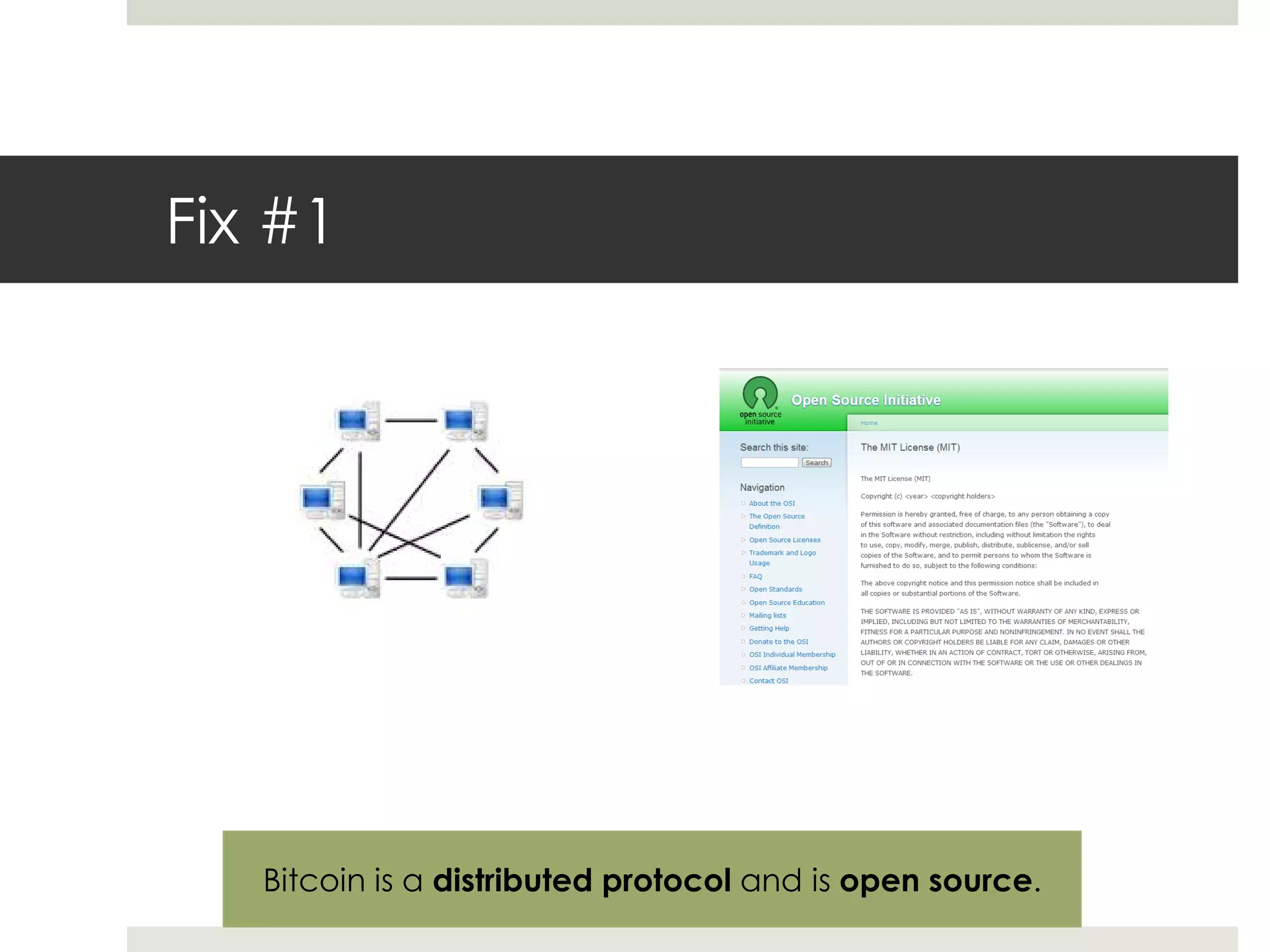
1. Bitcoin is a digital currency that exists on a distributed network, not controlled by any central authority. It uses cryptography and a public ledger called the blockchain to record transactions.
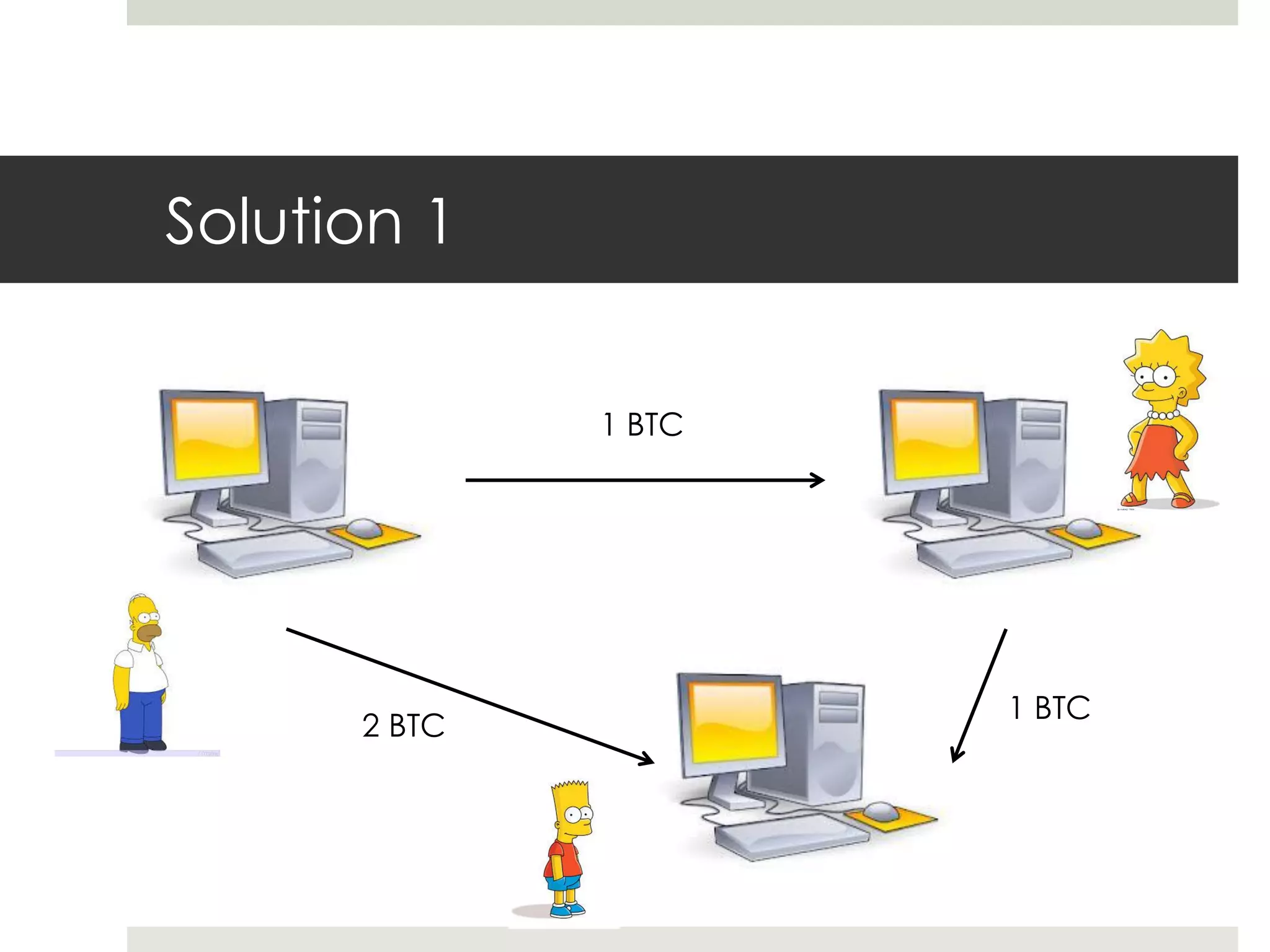
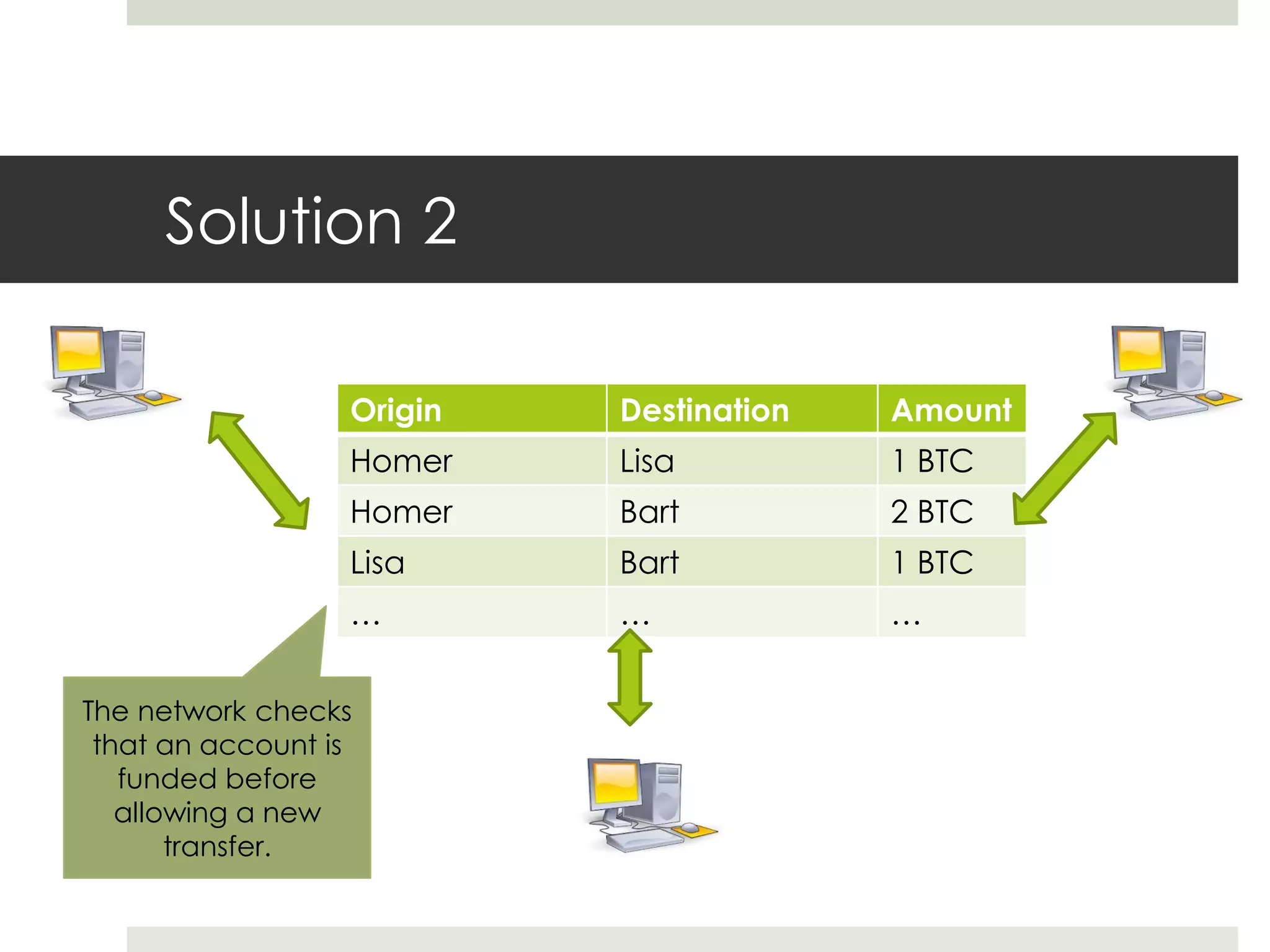
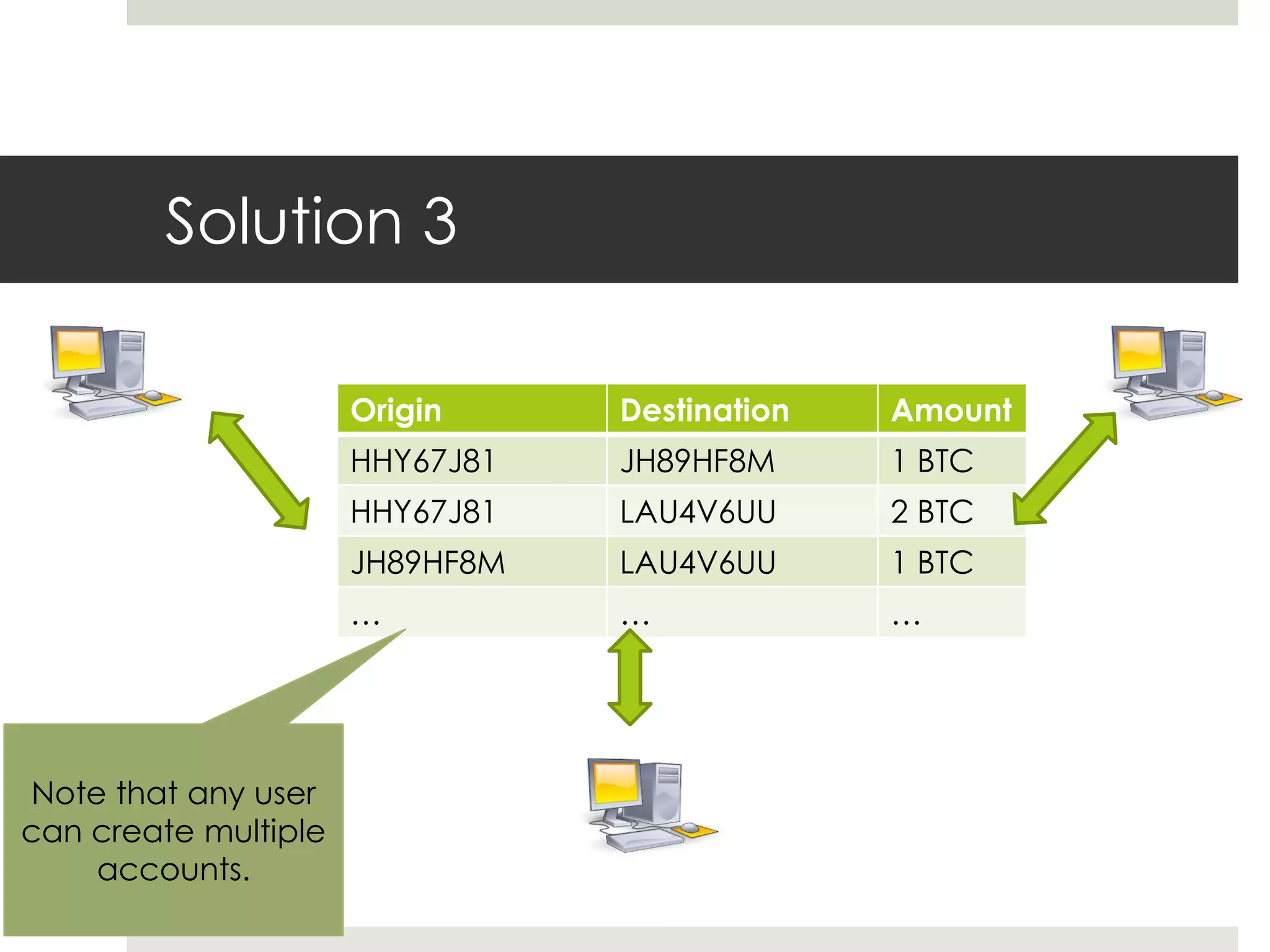
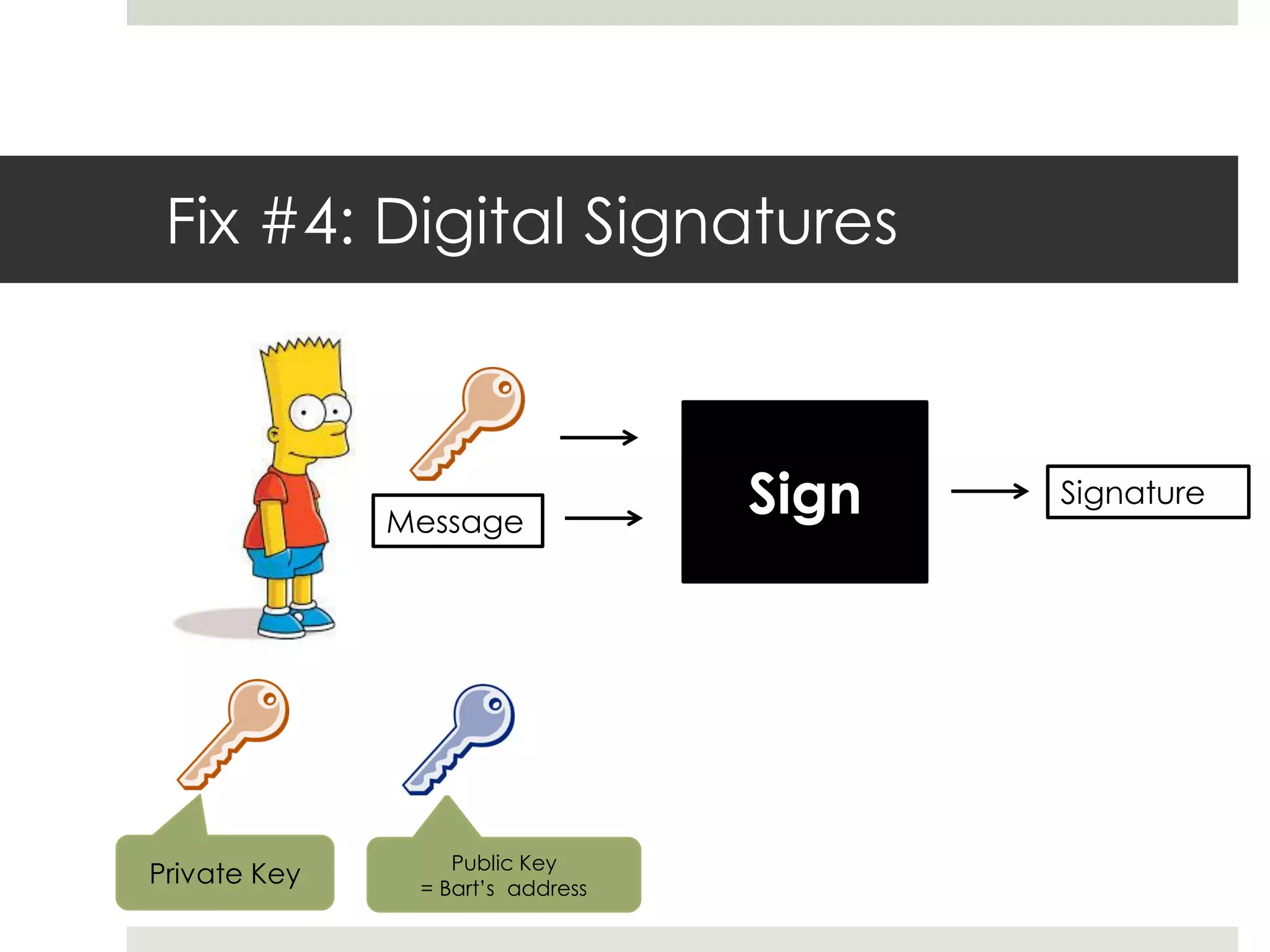
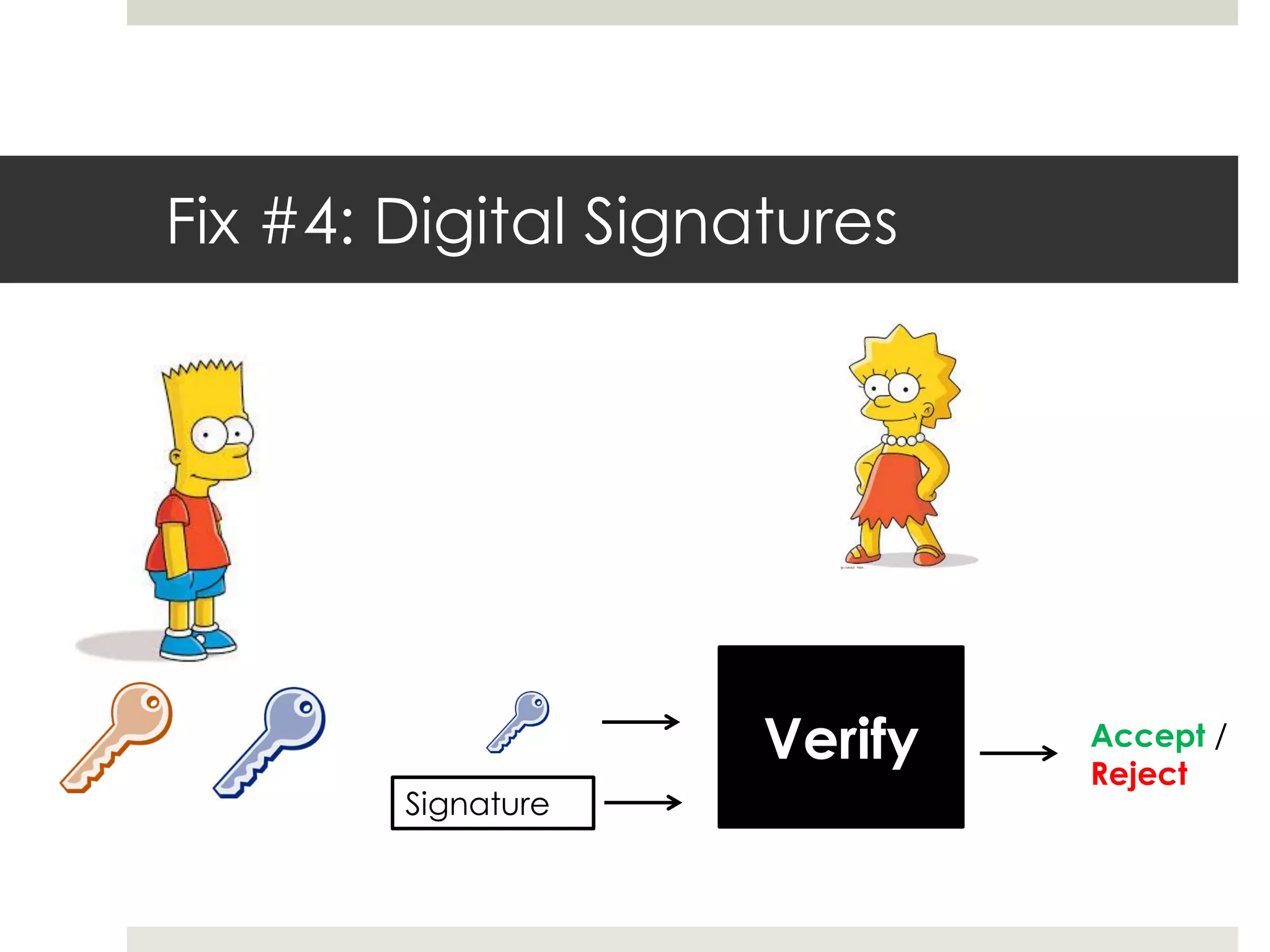
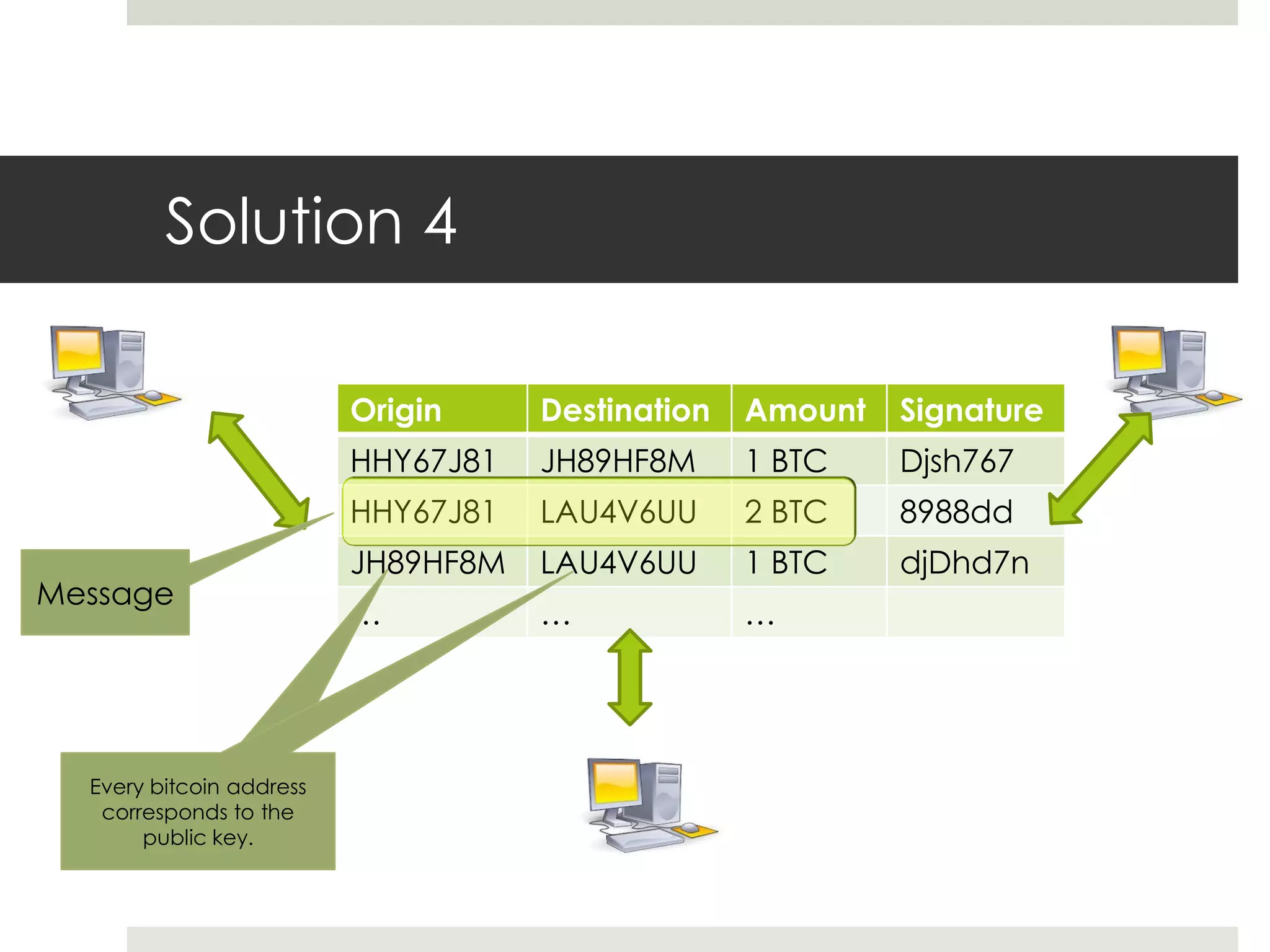
2. Users can transfer bitcoin to each other via digital signatures to authorize transactions without revealing their identities. The network checks that funds are available before allowing transfers to prevent double spending.
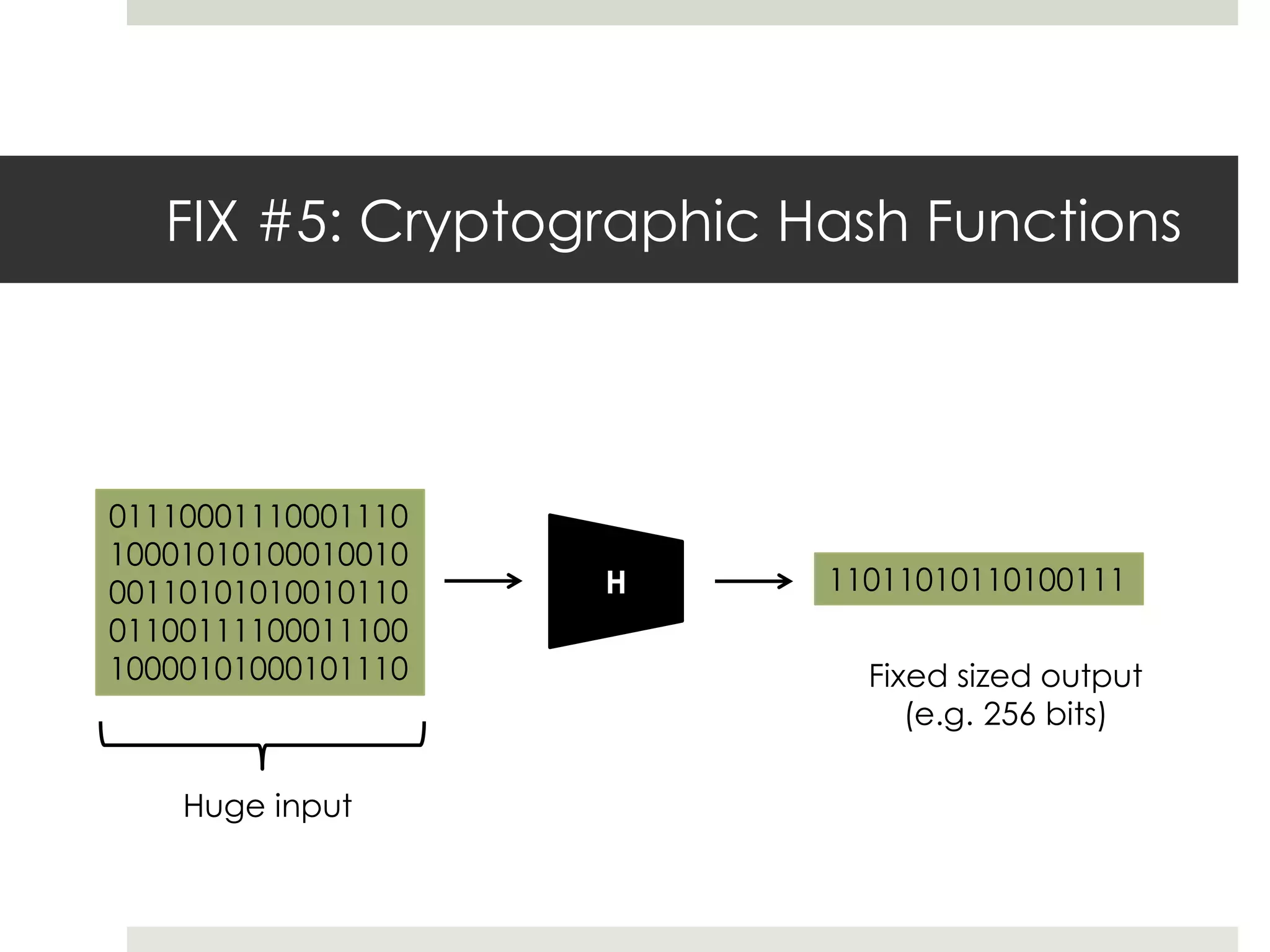
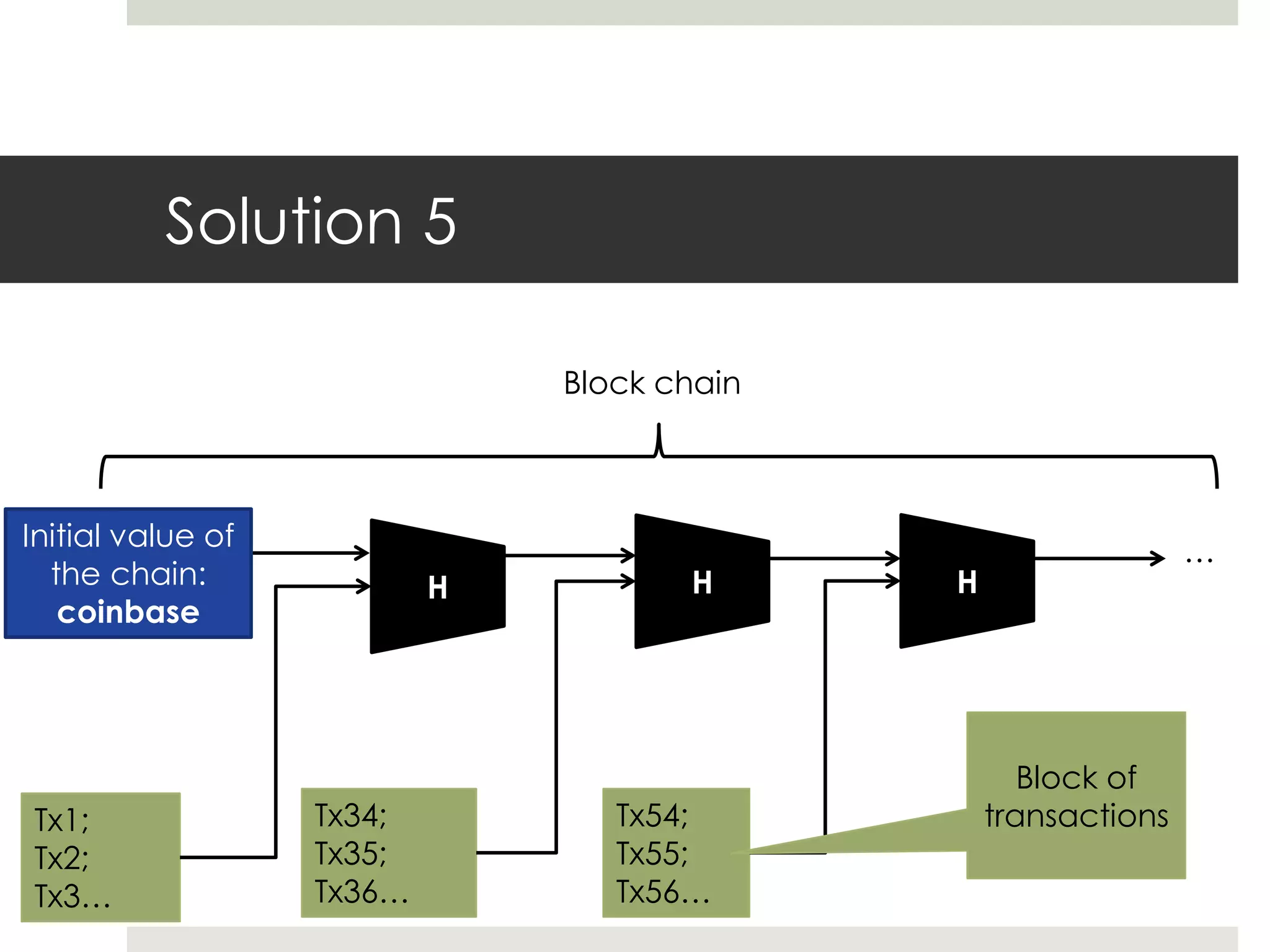
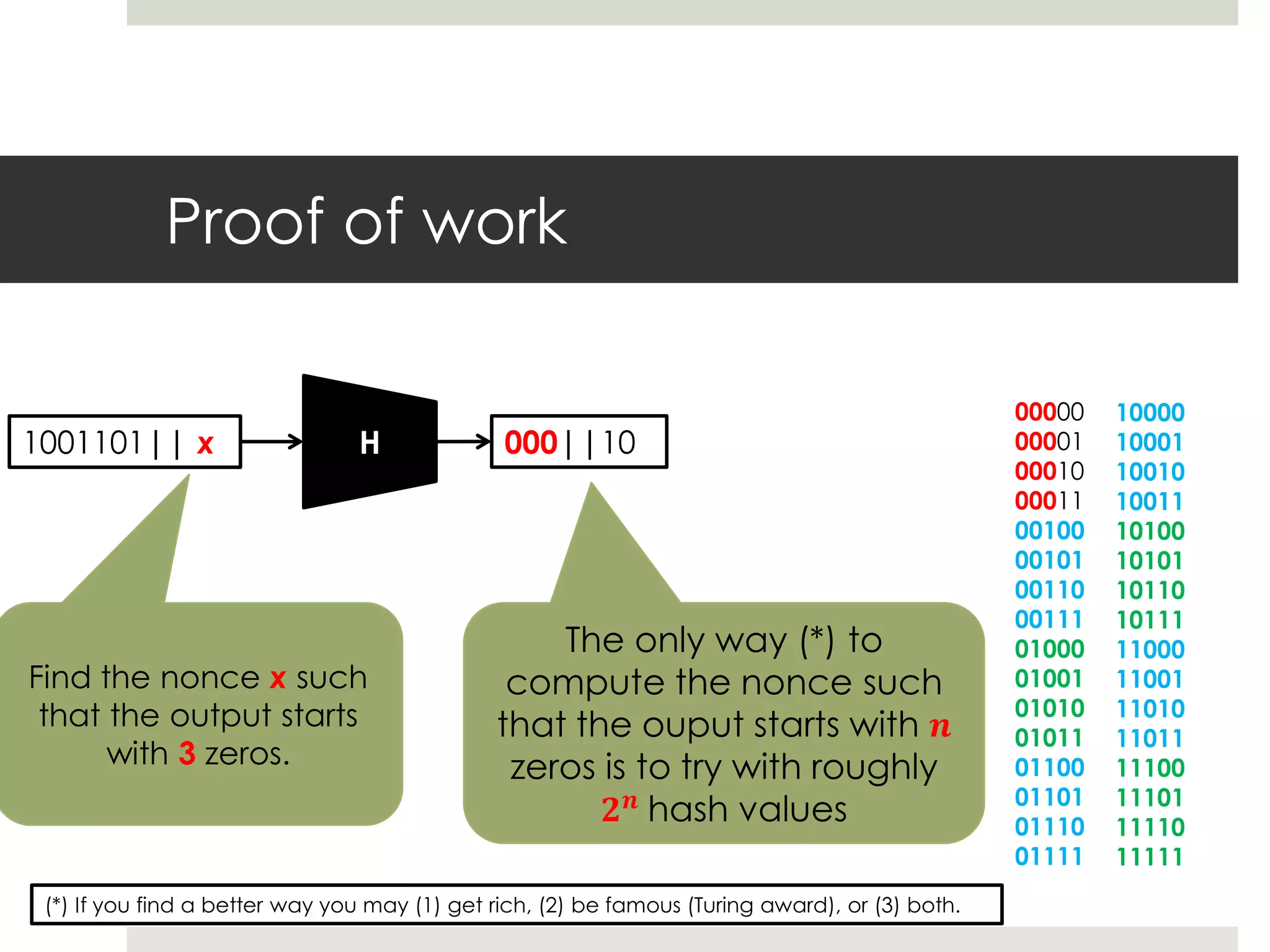
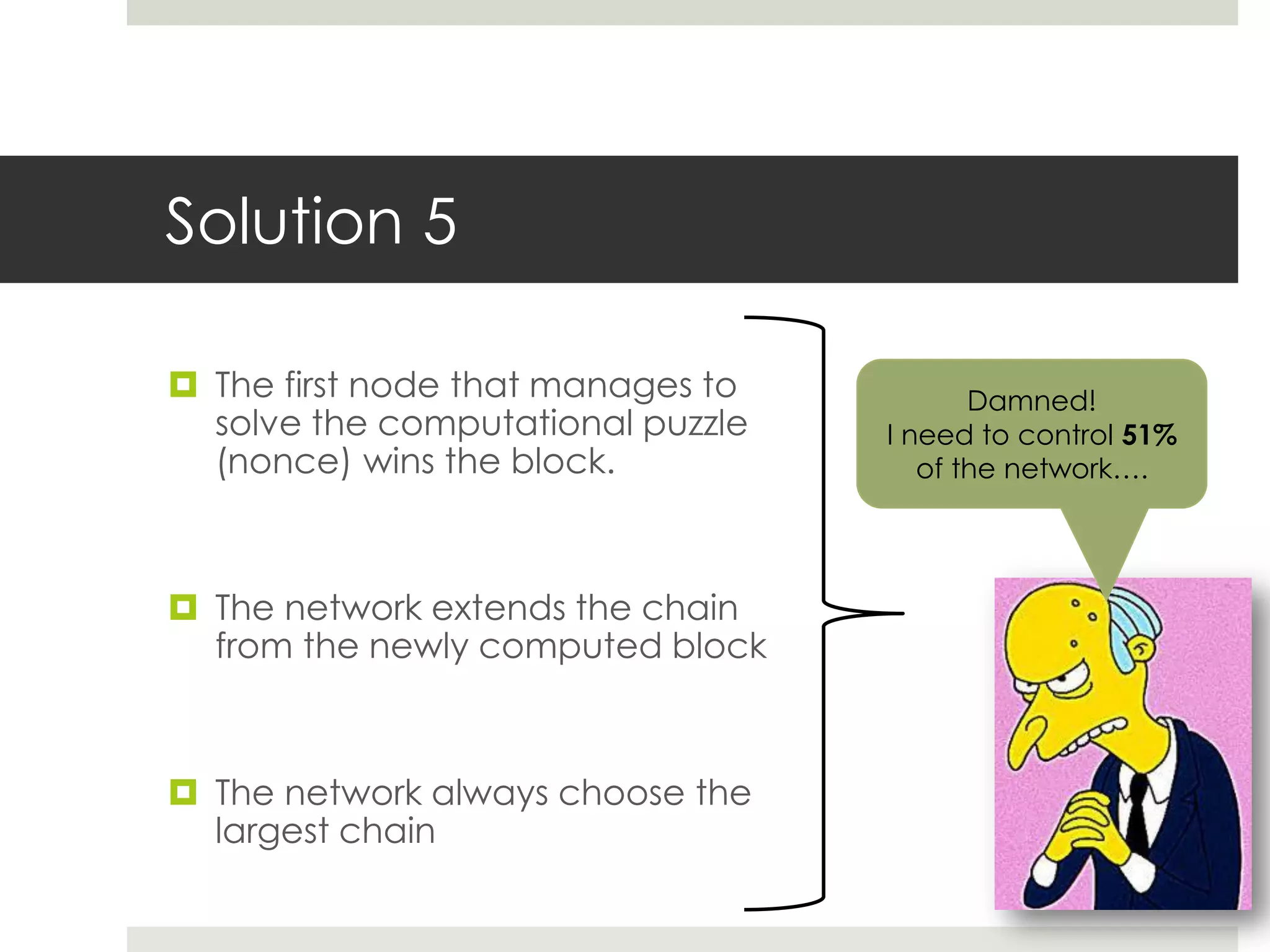
3. Miners on the network validate transactions by competing to solve computational puzzles and add verified transactions to the blockchain. Solving a puzzle first earns the miner a reward of new bitcoins, providing an incentive to secure the network.