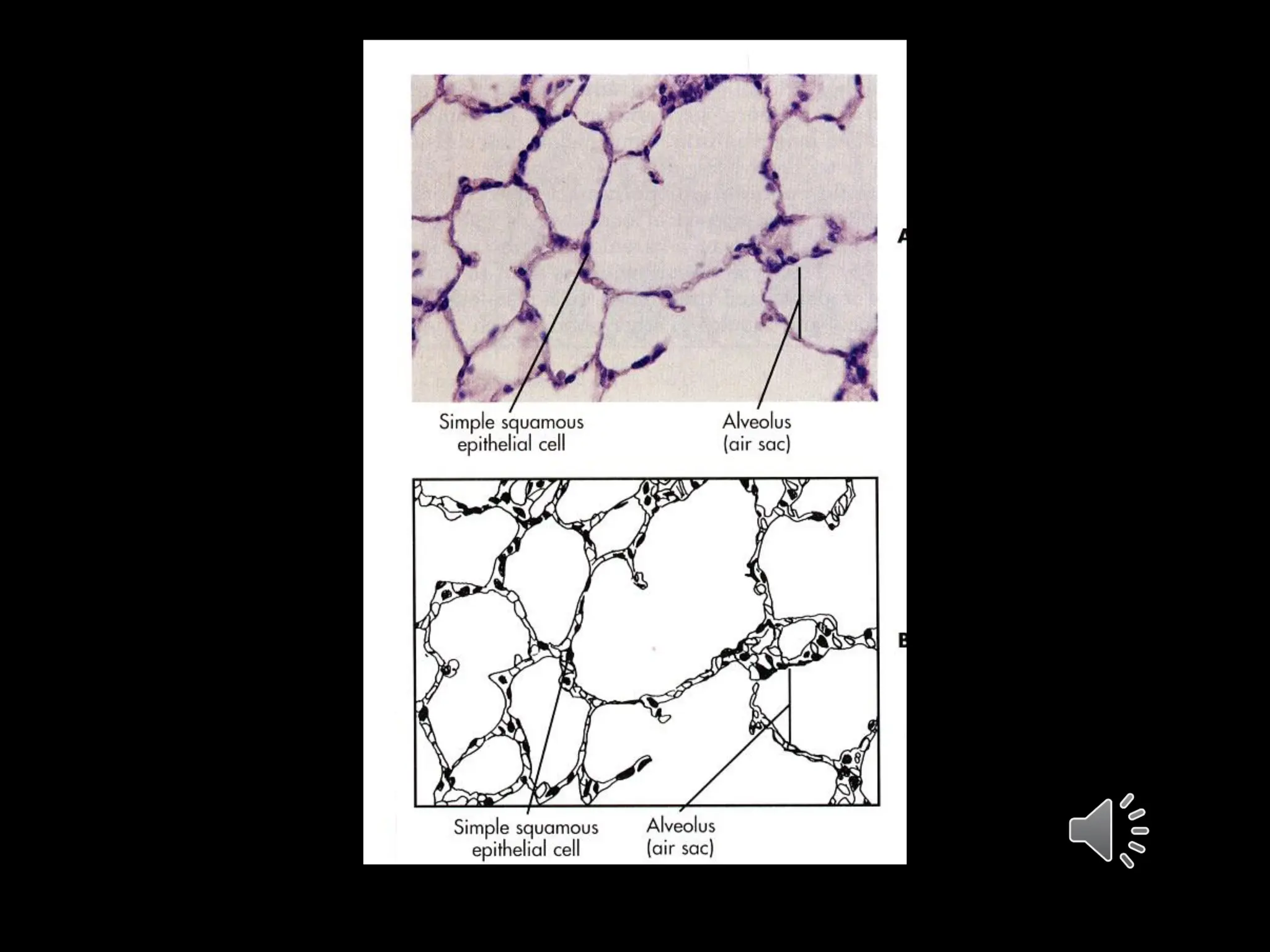
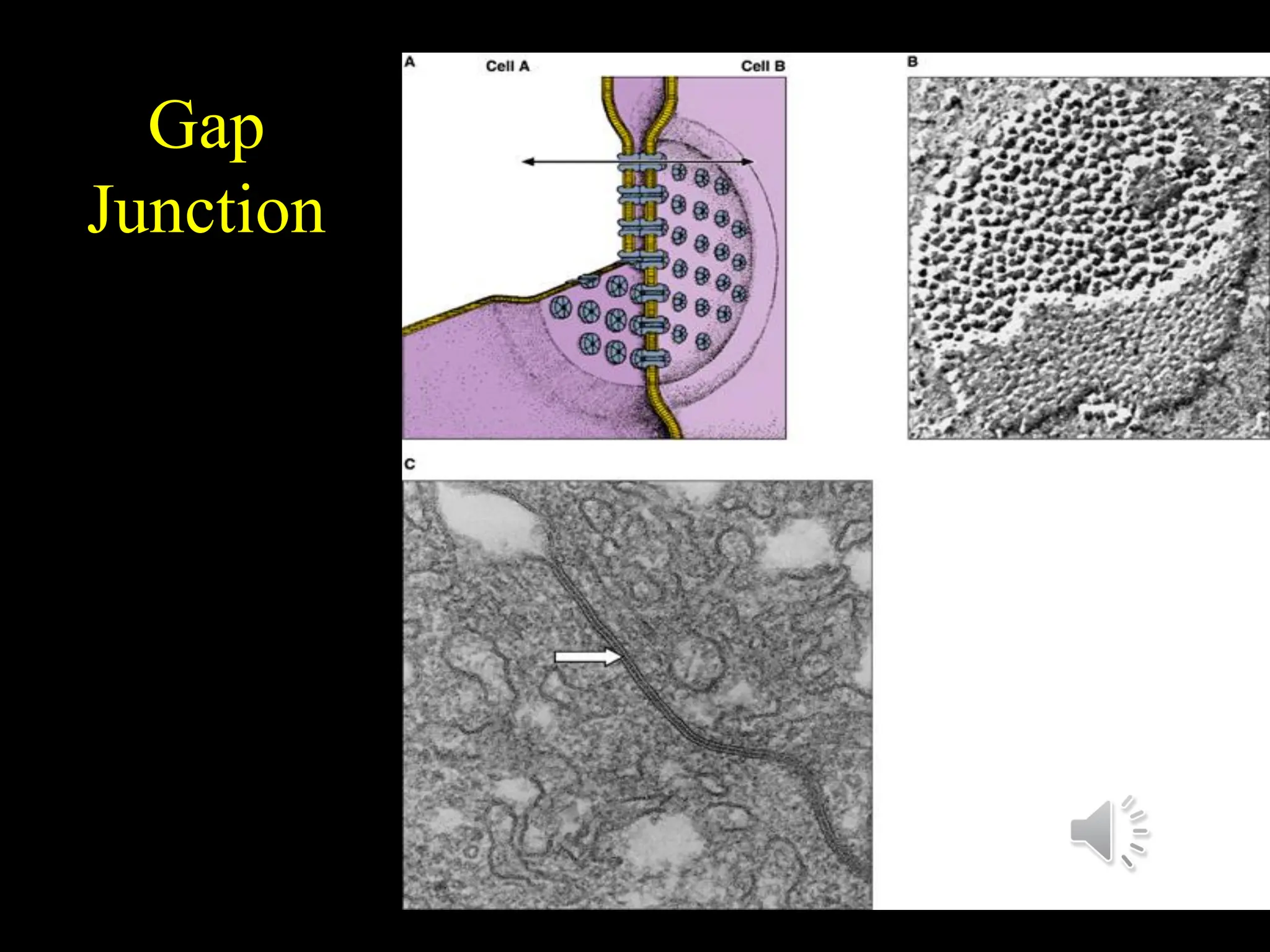
This document discusses epithelial tissues. It defines tissue and lists the main categories. Epithelial tissues are covered in detail, including their general features, structural classifications based on cell shape and layers, and major types such as simple squamous epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium, and pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Functions and sample locations are provided for each type. Intercellular junctions and specializations of the cell surface like microvilli and cilia are also described.