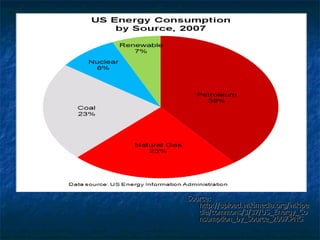
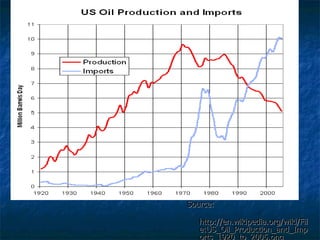
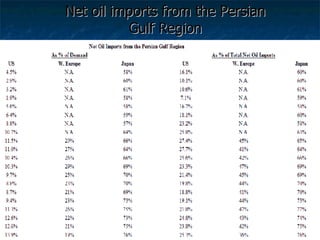
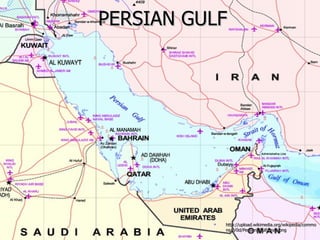
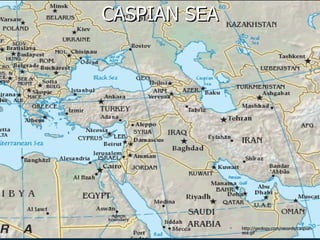
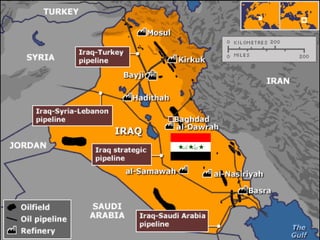
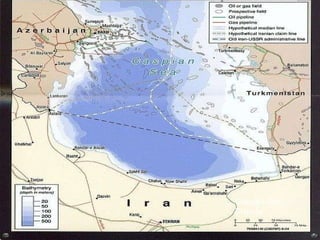
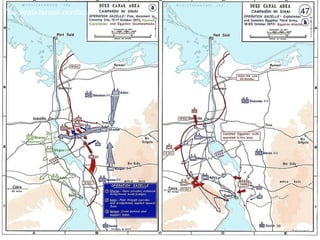
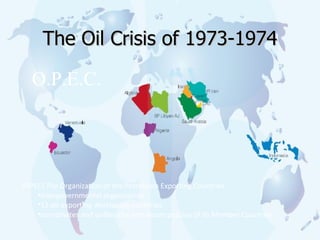
The document discusses how oil changed international politics in the 20th century by making the US dependent on foreign oil imports. It explores US strategies to decrease dependence such as drilling in ANWR, but notes constraints like high costs of domestic production and environmental concerns. It also examines the importance of the Persian Gulf as a major oil producer and exporter, and how conflicts in the Middle East impacted global oil prices and trade relations between oil producing and consuming nations.