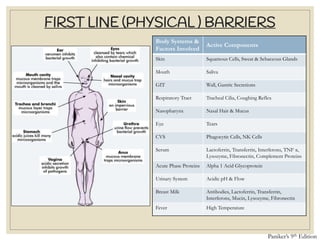
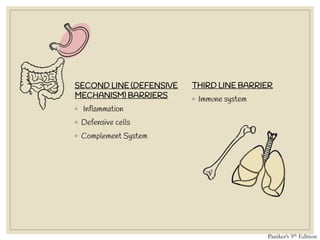
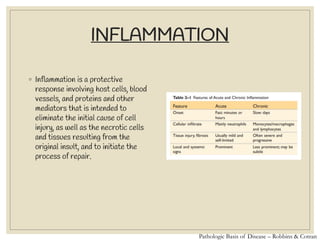
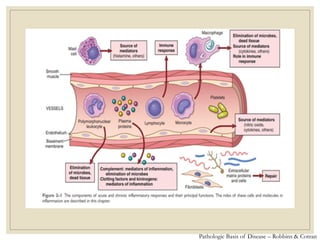
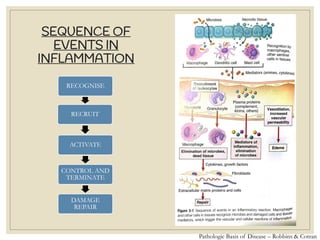
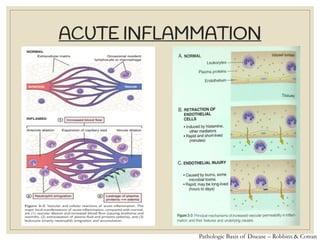
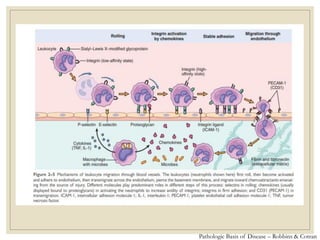
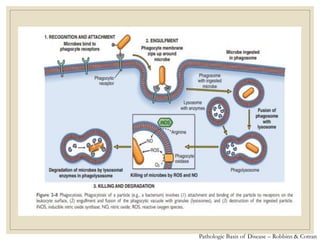
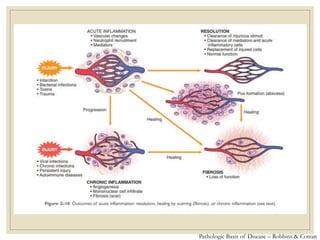
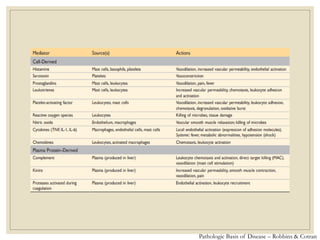
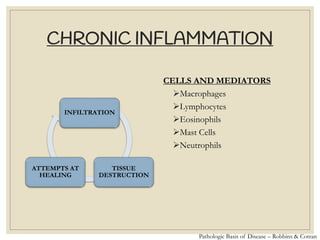
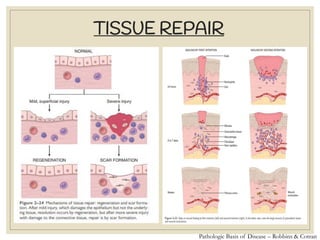
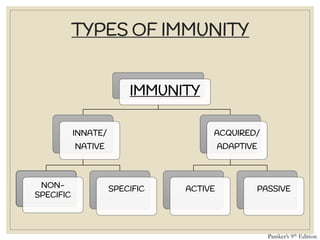
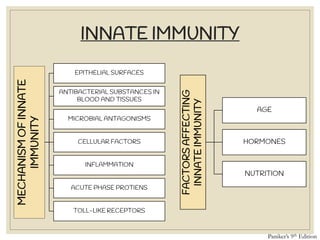
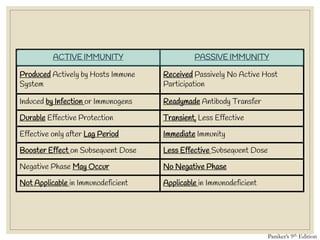
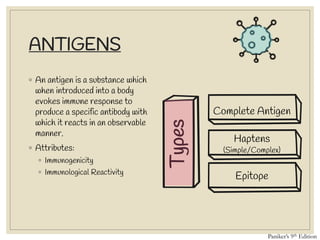
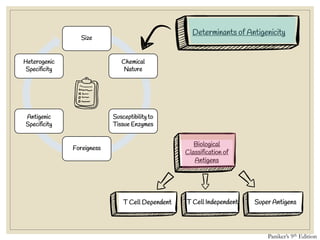
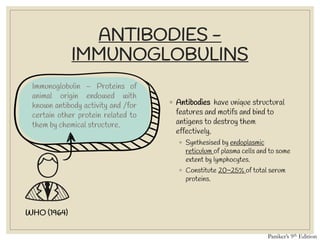
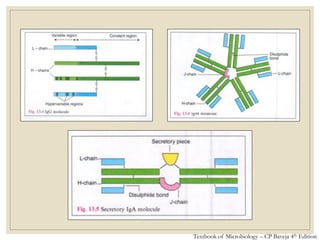
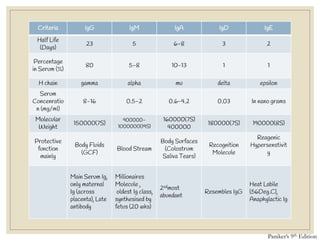
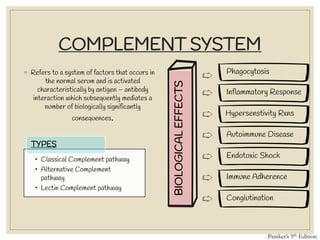
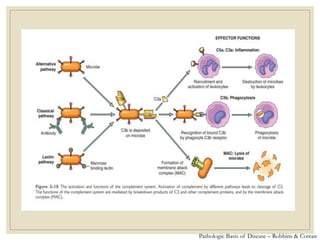
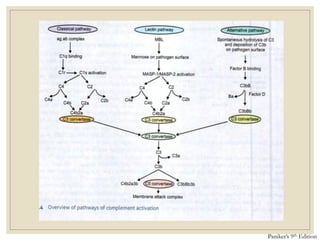
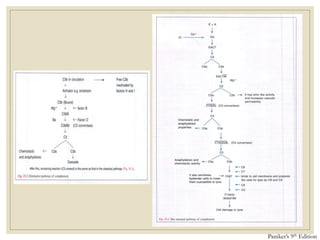
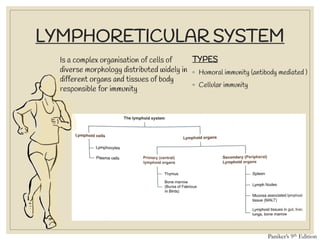
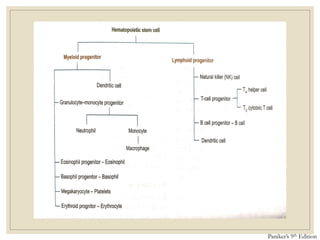
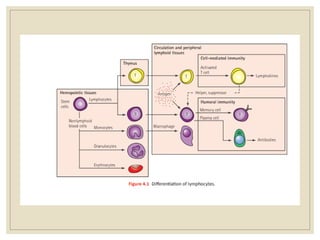
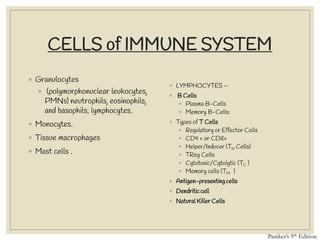
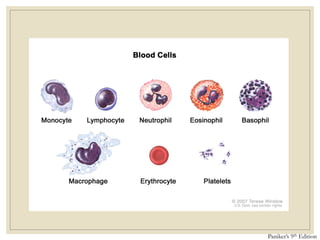
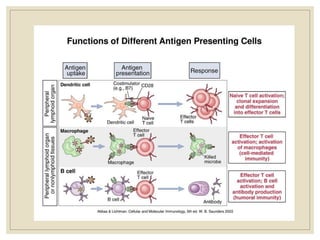
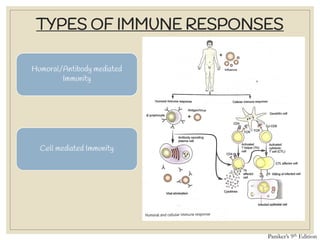
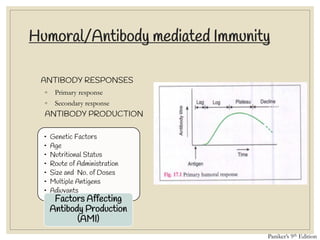
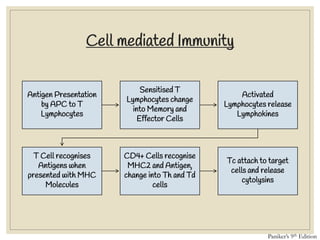
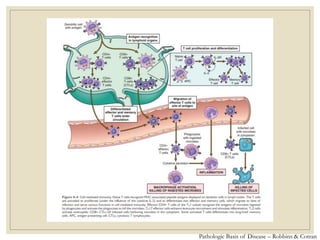
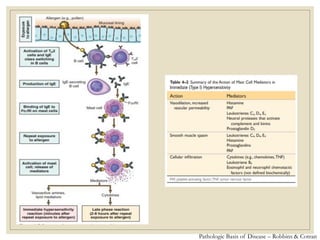
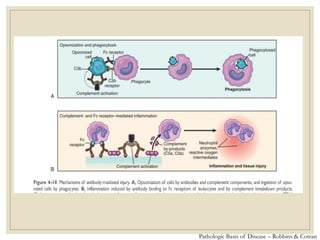
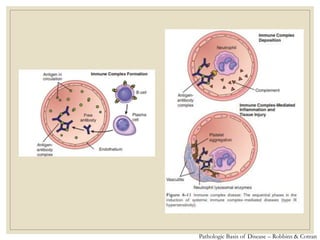
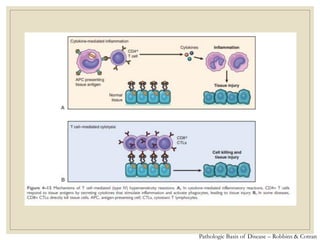
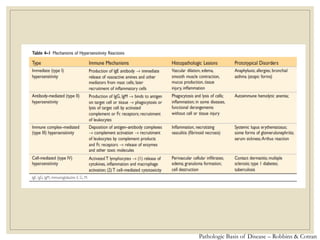
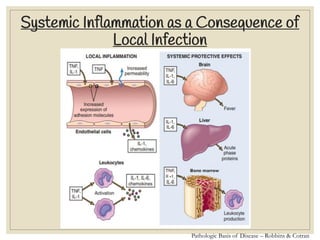
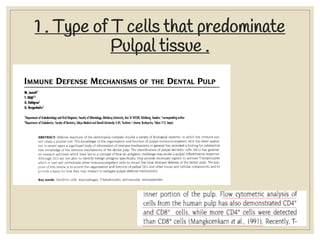
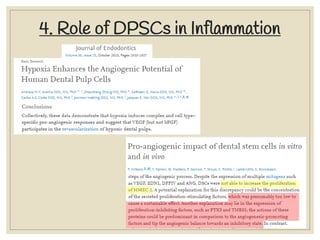
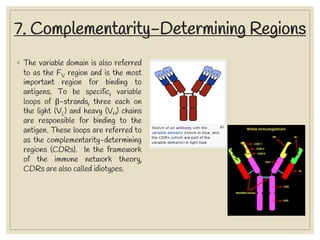
The document discusses host defense mechanisms against pathogens. It describes three lines of defense: 1) physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes, 2) inflammatory response and defensive cells, and 3) the immune system. The immune system has both innate and acquired branches. Innate immunity provides non-specific protection using physical and chemical barriers while acquired immunity involves adaptive, antigen-specific responses. Key cells of the immune system that provide defense include macrophages, neutrophils, lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Antibodies and the complement system are important components that help eliminate pathogens.