The document discusses the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and its privacy and security rules. It provides an overview of HIPAA, explaining its purpose of protecting patient health information and establishing national standards for electronic transactions. It outlines HIPAA's privacy rule, including provisions regarding patient consent, authorization exceptions, and penalties for noncompliance. The document also addresses hypothetical scenarios regarding the appropriate disclosure of patient information under HIPAA.



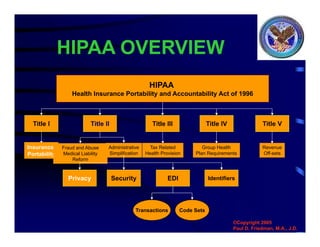


![Administrative
Simplification
[Accountability]
Insurance
Reform
[Portability]
Health Insurance
Portability and Accountability Act
(HIPAA)
HIPAA - 2003
Transactions,
Code Sets, &
Identifiers
PRIVACY
Compliance
Date:
4/14/2003
Security
©Copyright 2005
Paul D. Friedman, M.A., J.D.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edd5a57c-3d8d-45bf-8925-7720445c59f8-150330130130-conversion-gate01/85/HIPAA-7-320.jpg)

















![HYPOTHETICAL NUMBER ONE
Ask yourself the following questions:
1) Does your friend need to know if the patient is being
treated in your facility?
2) Does your friend need to know if the patient is being
treated in intensive care?
3) Does your friend need to know if the patient
overdosed to do his [the nurse’s] job?
4) If you were the patient, would you want this person
[the inquiring nurse] to know about your treatment?
©Copyright 2005
Paul D. Friedman, M.A., J.D.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edd5a57c-3d8d-45bf-8925-7720445c59f8-150330130130-conversion-gate01/85/HIPAA-25-320.jpg)






