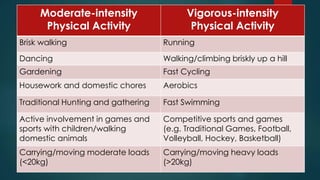
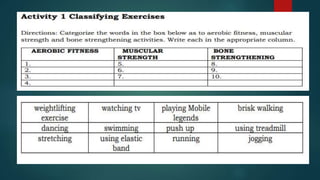
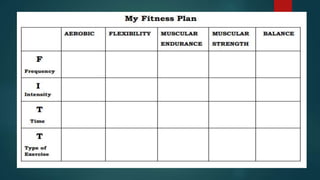
This document discusses different types of physical exercise and fitness. It defines aerobic exercise as activity that elevates heart rate and makes you sweat. Aerobic fitness improves heart health. Examples are walking, swimming, and dancing. It also discusses strength training to build muscles, weight-bearing exercise for bone strength, and flexibility exercises to improve range of motion. The document contrasts moderate and vigorous intensity physical activity and provides methods to assess fitness level including tracking resting and maximum heart rate.