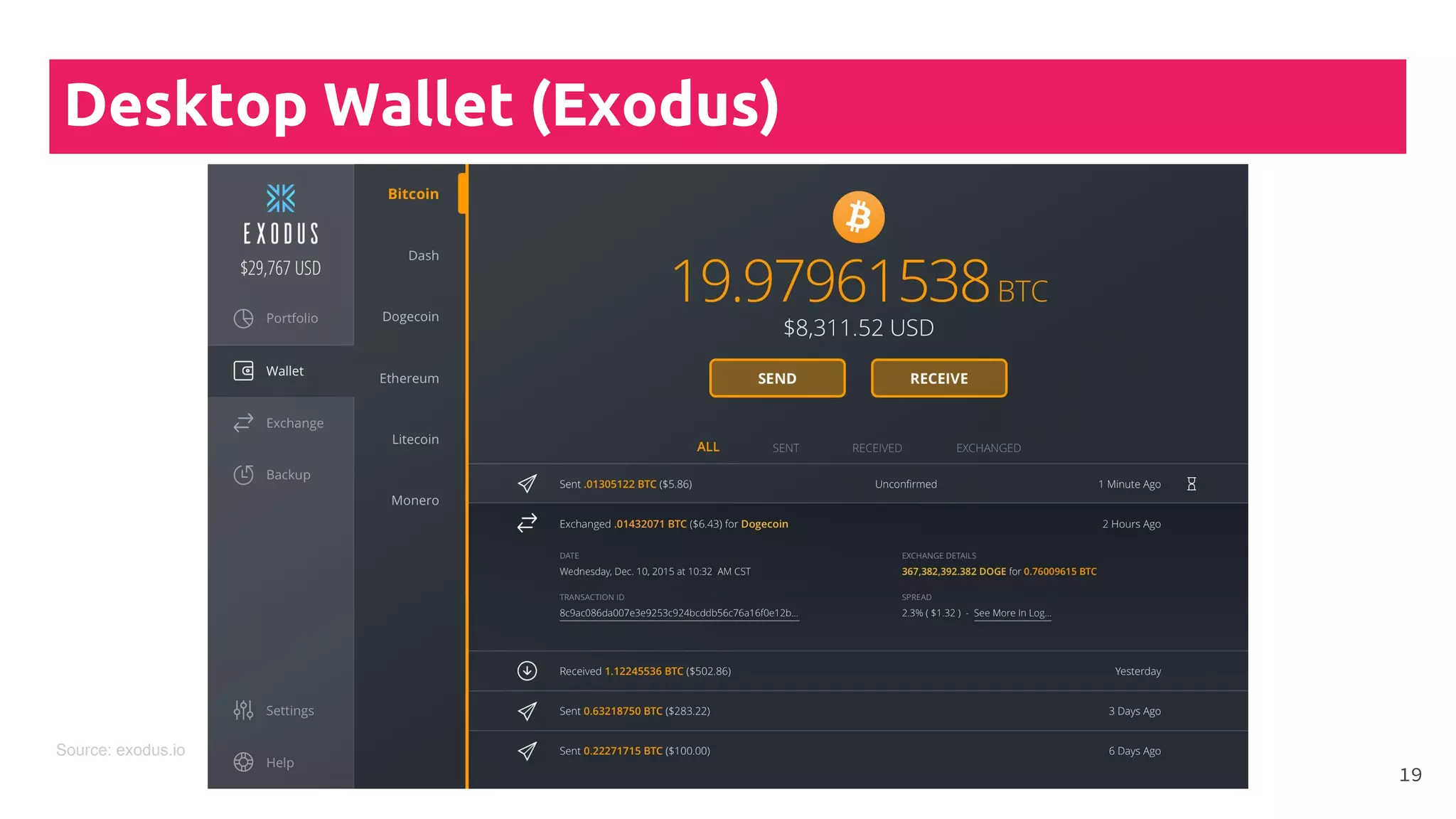
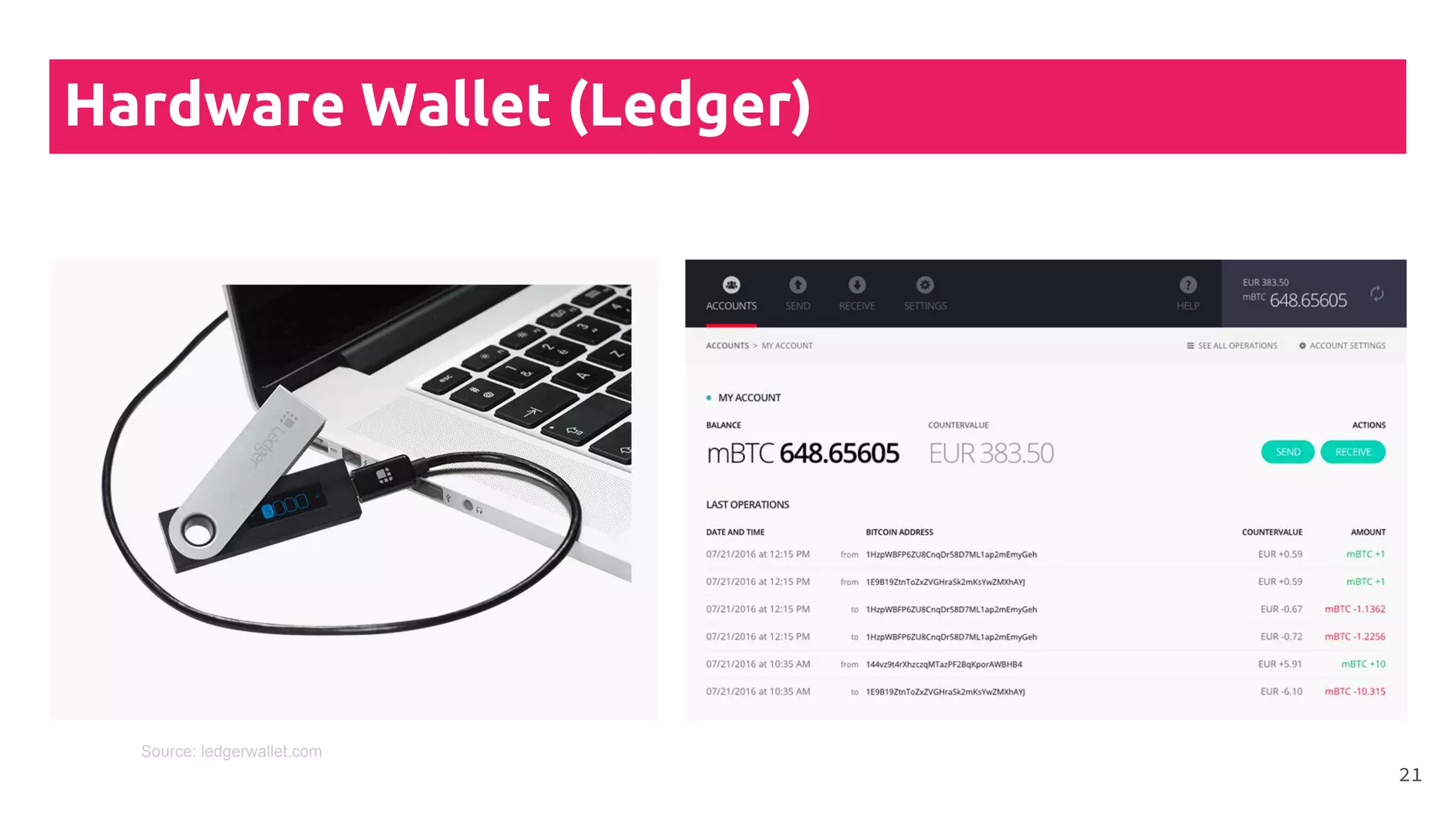
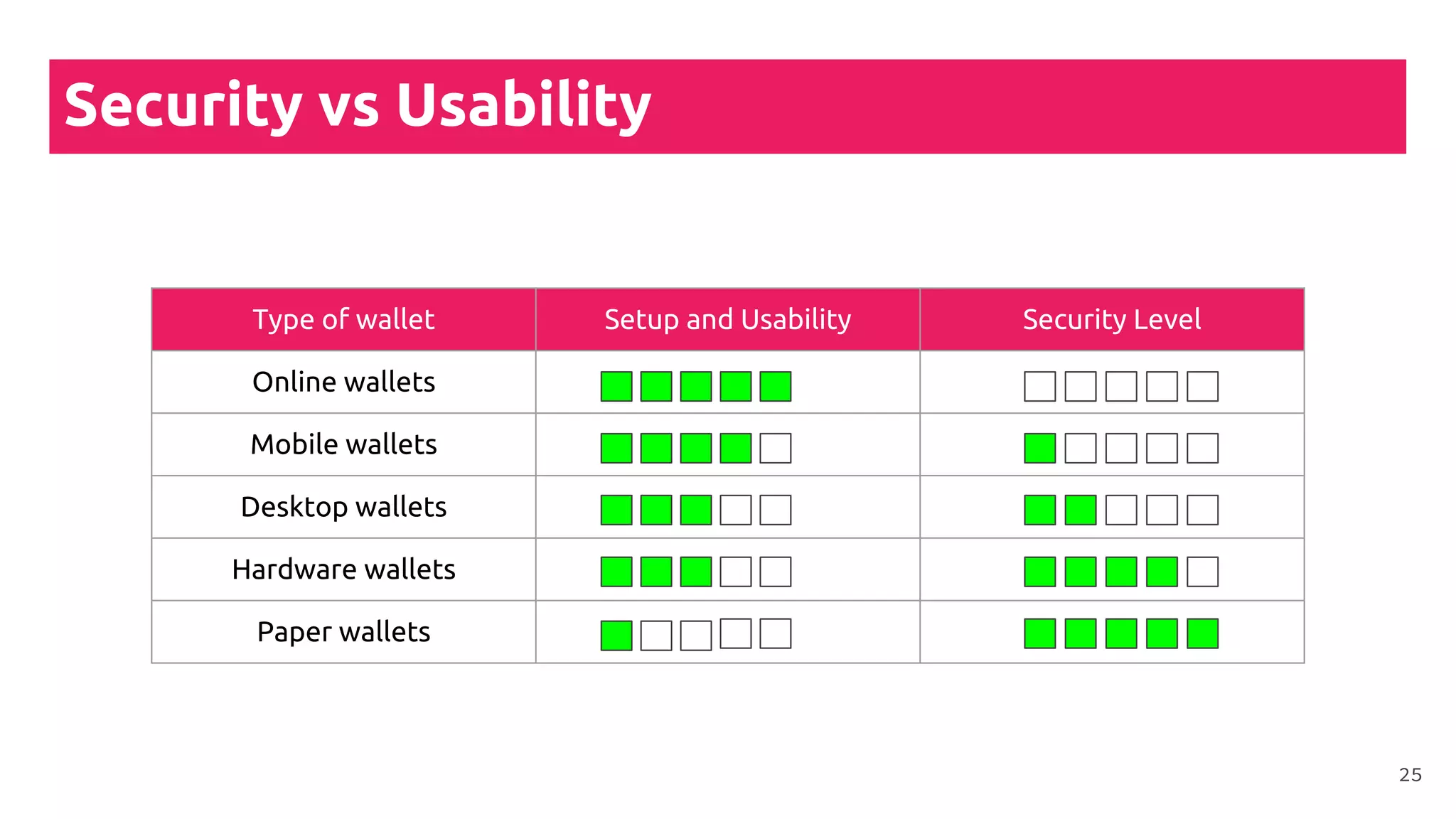
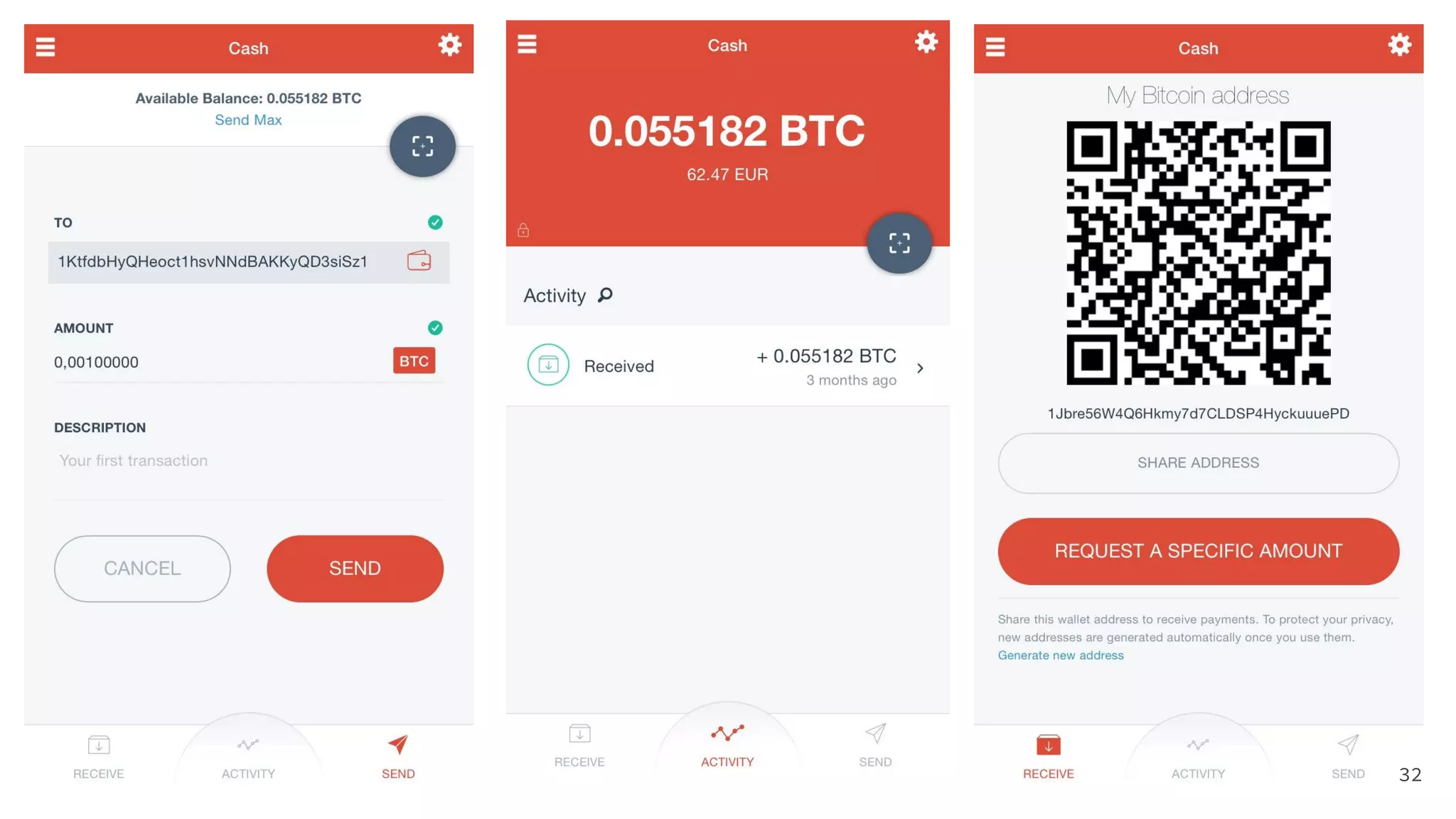
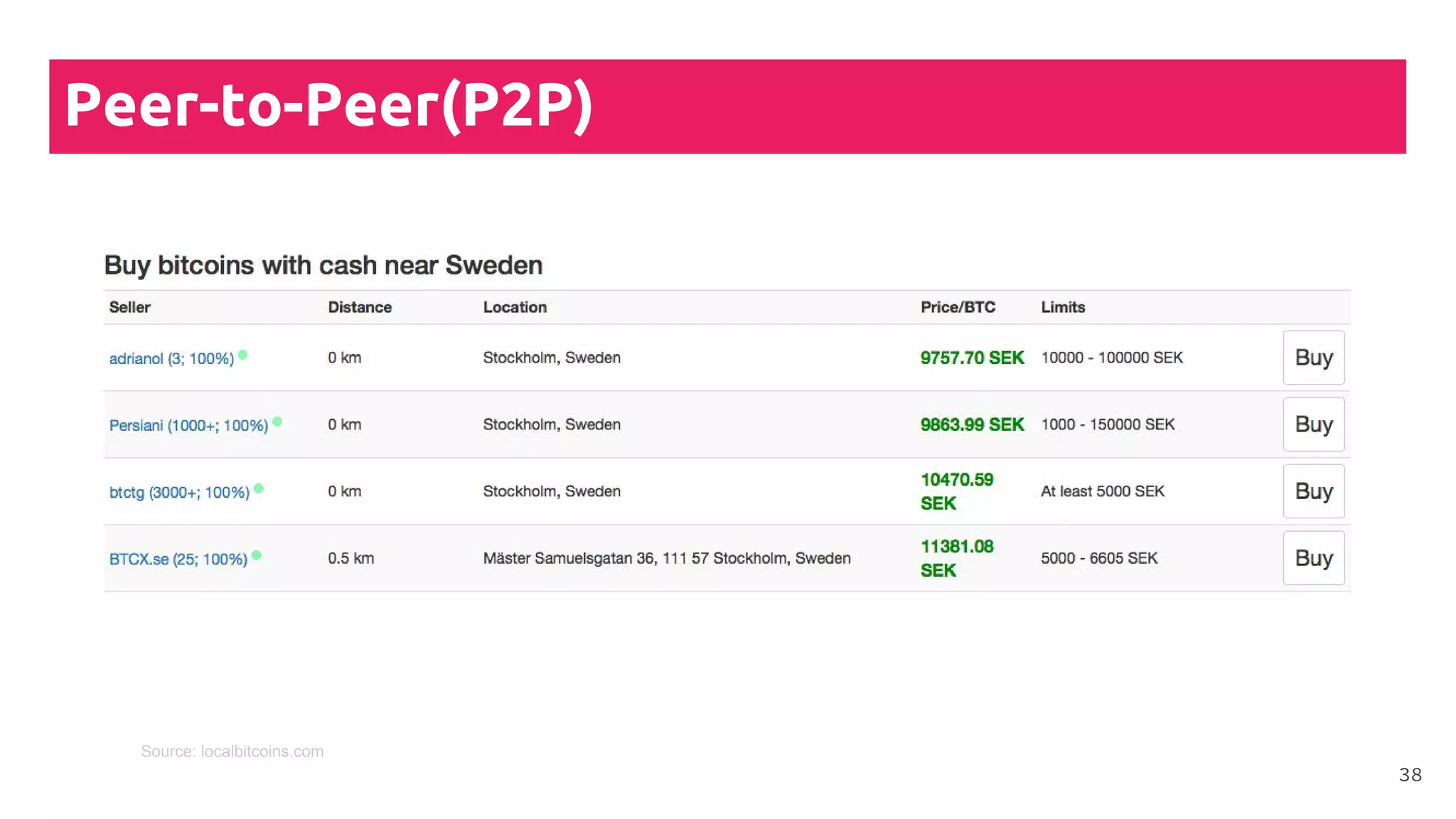
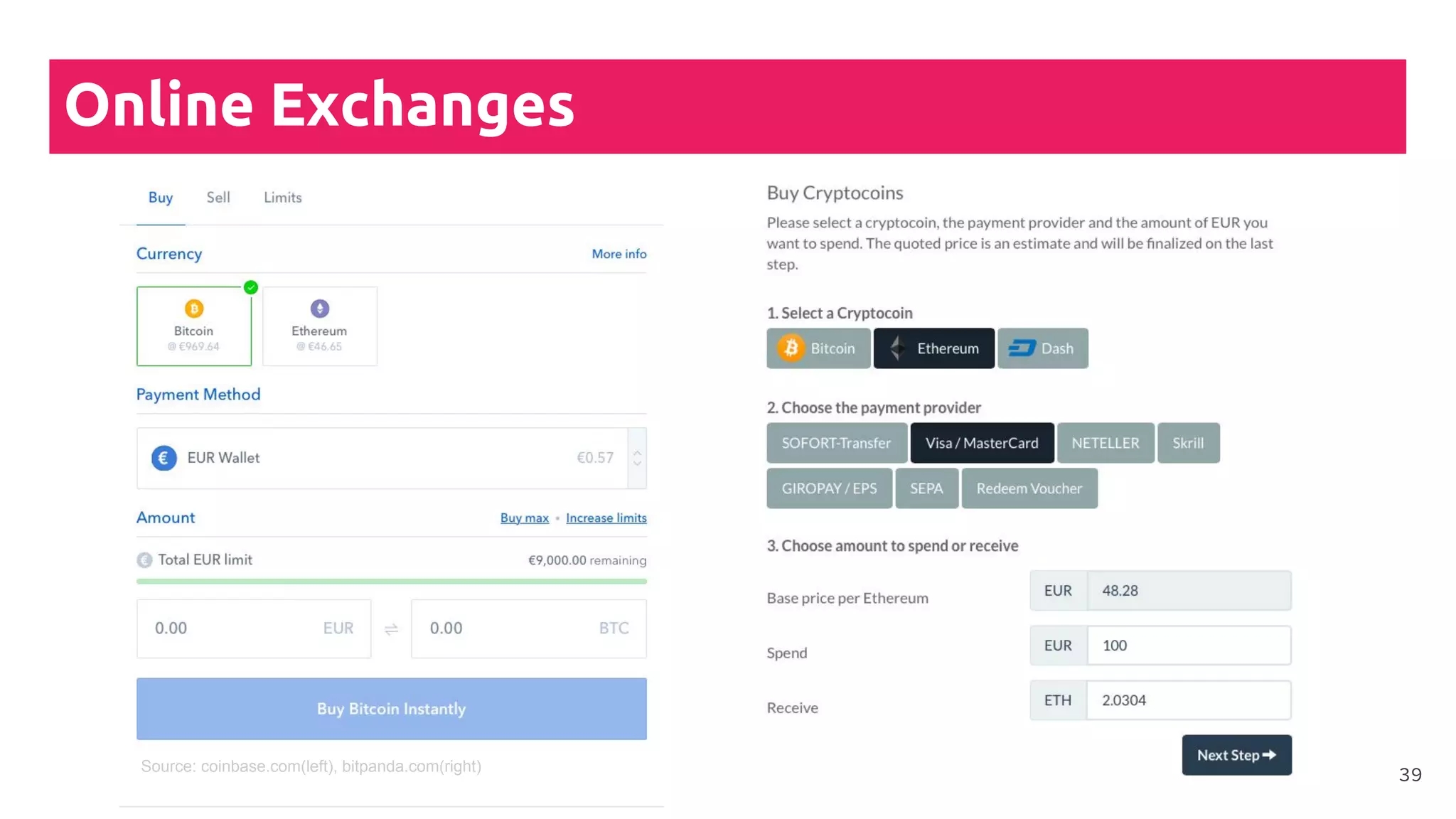
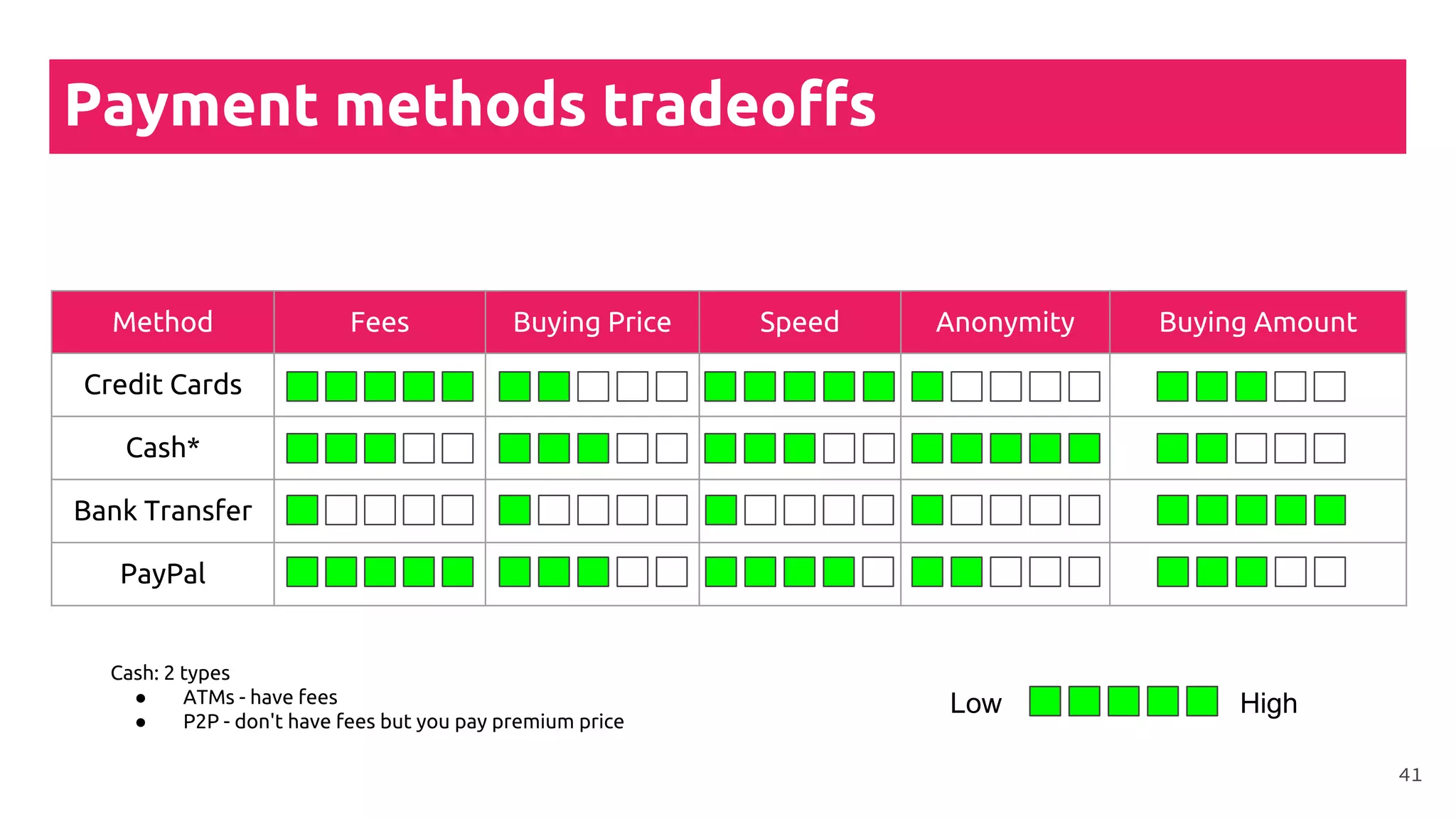
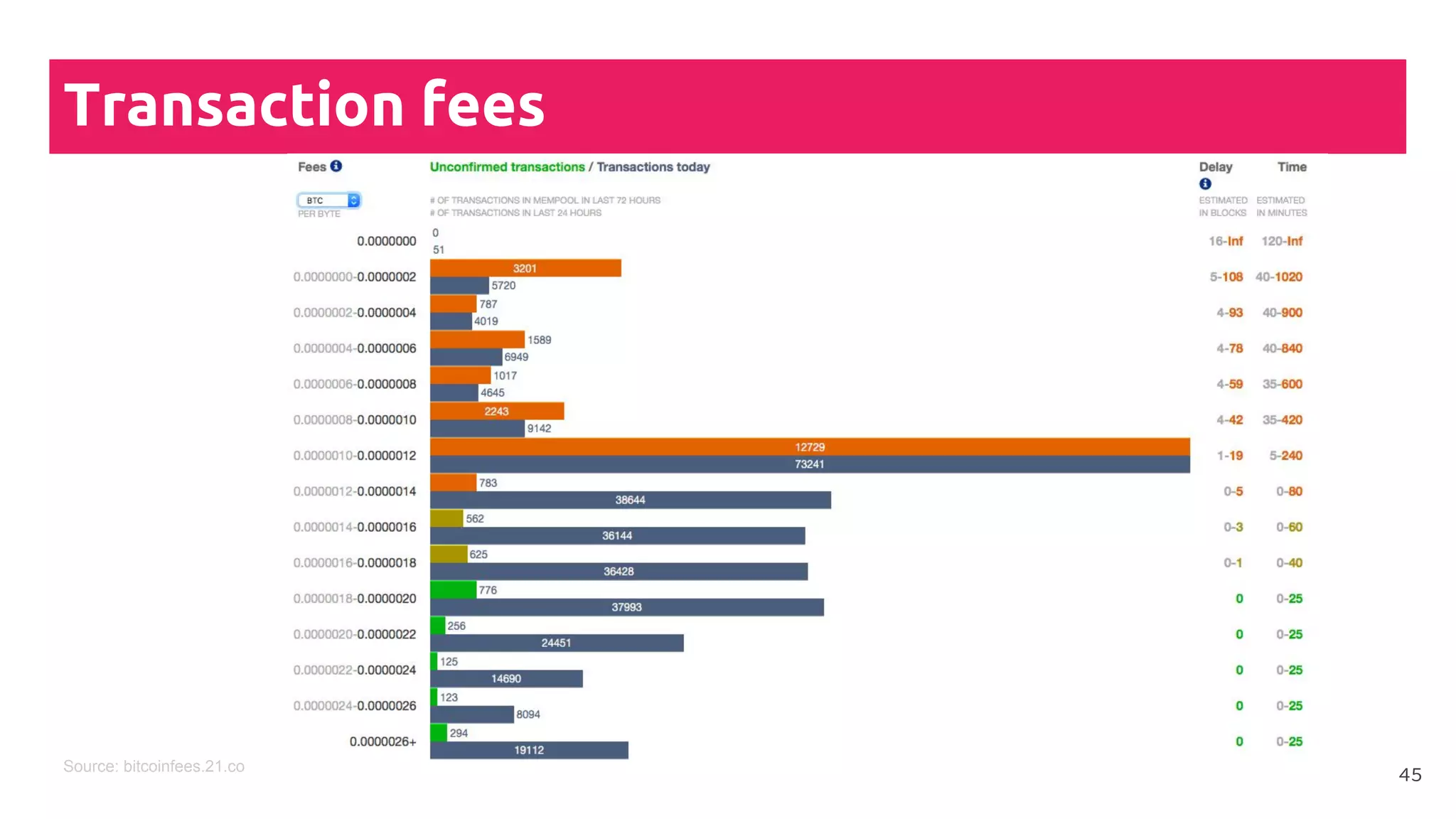
This document is a comprehensive tutorial on cryptocurrency, covering topics such as online security, various types of cryptocurrency wallets, and methods for buying cryptocurrency. It details the importance of backups, transaction fees, and how to track transactions on a blockchain explorer. Recommended wallets and exchanges are also provided, emphasizing the need for security and the implications of losing access to private keys.