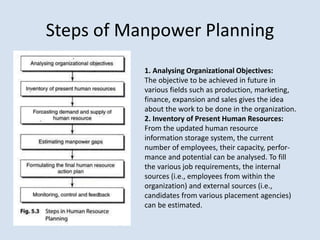
This document discusses human resource planning and manpower planning in organizations. It provides an overview of the objectives, benefits, and steps involved in human resource planning. Some key points include:
Human resource planning helps ensure the availability of qualified employees when needed and counterbalances uncertainties. It anticipates shortages or surpluses of workers and helps correct imbalances. The planning process involves forecasting future needs, assessing current resources, identifying gaps, and creating action plans to address deficits or surpluses. Workload analysis is one technique used to estimate human resource requirements based on projected workloads and employee productivity.