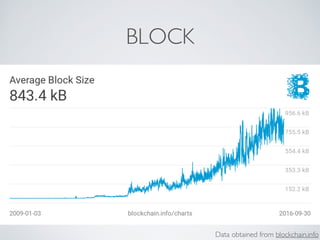
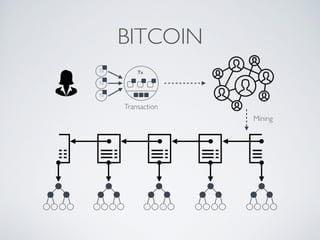
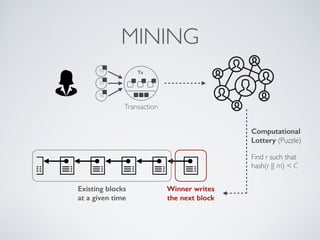
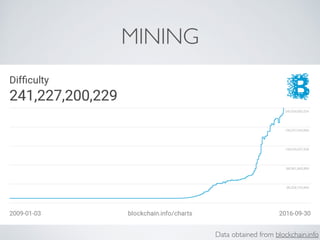
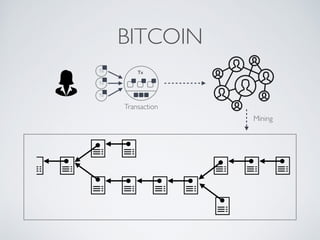
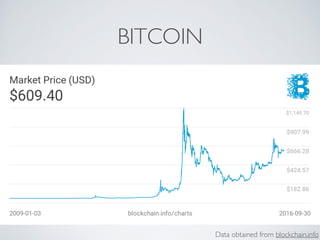
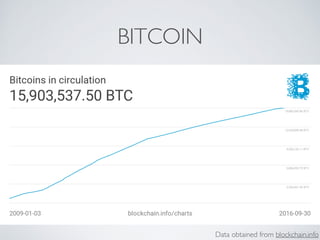
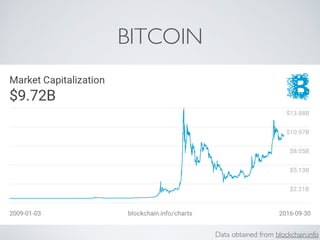
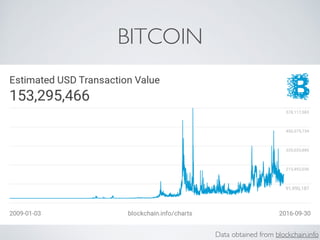
The document discusses blockchain and cryptocurrency technologies. It provides information on the following key points:
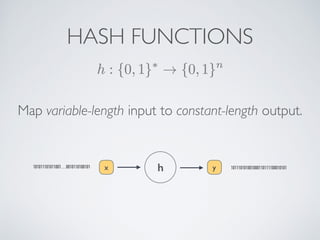
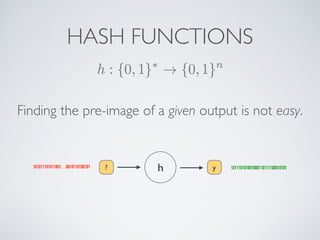
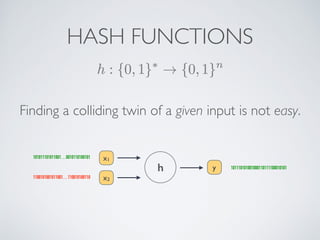
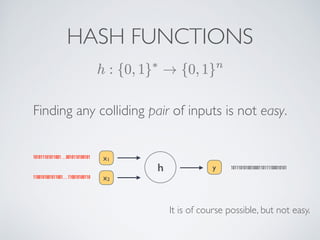
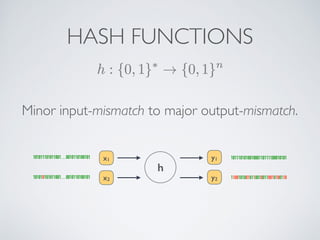
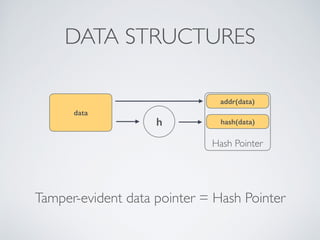
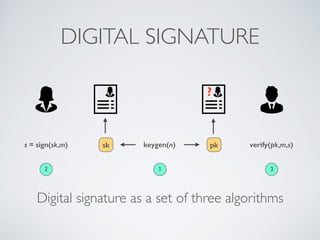
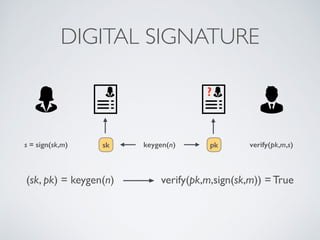
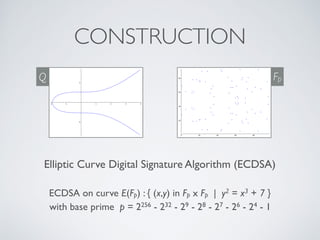
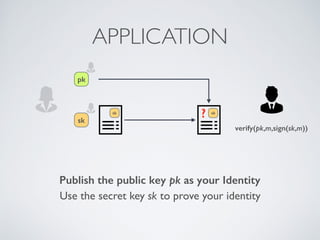
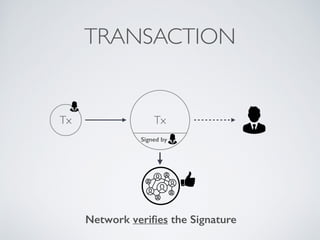
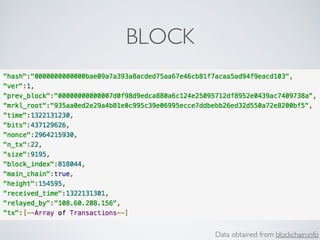
- Cryptographic hash functions are the backbone of blockchain and map variable-length inputs to fixed-length outputs, making it difficult to determine the input from the output or find colliding inputs.
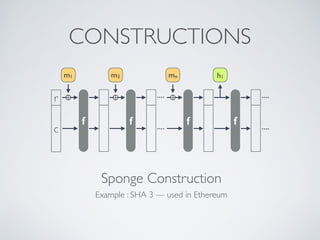
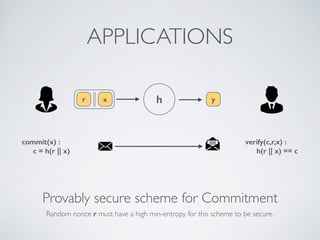
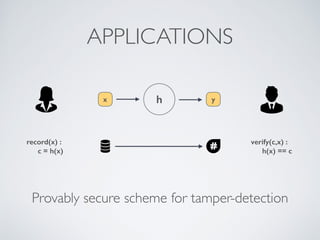
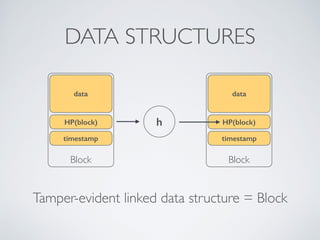
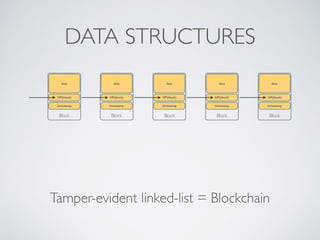
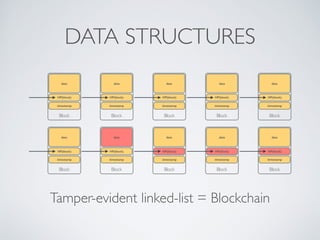
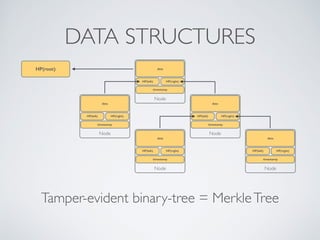
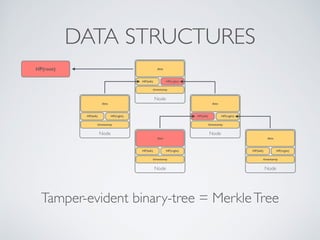
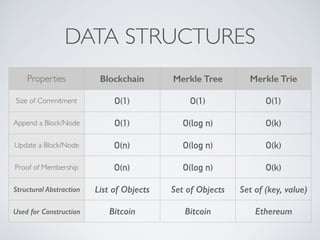
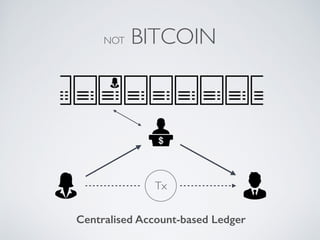
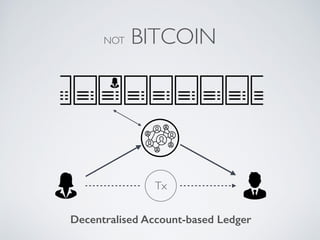
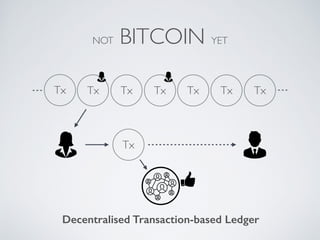
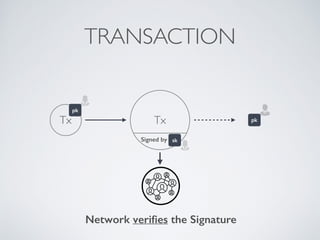
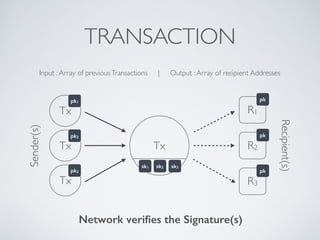
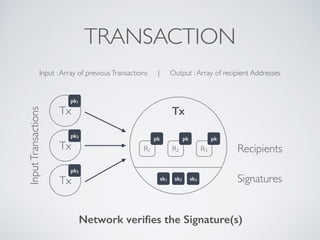
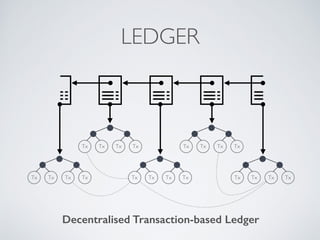
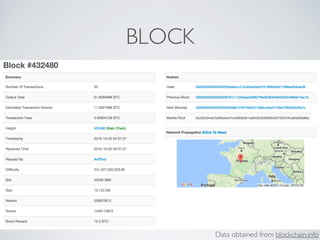
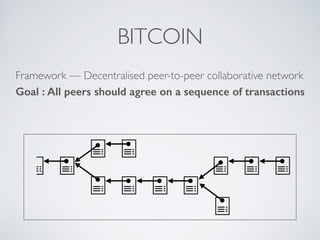
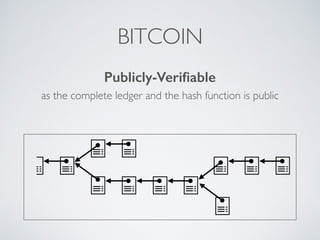
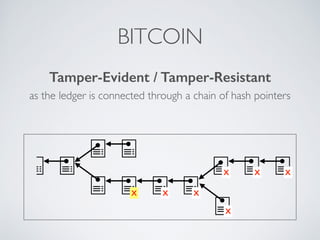
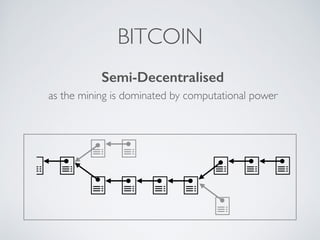
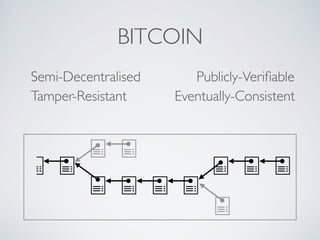
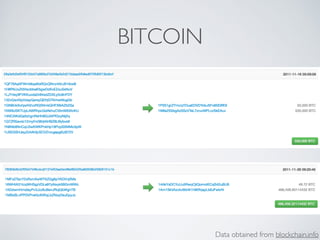
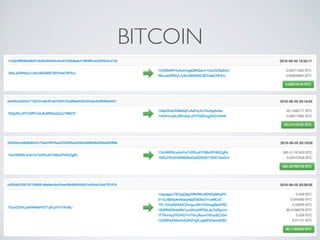
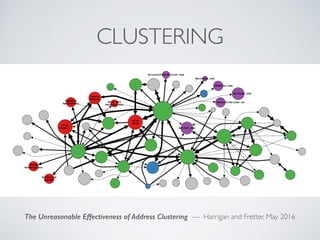
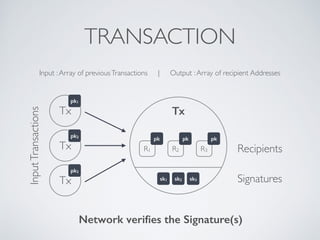
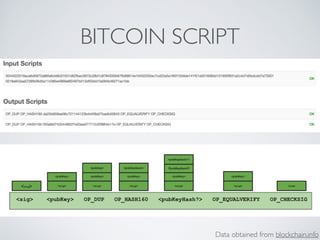
- Blockchain uses these hash functions to create tamper-evident linked data structures like blocks in a blockchain or nodes in a Merkle tree. This allows transactions in a blockchain to be publicly verifiable and tamper-resistant.
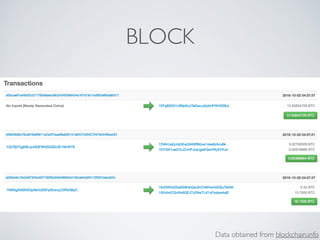
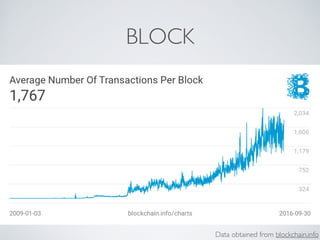
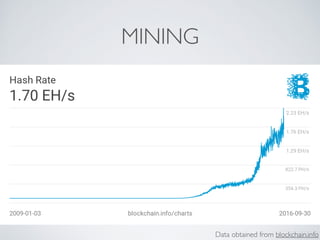
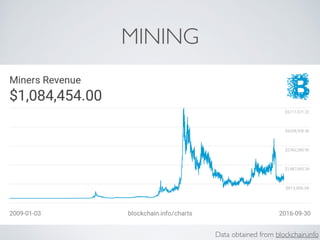
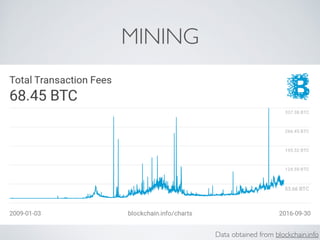
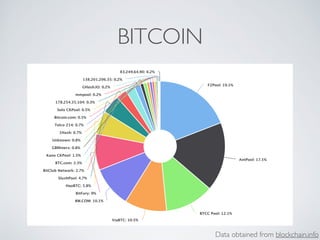
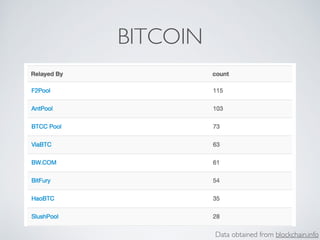
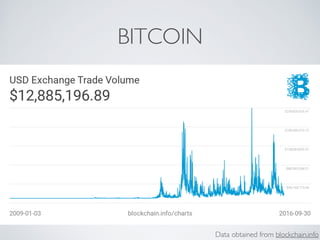
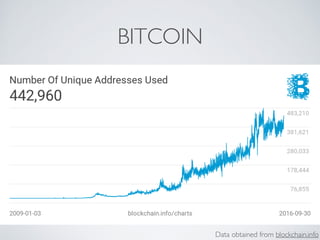
- Bitcoin implements blockchain technology to create a decentralized transaction ledger. Transactions are grouped into blocks and miners compete to add new blocks through a computational puzzle. This consensus mechanism allows all nodes to agree