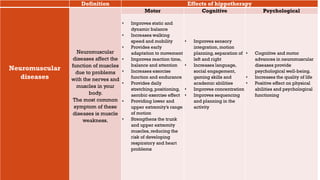
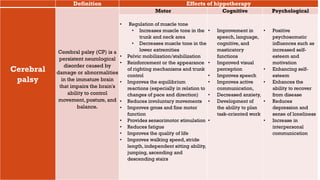
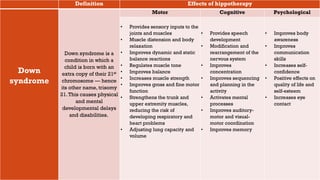
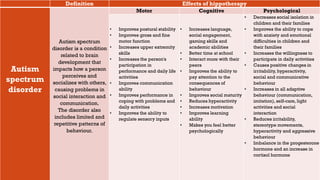
This document discusses how hippotherapy can benefit children with various intellectual, physical, and neurological disabilities. It describes several conditions such as muscular diseases, spinal muscular atrophy, cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, and autism. For each condition, it explains how hippotherapy provides physical, cognitive, and emotional benefits through the repetitive and rhythmic movement of the horse, which can improve areas like balance, mobility, muscle tone, coordination, language skills, and self-confidence. Hippotherapy is presented as an effective rehabilitation treatment that can enhance quality of life for children with disabilities.