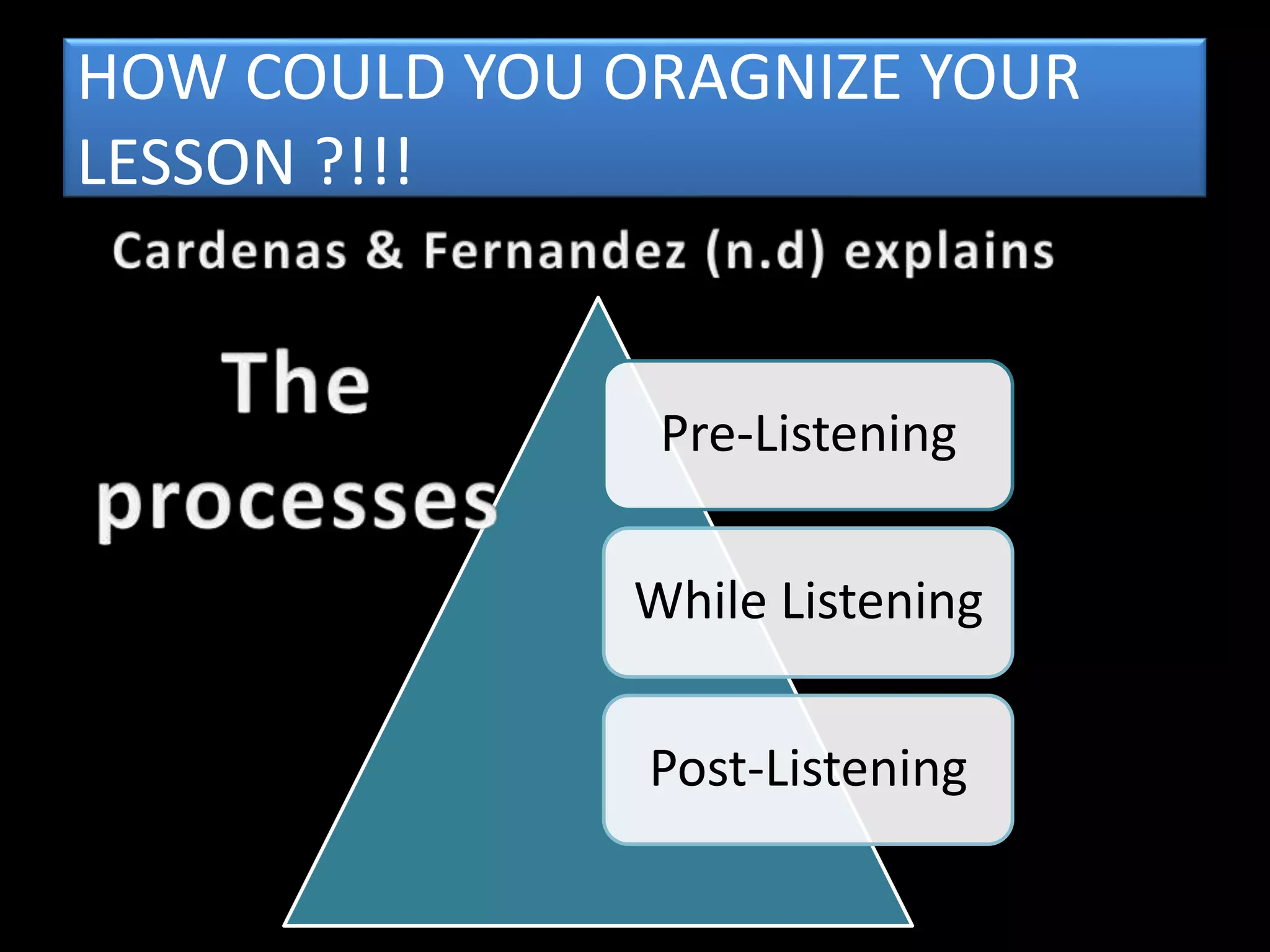
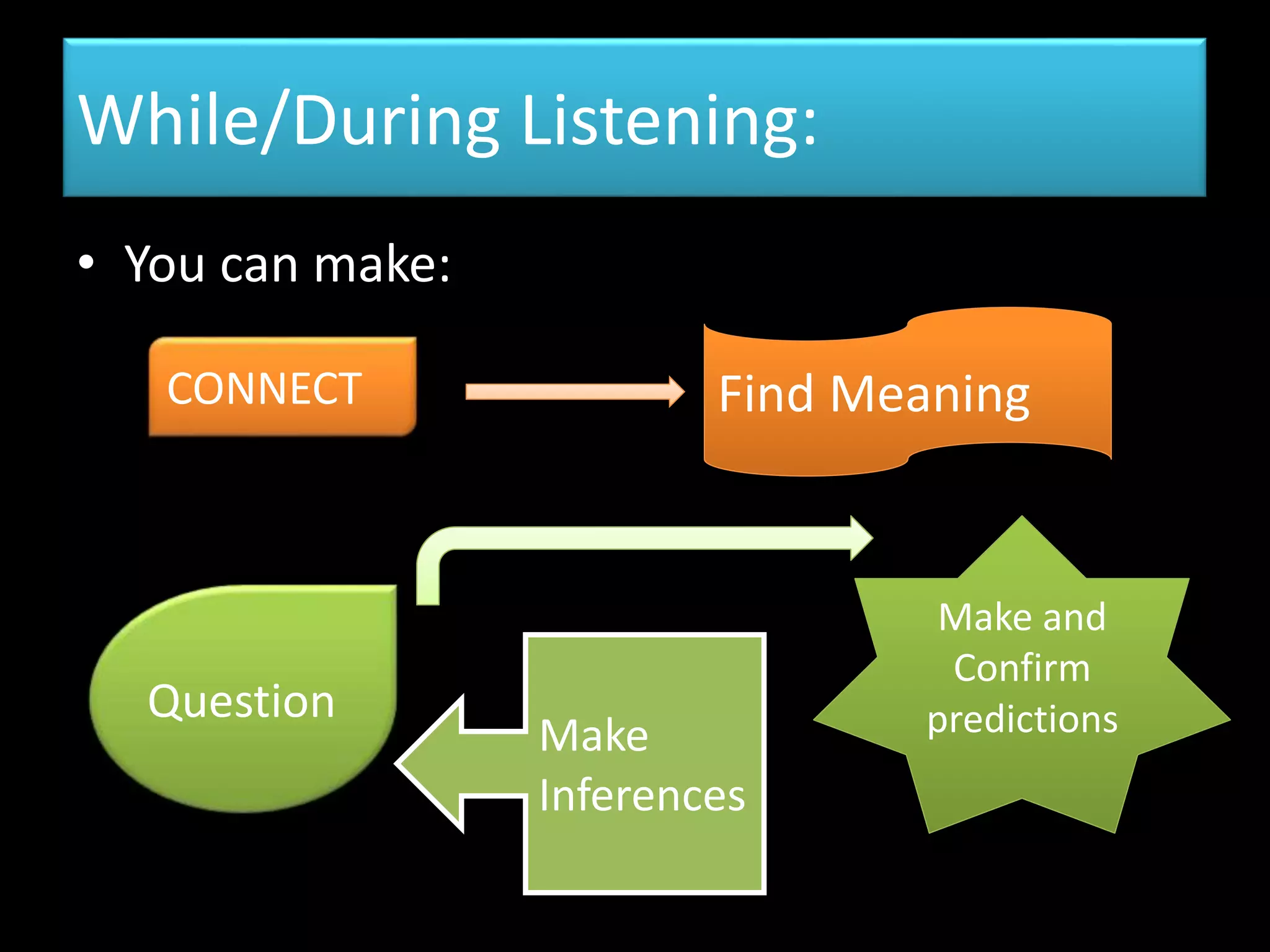
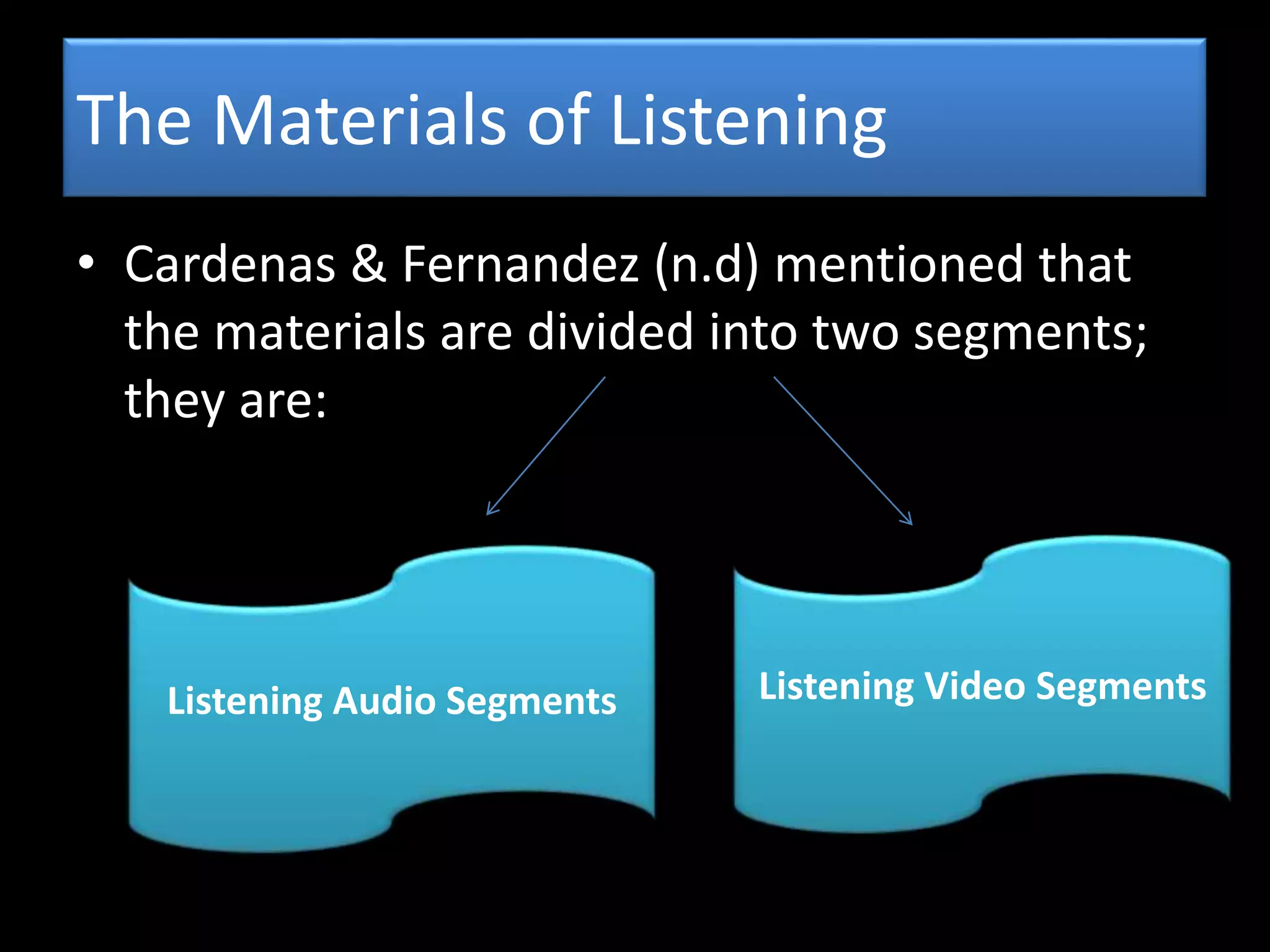
The document goes on to discuss two types of listening - intensive and extensive. Techniques for teaching listening are categorized as top-down or bottom-up. Principles for effective listening instruction are presented, along with considerations for pre, during, and post listening activities. Materials that can be used and goals of developing listening comprehension are also