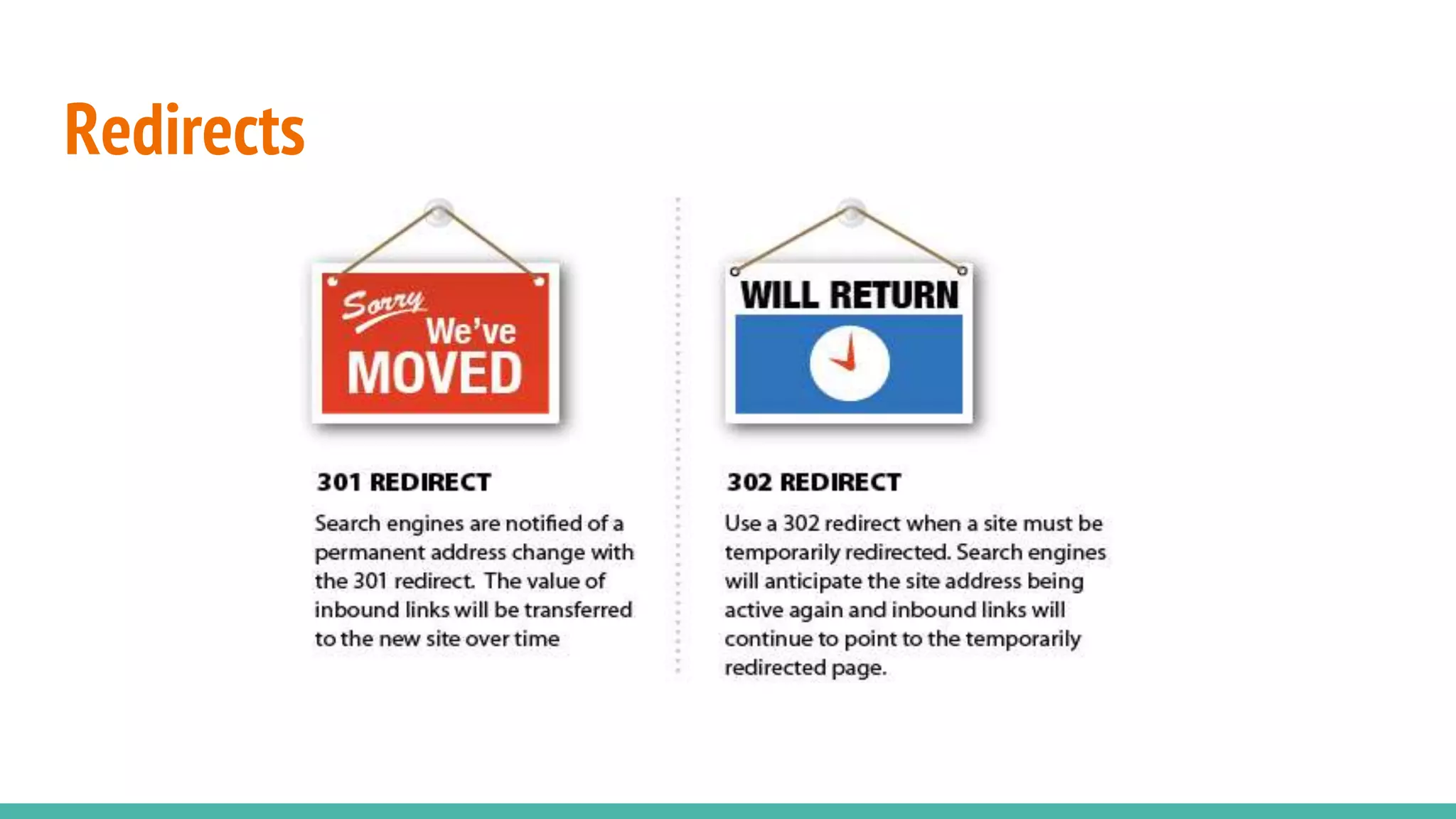
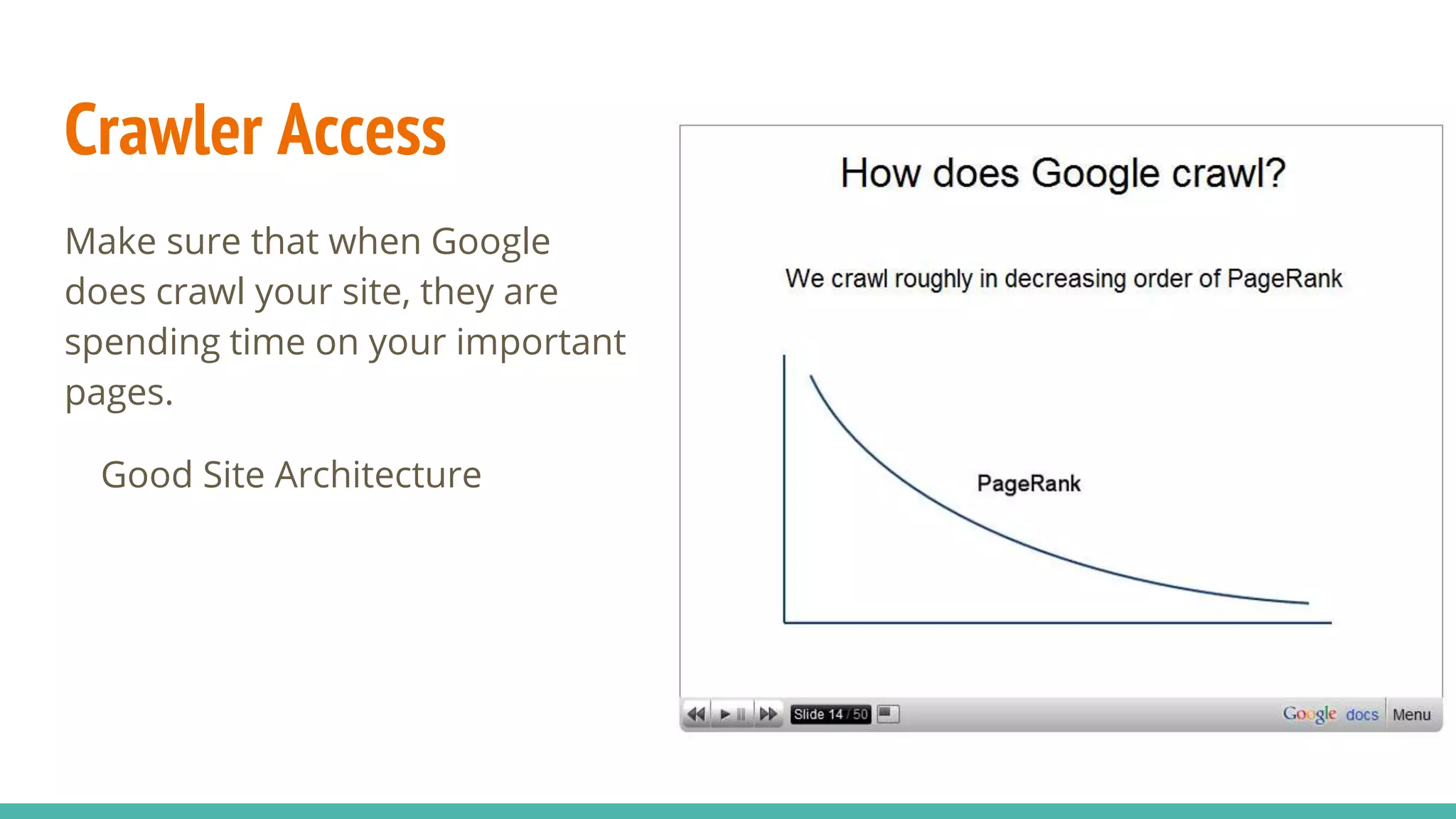
The document emphasizes the importance of SEO for software developers, highlighting that 60% of web traffic comes from search engines and that developers can improve their sites' visibility through speed optimization, proper redirects, semantic markup, and well-structured URLs. It explains that SEO is crucial not only for search engines but also for users, including those utilizing assistive technologies. Additionally, it stresses the need for careful management of staging sites and single page applications to avoid harming organic search traffic.