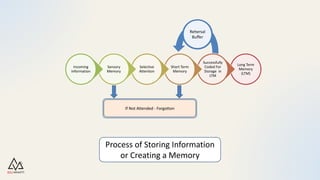
Human memory involves the processes of acquiring, storing, and retrieving information but is not flawless, leading to forgetfulness and misremembering. Key factors affecting memory include encoding, storage, and retrieval, along with types of memory such as sensory, short-term, and long-term. Strategies to enhance memory include writing things down, attaching meaning to information, repetition, and maintaining a healthy brain through various activities.