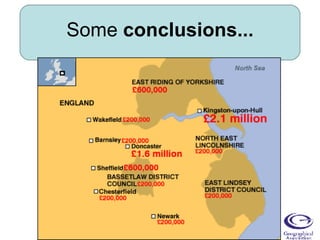
The document discusses the impact of the June 2007 floods in Yorkshire, exploring the causes, effects, and lessons learned from this significant weather event. It highlights the extensive damage, with over 8,600 households affected, and emphasizes the importance of flood risk management and resilience. Key statistics include £3 billion in insurance claims and ongoing challenges faced by impacted communities, particularly in Hull, one year after the event.

![High and Dry ? Geographical Lessons from the Yorkshire Floods of June 2007 Alan Parkinson Secondary Curriculum Development Leader Geographical Association [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/high-and-dry-1221683408075745-8/85/High-And-Dry-2-320.jpg)