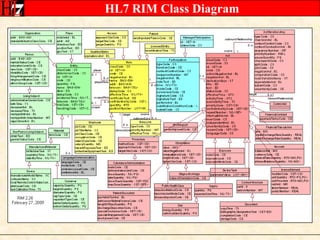
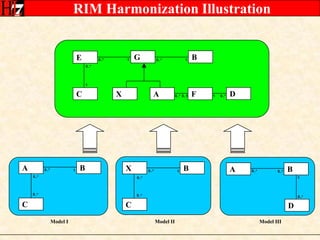
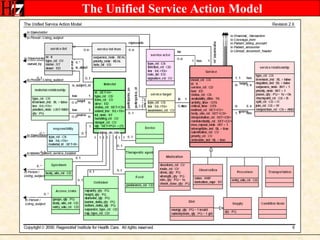
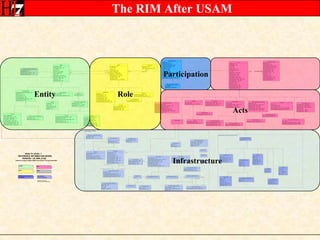
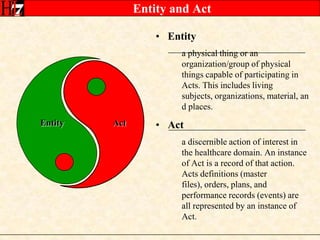
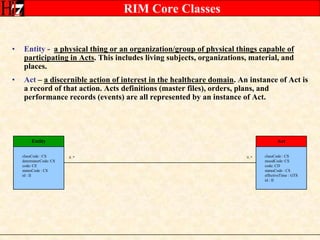
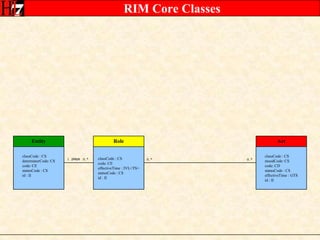
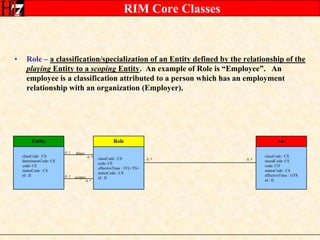
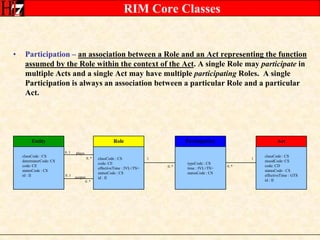
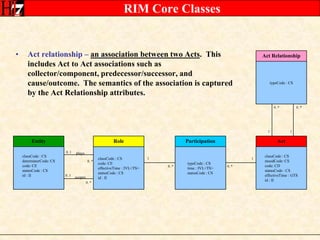
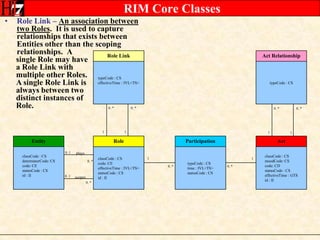
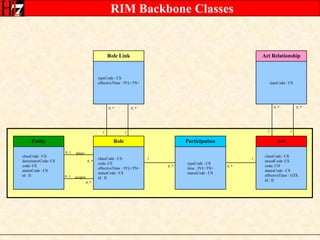
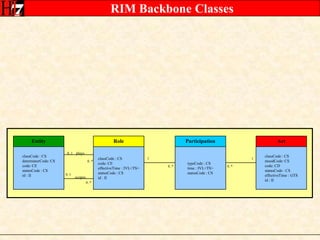
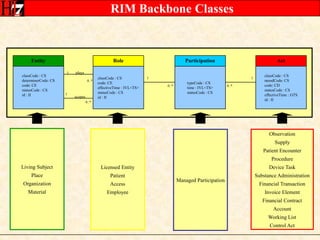
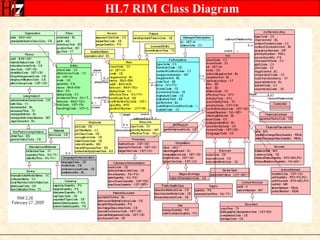
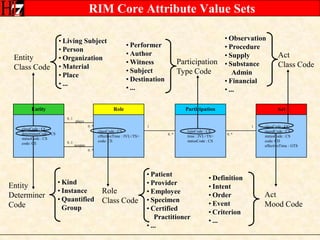
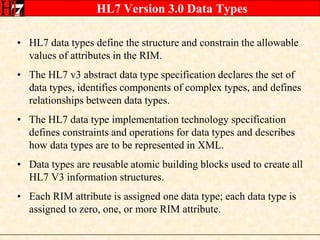
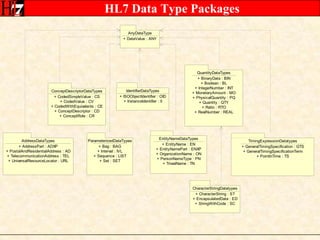
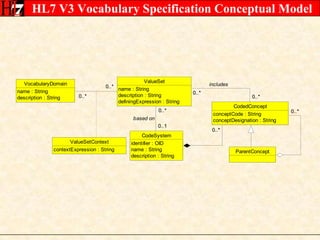
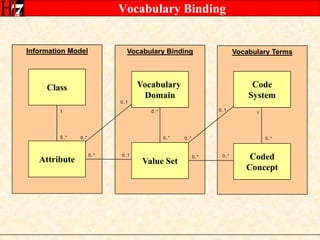
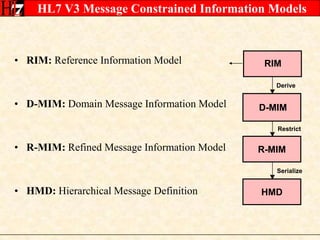
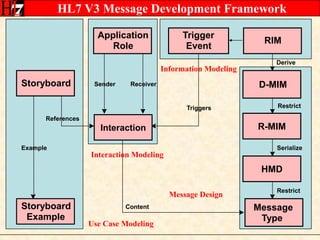
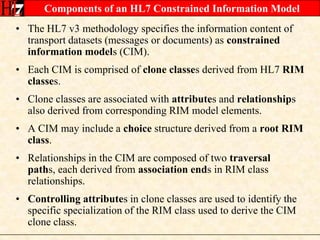
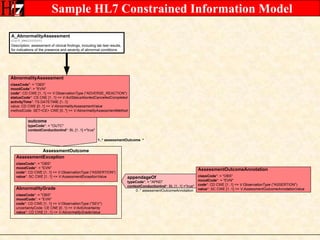
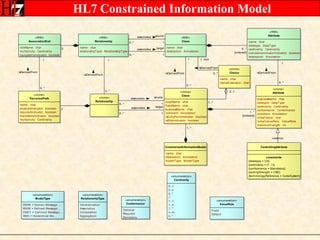
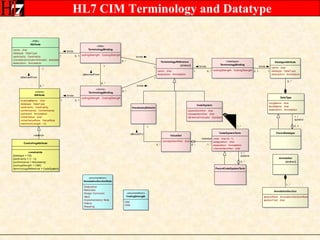
The document provides an overview of the HL7 Version 3 Reference Models, which include the Reference Information Model (RIM), Data Type Specification, and Vocabulary Specification. The RIM is the foundational information model that all other HL7 models and specifications are derived from. It defines core classes like Entity, Role, Act, and Participation and their relationships. The RIM was developed over many years through a harmonization process and is now a stable standard.