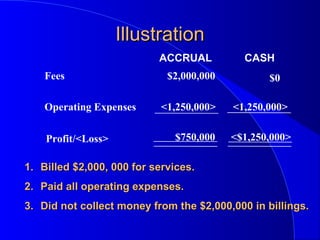
The document presented by Chaim Yudkowsky, CPA, discusses financial statements, their preparation, and the differences between cash and accrual accounting. It outlines the roles of accountants in compiling, reviewing, and auditing financial statements while adhering to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). The presentation emphasizes the importance of financial statements in revealing a company's assets, liabilities, and profitability.











![Compilation Report -Compilation Report -
Accrual BasisAccrual Basis
“. . .
A compilation is limited to presenting in the form of
financial statements information that is the representation of
management. We have not audited or reviewed the
accompanying financial statements [and supplementary
schedules] and, accordingly, do not express an opinion or
any other form of assurance on them.
. . .”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtomakemoremoneycirca1997-130705161826-phpapp01/85/How-to-make-more-money-Part-2-circa-1997-13-320.jpg)