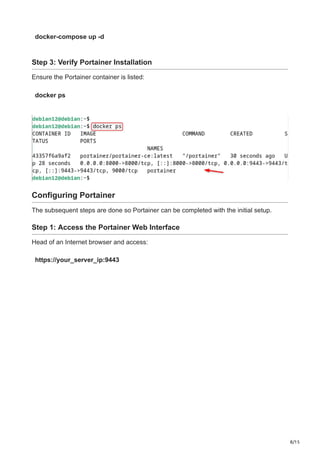
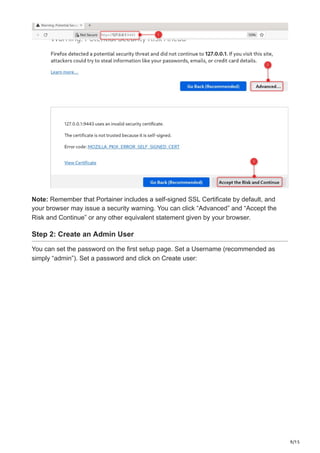
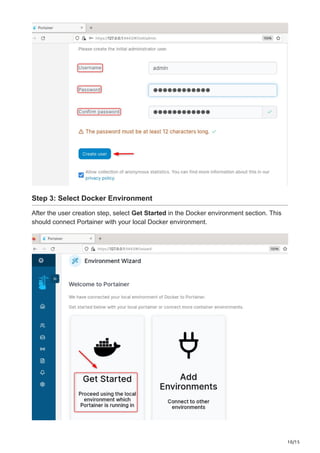
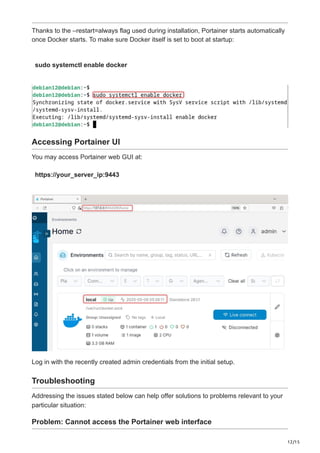
Portainer is a robust tool for container management that offers an intuitive web interface for easy management of Docker environments. It allows users to effortlessly control containers, images, networks, and volumes using a graphical interface rather than needing to navigate Docker’s intricate command line. From system preparation to the first login into the Portainer web interface, this manual will guide you through all the steps necessary for installing Portainer on Debian 12.
Keep reading:
https://greenwebpage.com/community/how-to-install-portainer-docker-ui-web-interface-on-debian-12/


![3/15
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo gpg –dearmor -o
/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
Step 4: Setting Up the Docker Repository
Add the Docker repository to your system:
echo “deb [arch=$(dpkg –print-architecture) signed-
by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg]
https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable” | sudo tee
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Step 5: Install Docker Engine
Update unused packages and install the program:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtoinstallportainerdockeruiwebinterfaceondebian12-250512054929-4fcacc4e/85/How-to-Install-Portainer-Docker-UI-Web-Interface-on-Debian-12-pdf-3-320.jpg)