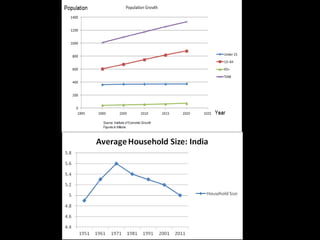
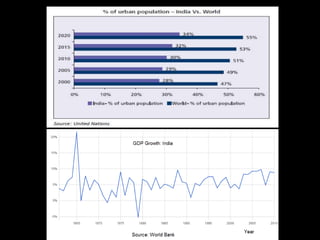
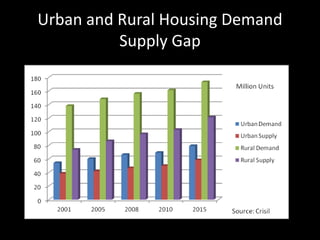
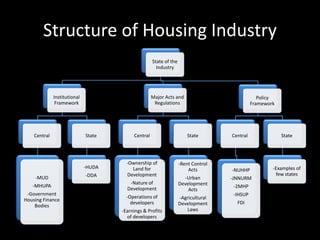
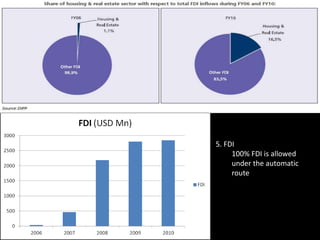
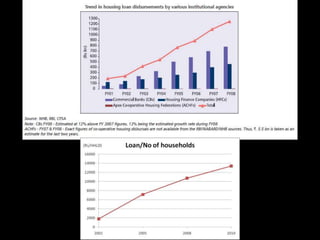
The document provides an in-depth analysis of the housing sector in India, detailing demand drivers such as population growth, urbanization, and economic factors. It outlines the institutional framework, central and state regulations, and key government programs aimed at addressing housing shortages, including various acts related to land ownership, development regulations, and financial incentives. The challenges faced by the industry, major players, and the impact of recent policies and budget changes on affordable housing are also discussed.