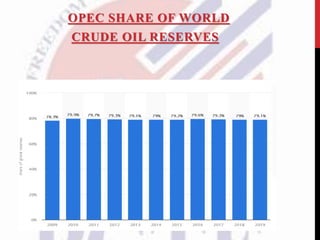
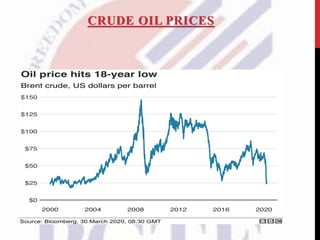
OPEC was established in 1960 in Baghdad by 5 founding members: Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela. It is headquartered in Vienna and coordinates policies among its 13 member countries, who collectively possess over 70% of global crude oil reserves. OPEC aims to ensure stable oil supplies and prices to both producing and consuming countries. In recent years, price wars between Russia and Saudi Arabia have led to sharp drops in crude prices, greatly impacting oil-exporting countries and global energy markets. The COVID-19 pandemic has further disrupted supply and demand, threatening the oil industry. OPEC and its members must now realign strategies to navigate these challenges and changing energy landscapes over the long