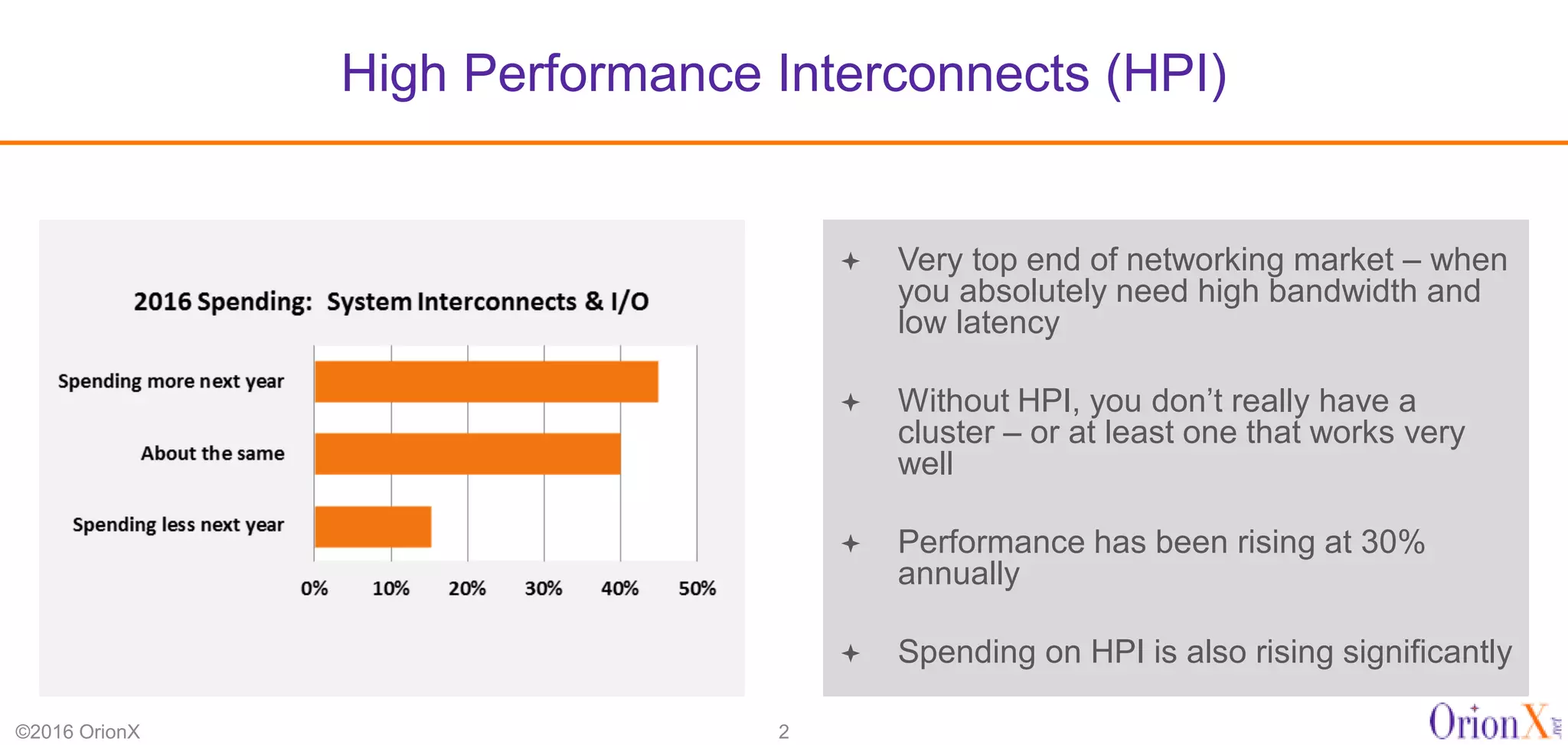
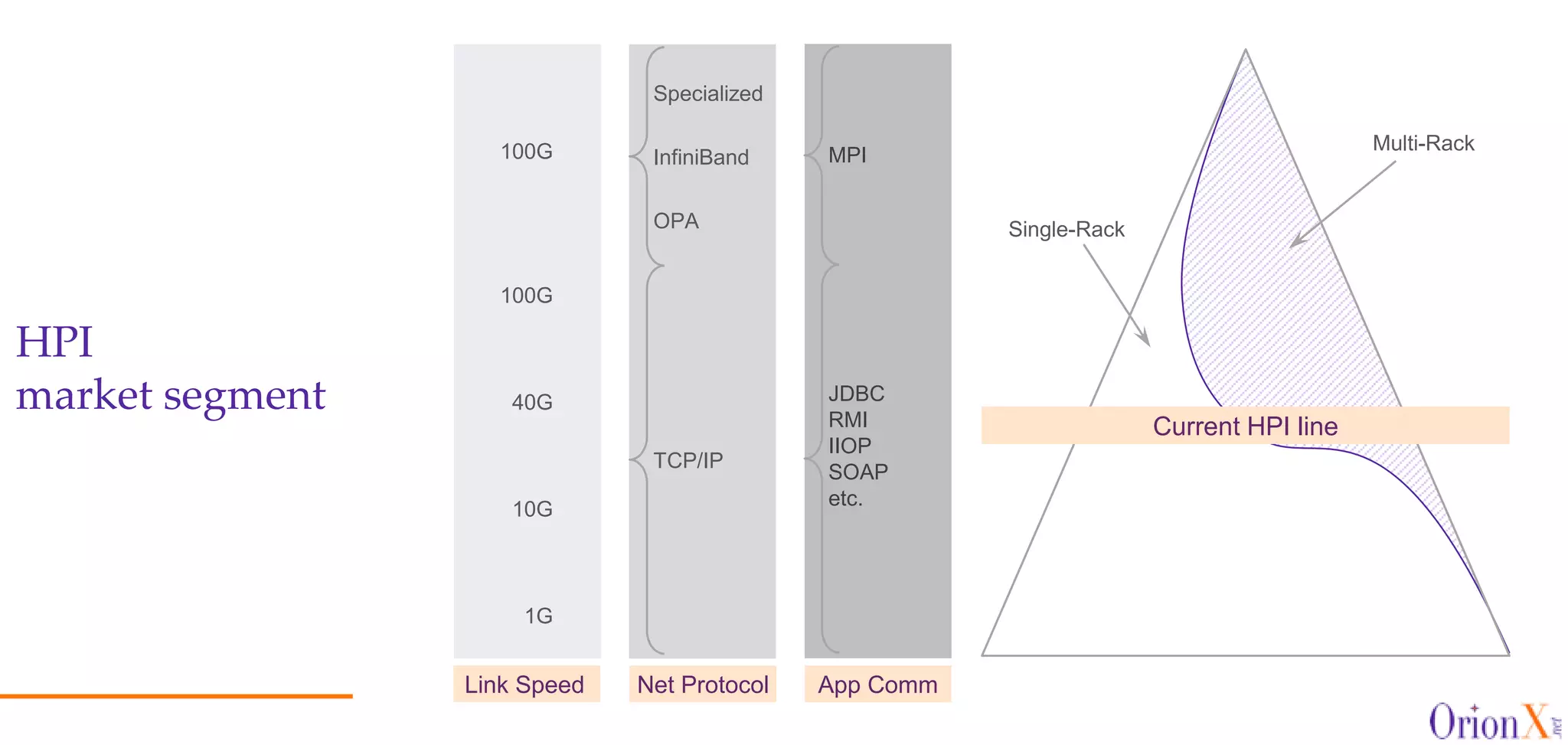
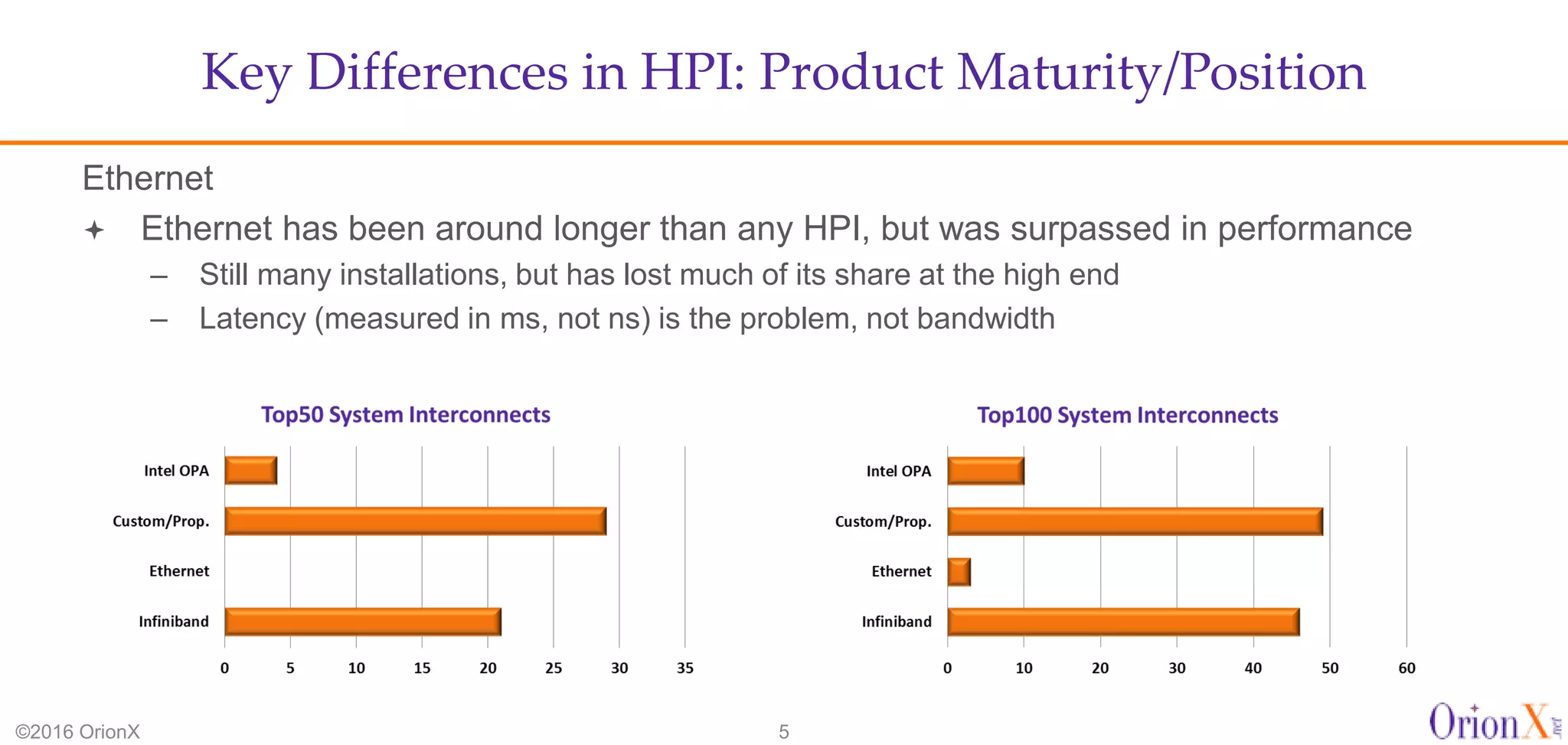
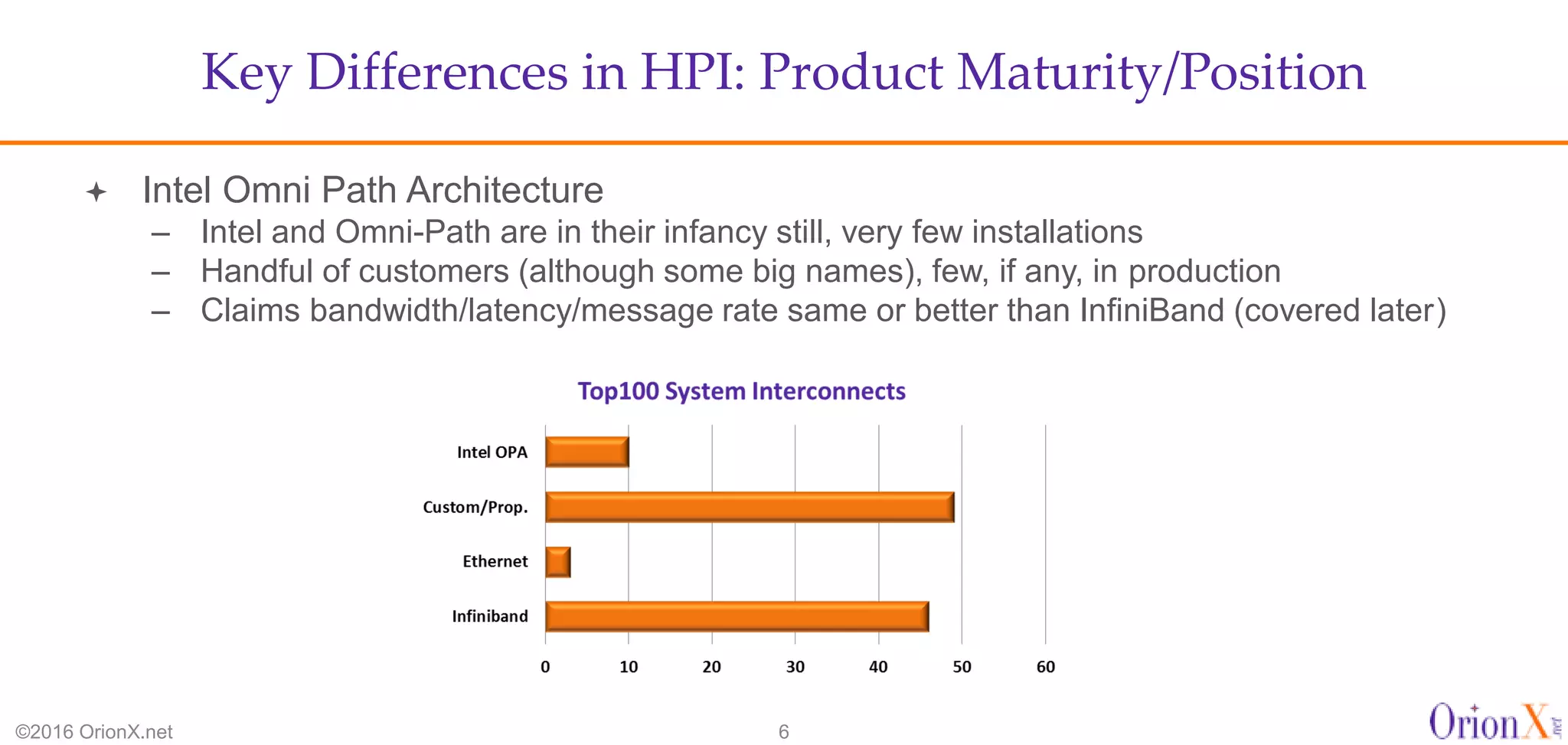
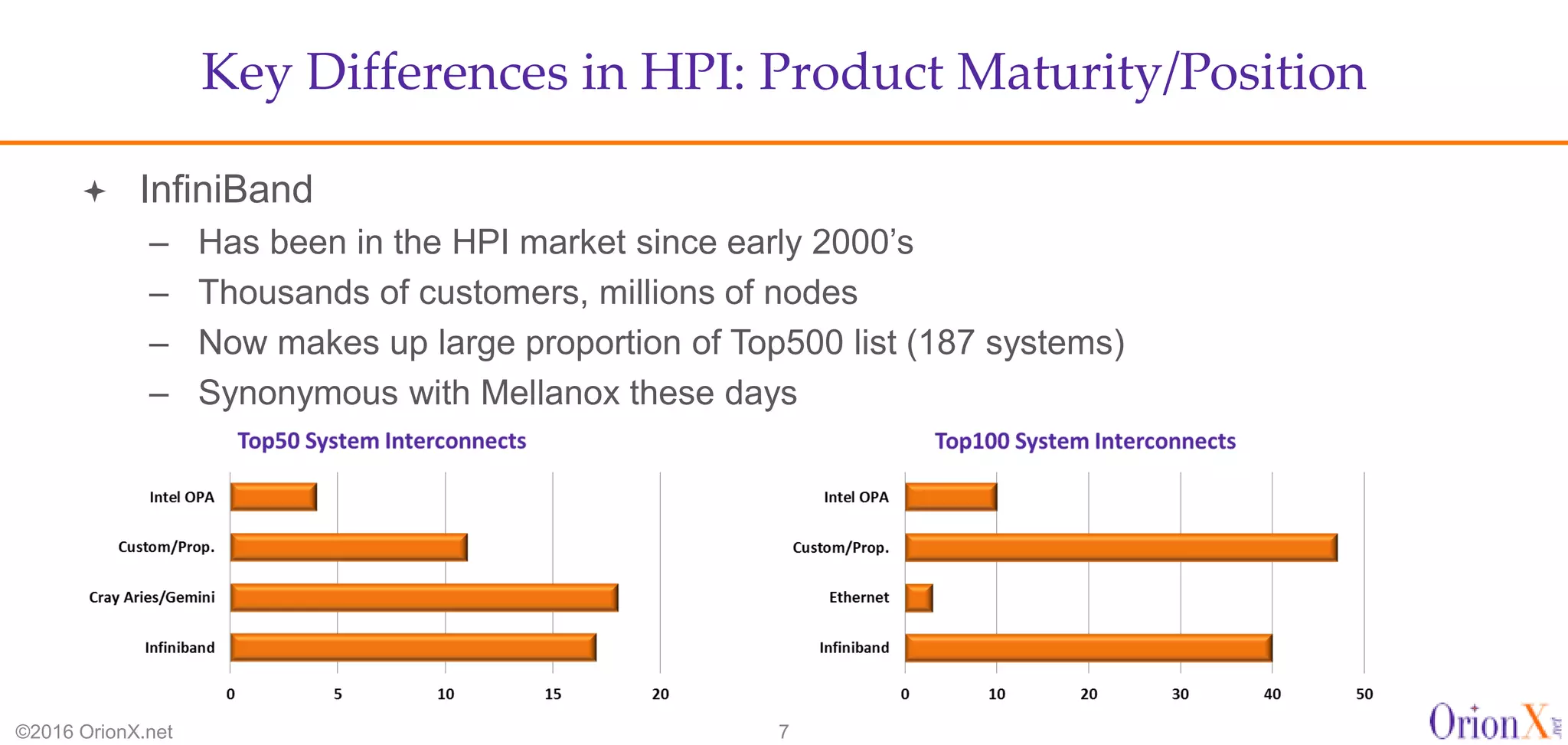
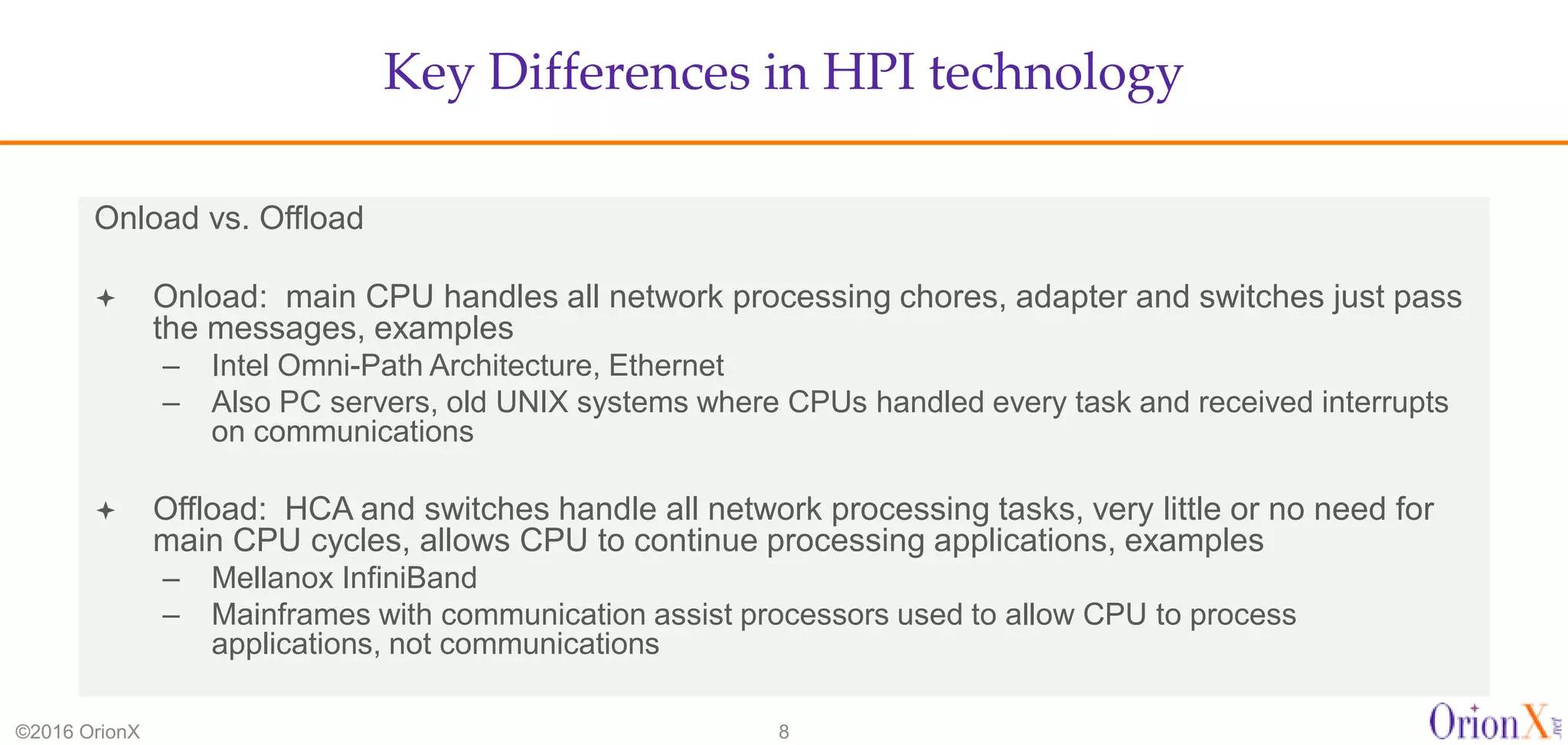
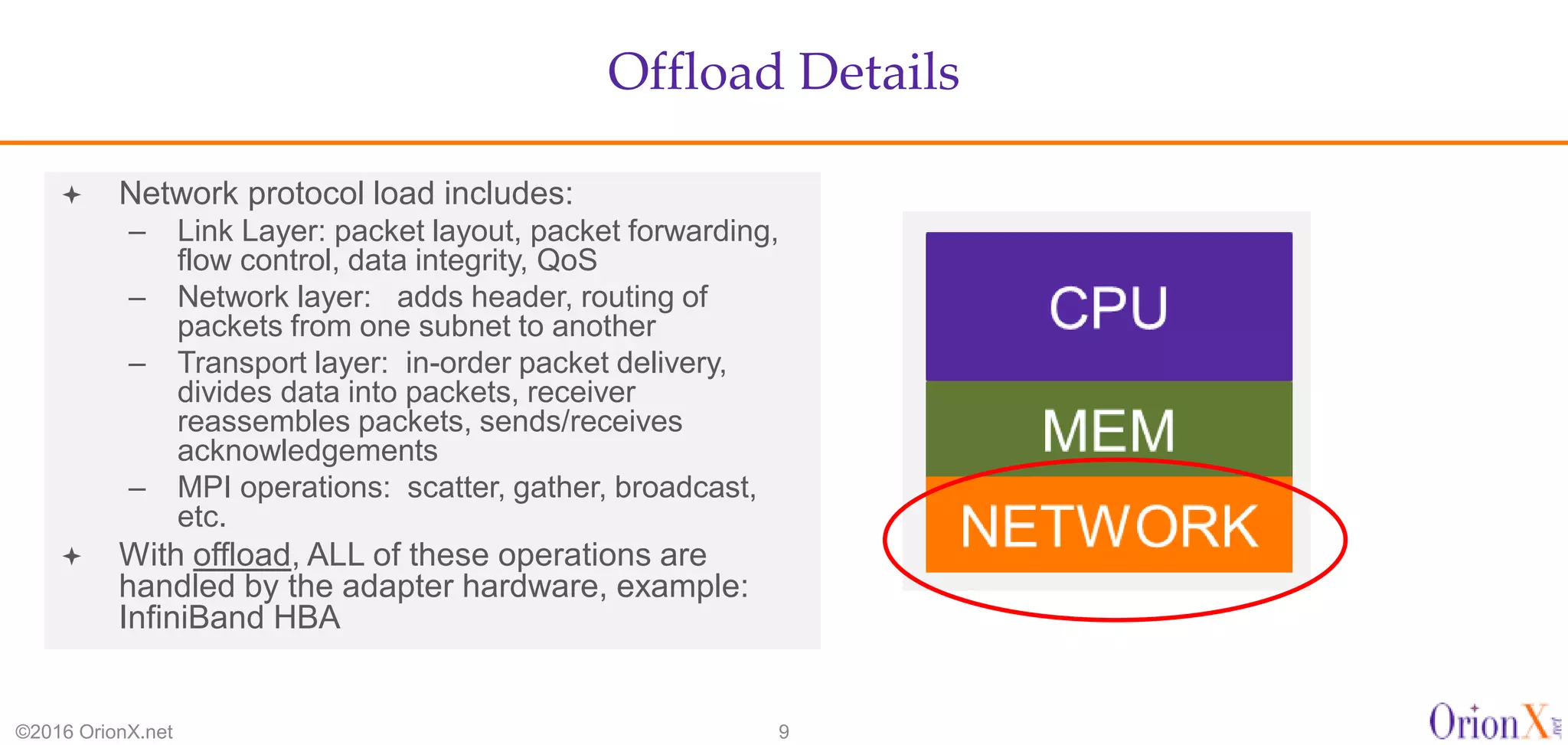
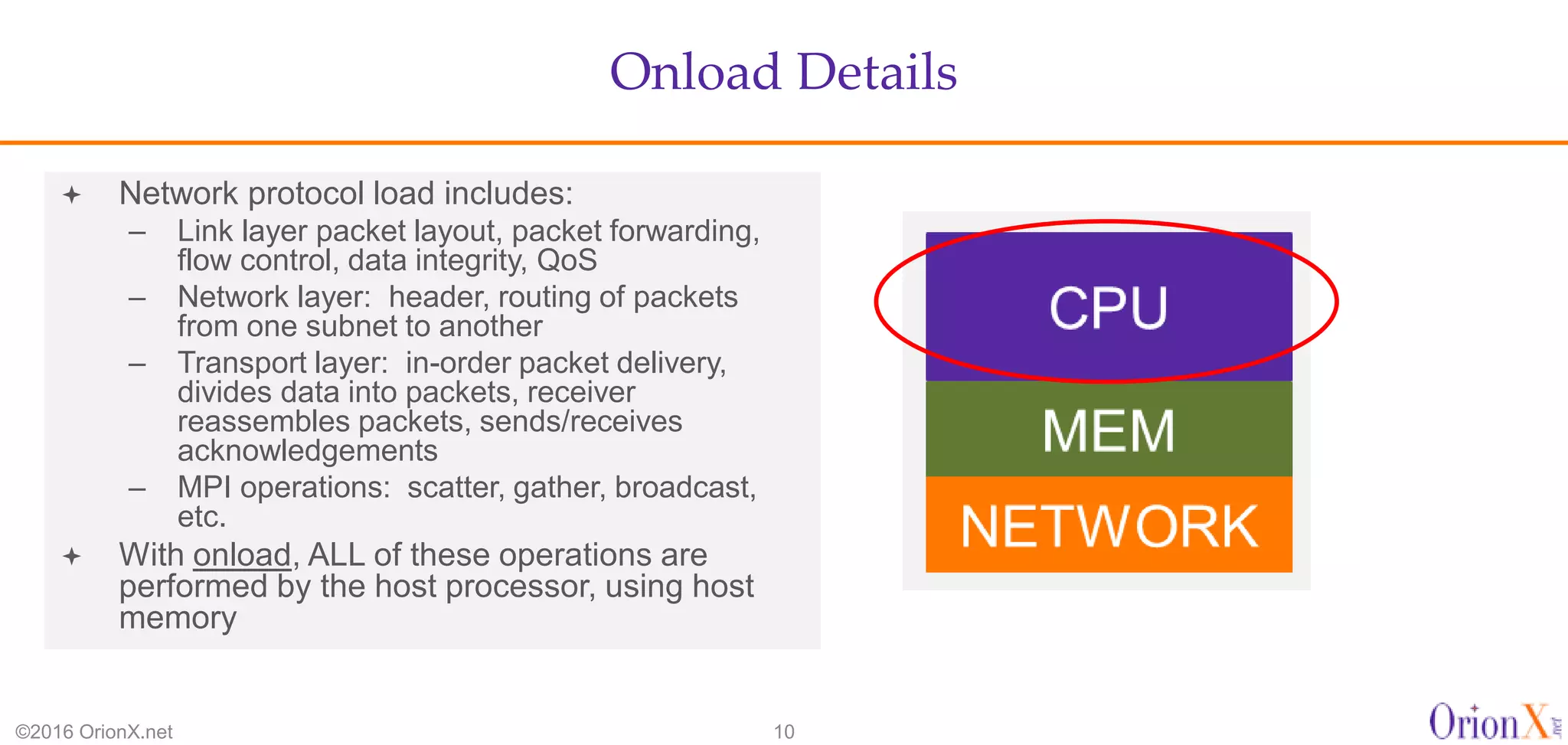
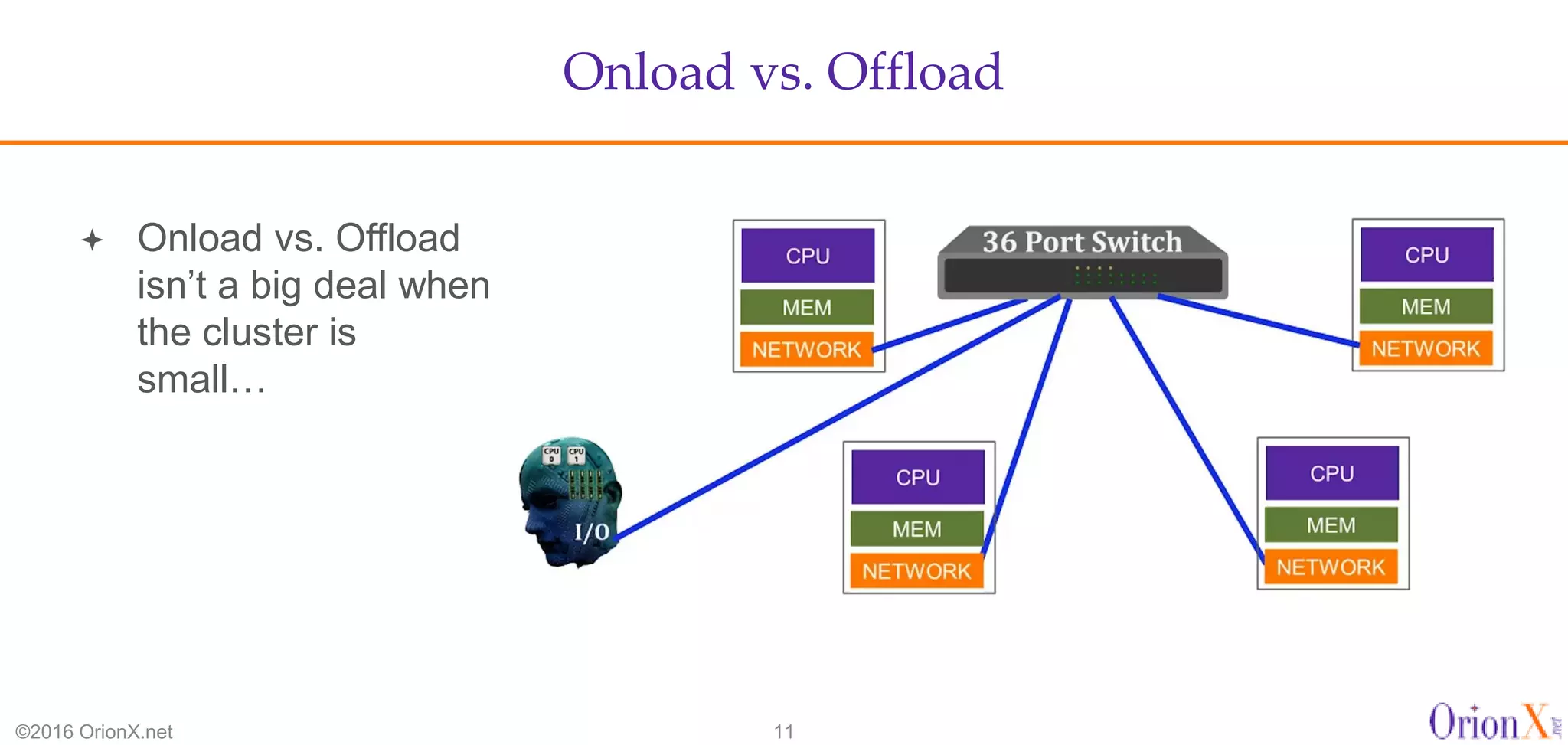
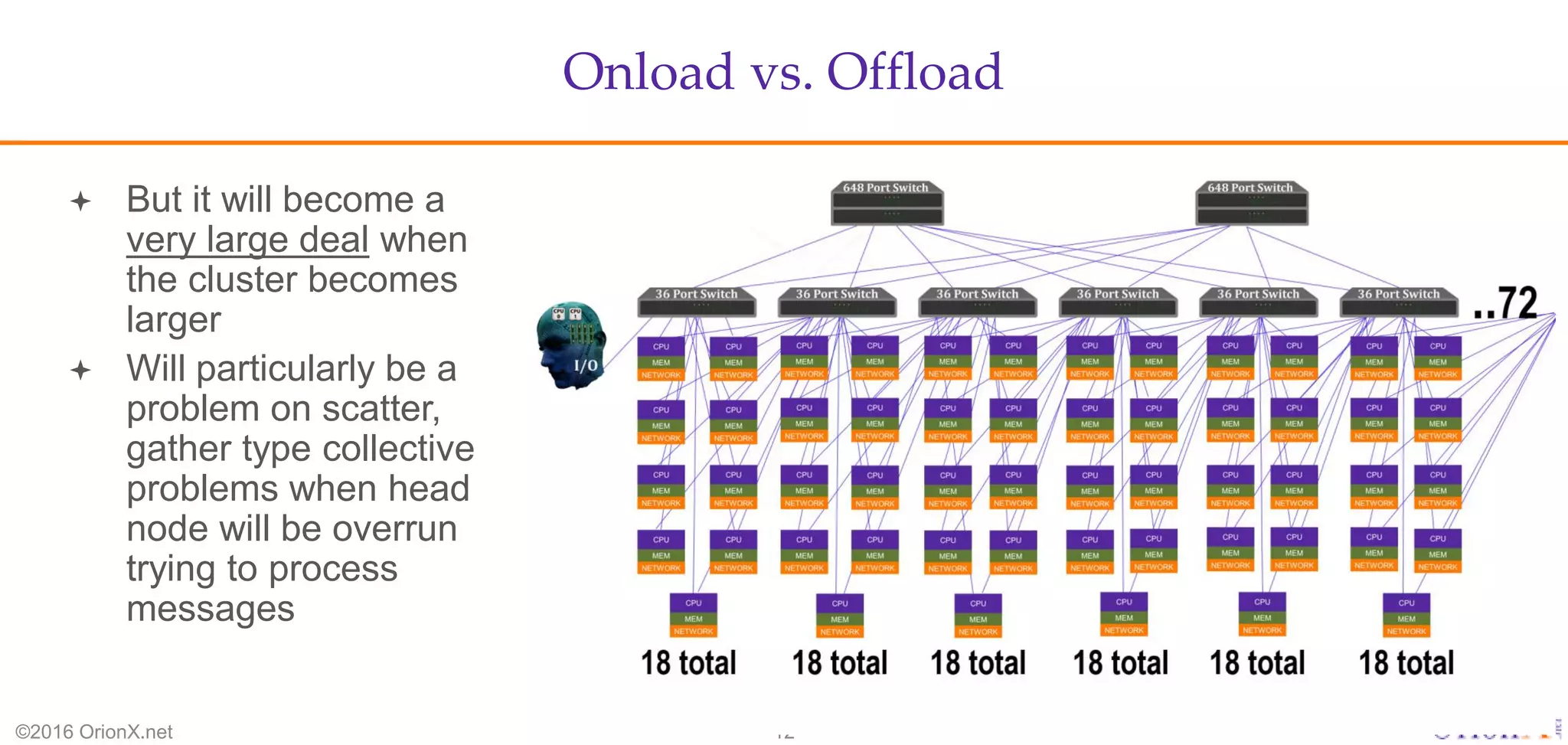
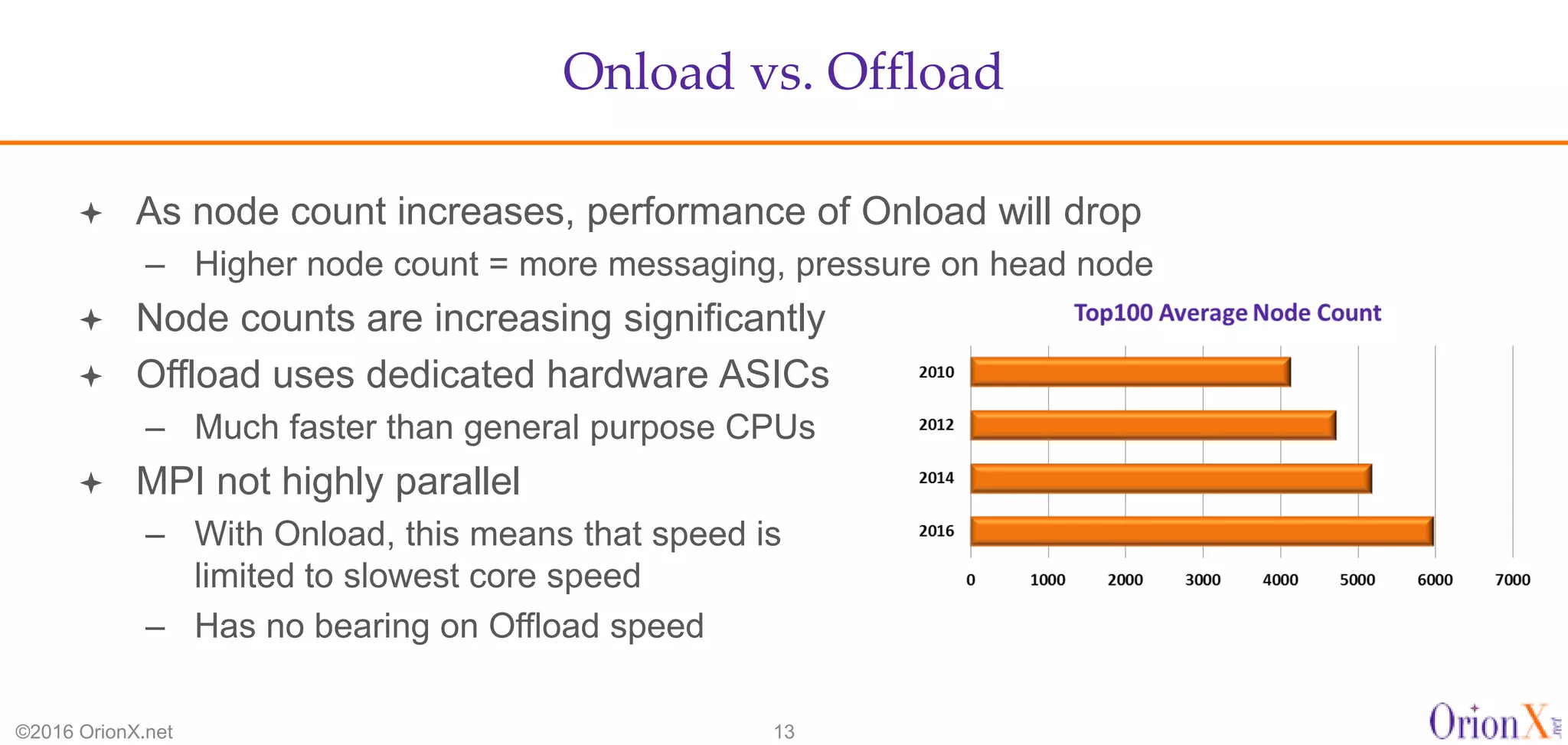
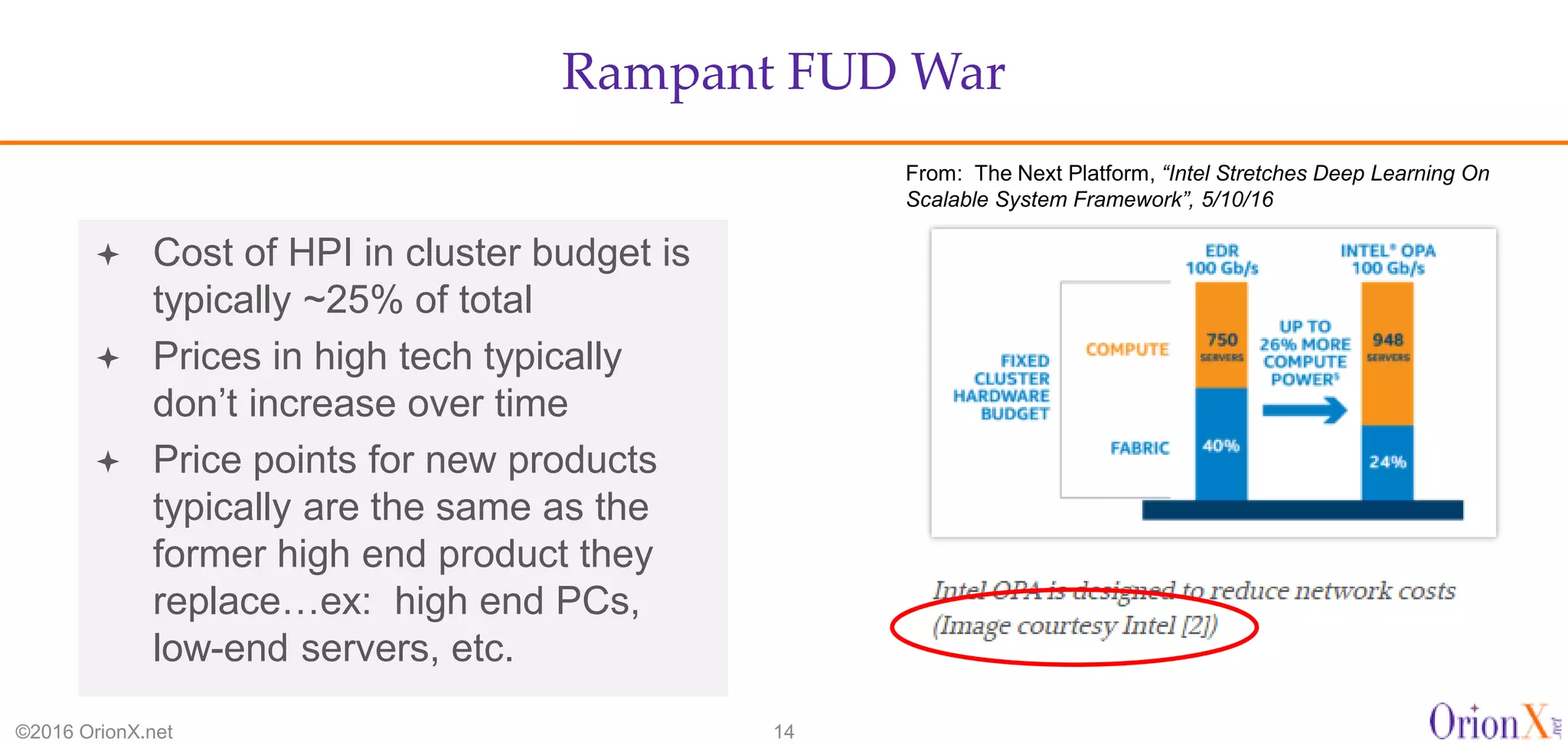
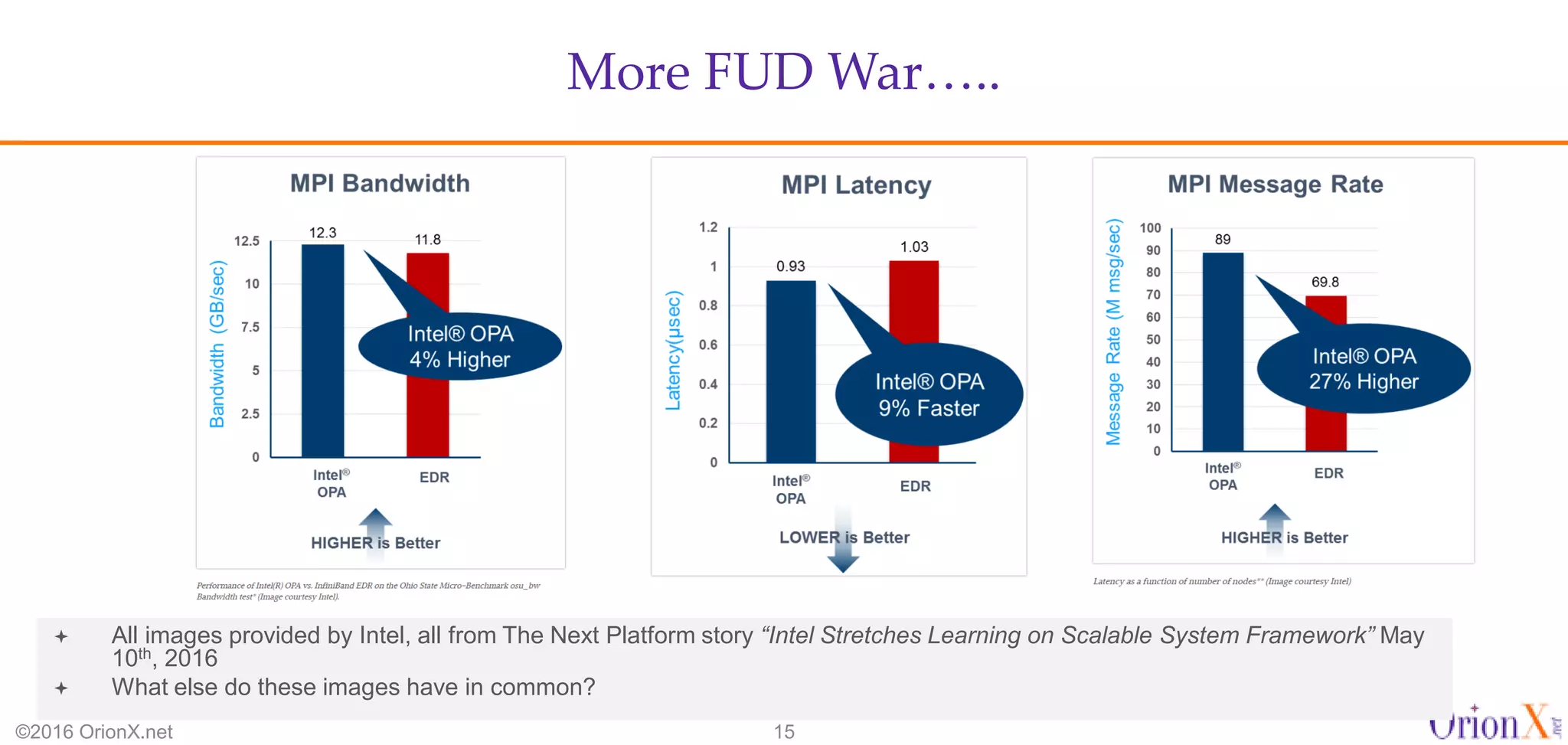
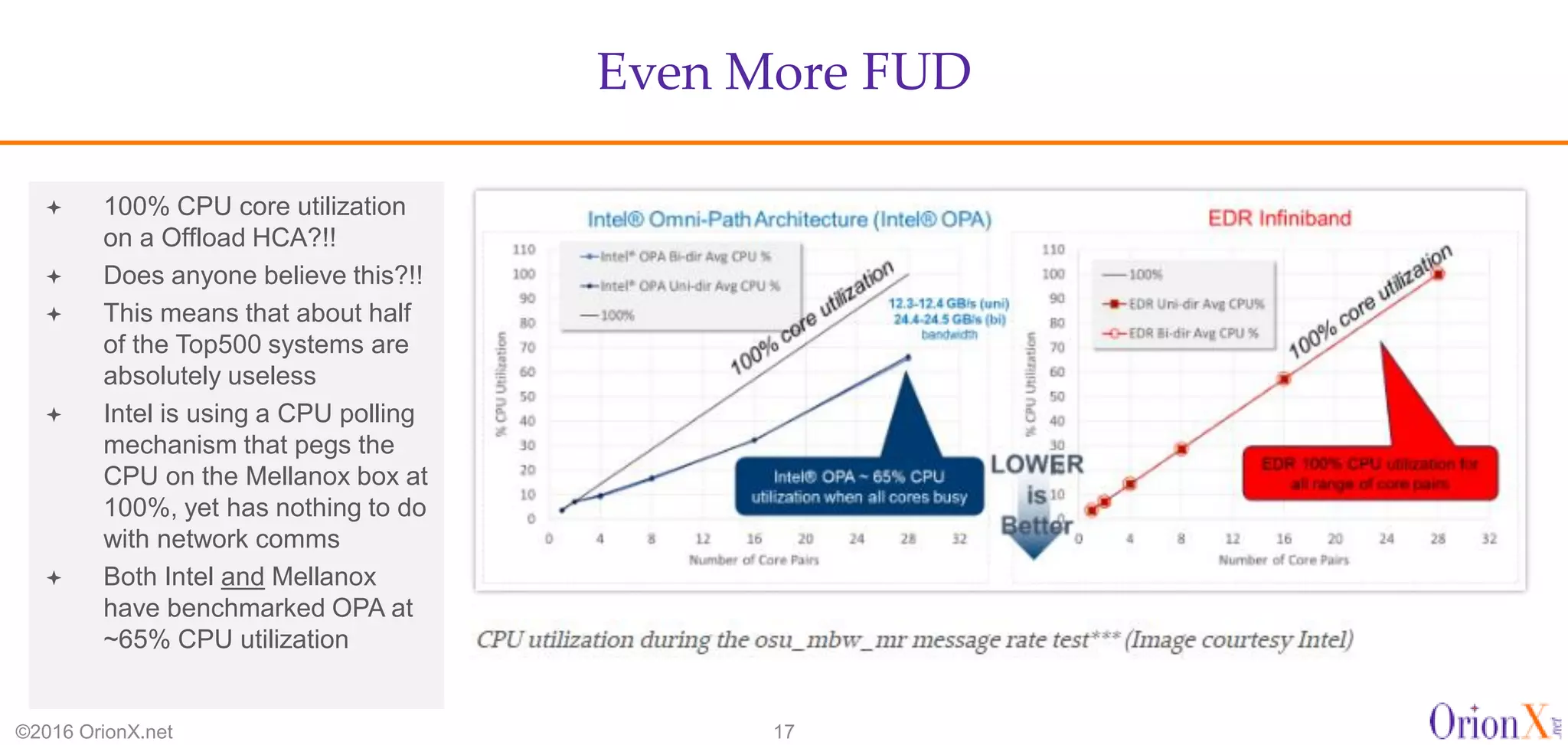
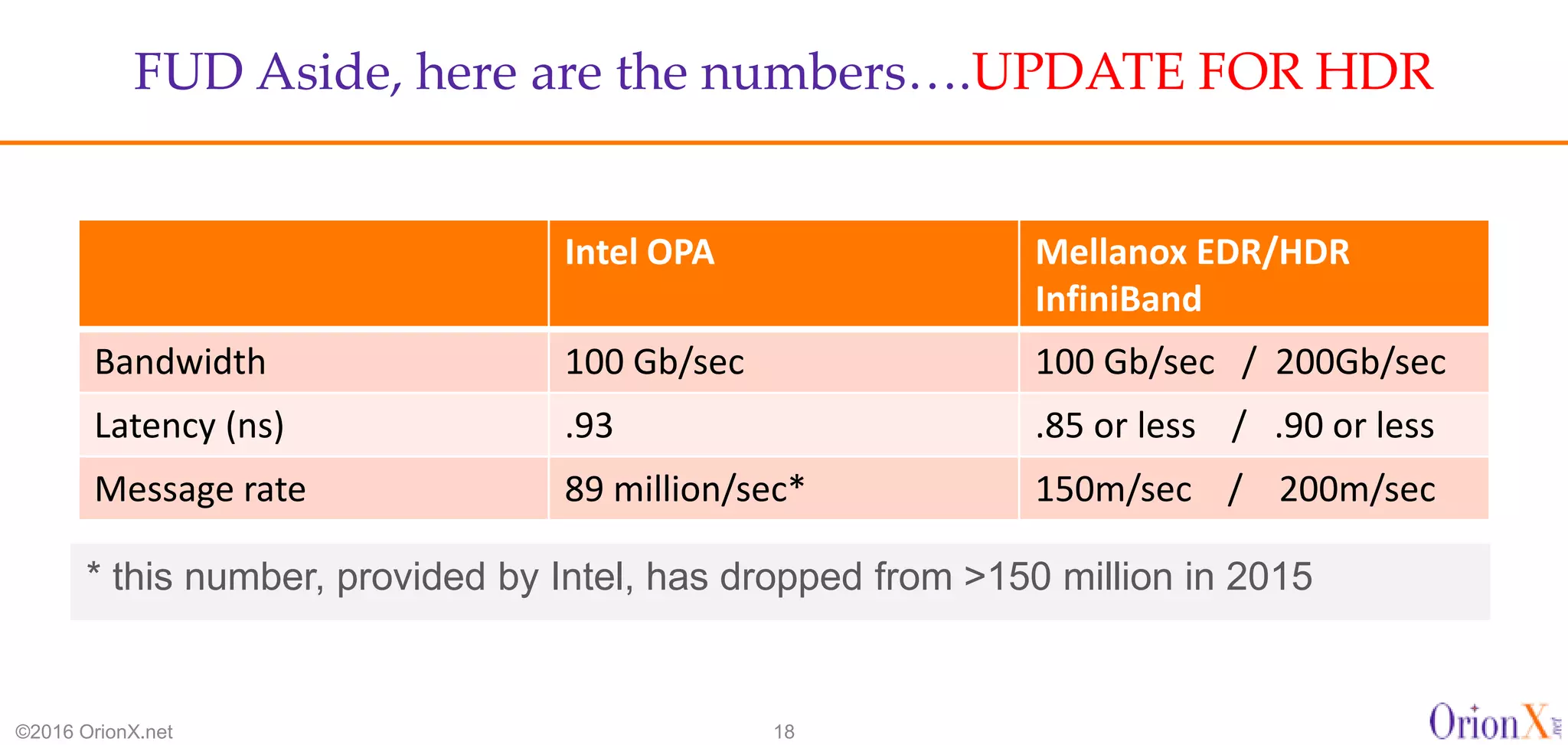
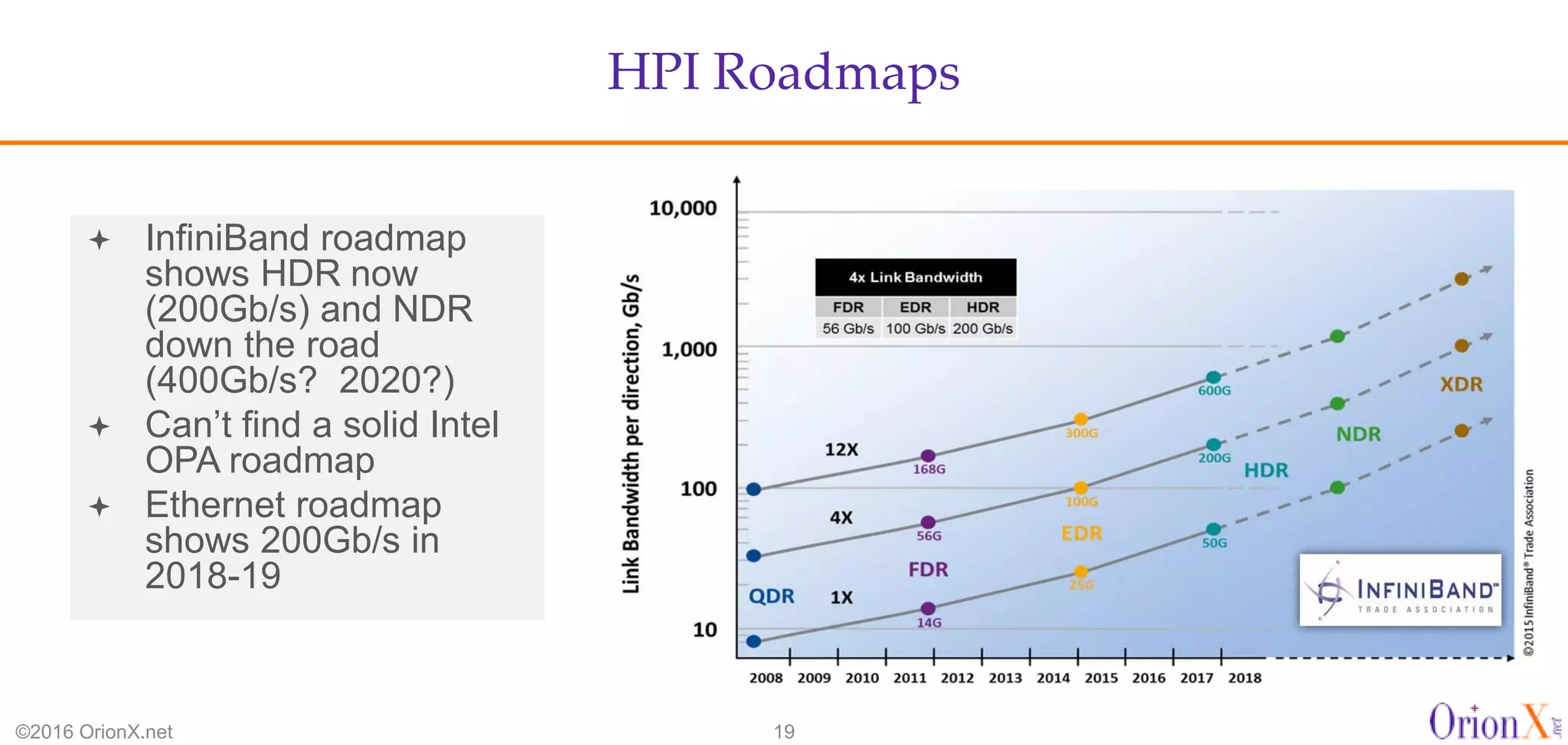
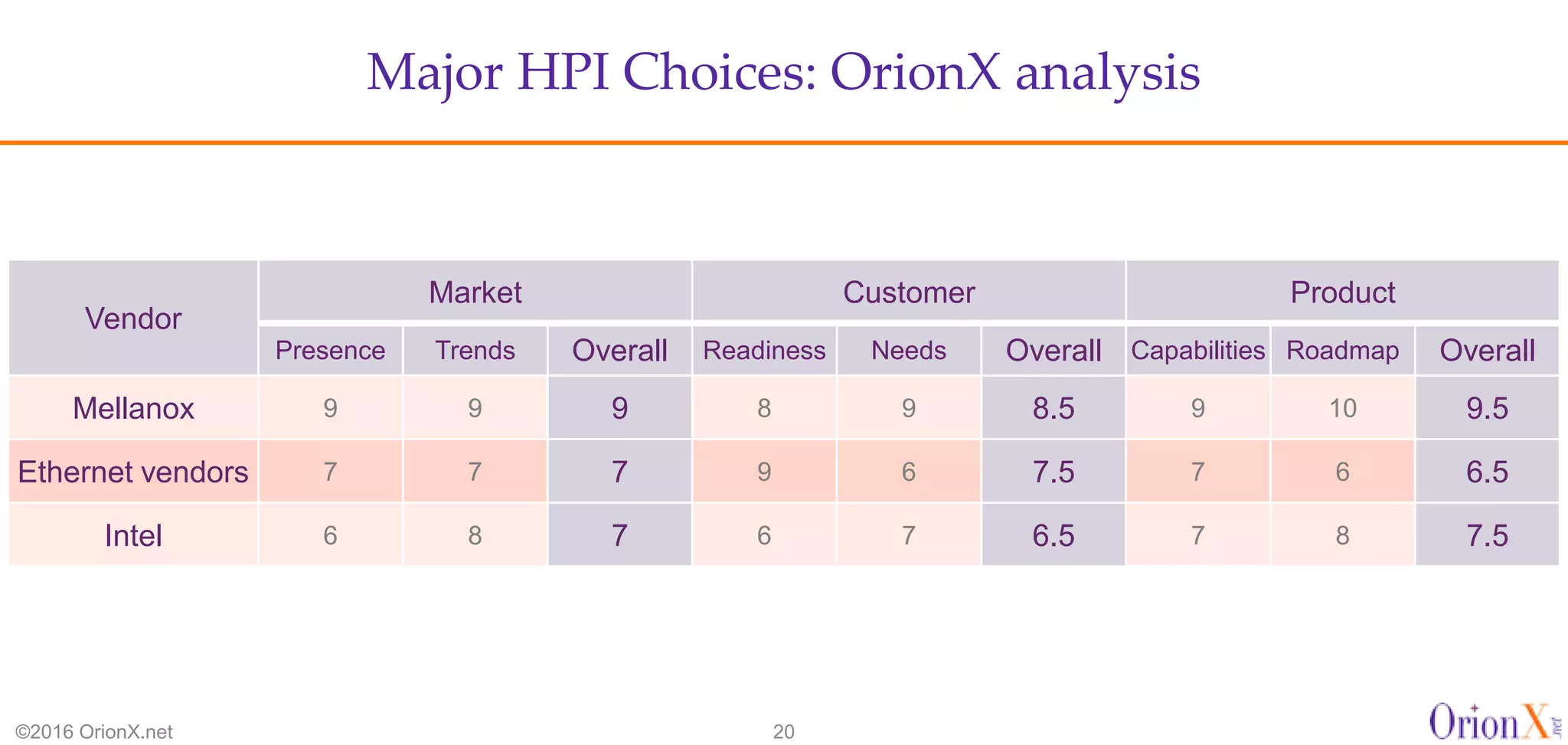
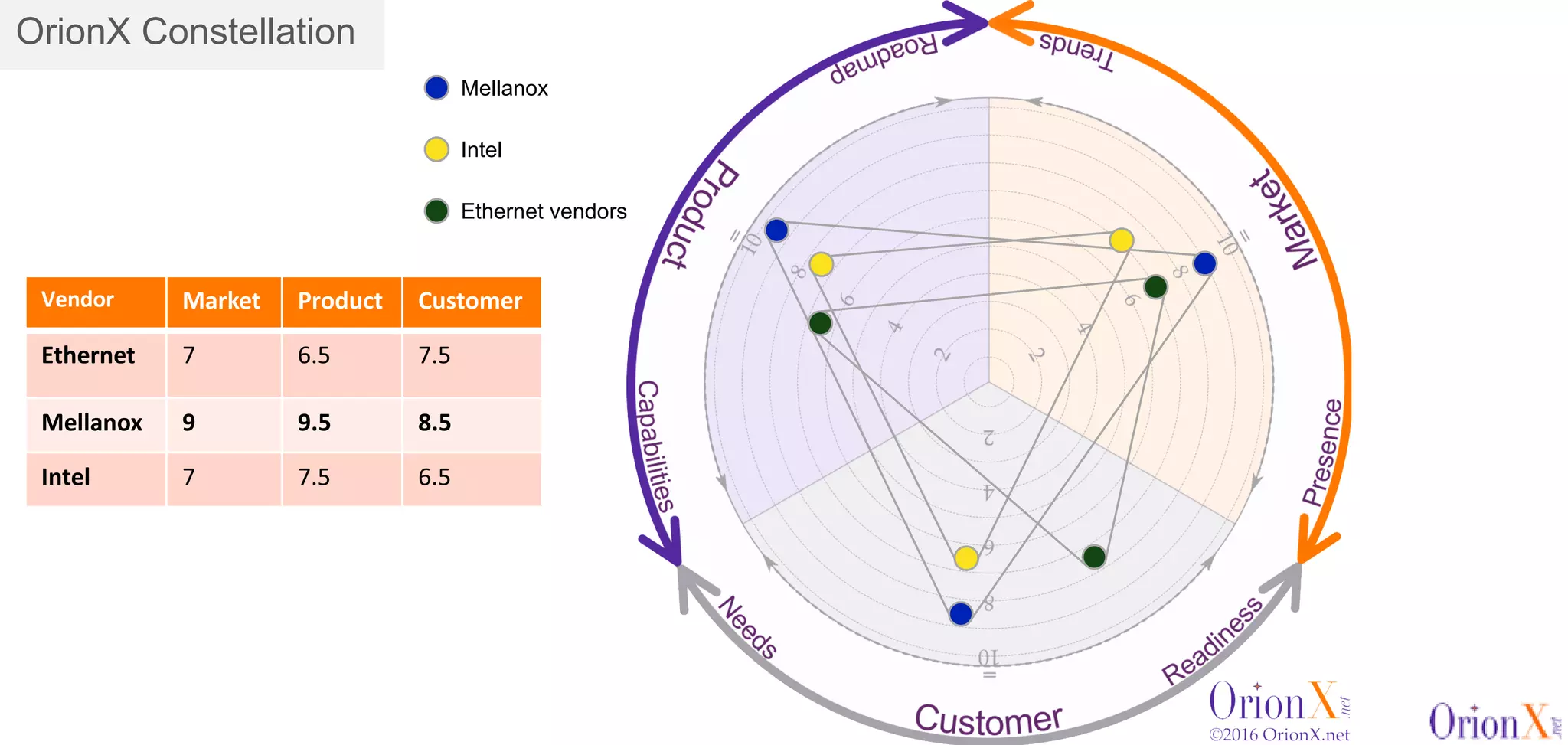
The document discusses the high-performance interconnects (HPI) market, detailing various HPI types, their performance, market presence, and technological differences. It highlights the dominance of Infiniband and evaluates newer entrants like Intel's Omni-Path architecture, as well as the challenges presented by onload versus offload processing methods. Key insights cover market trends, vendor readiness, and performance metrics critical for efficient high-bandwidth and low-latency networking solutions.