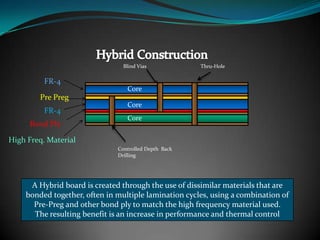
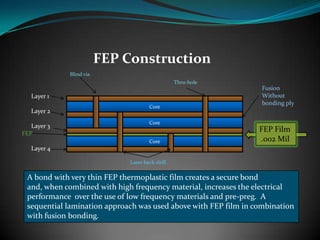
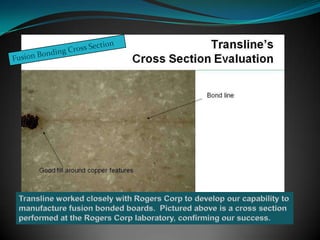
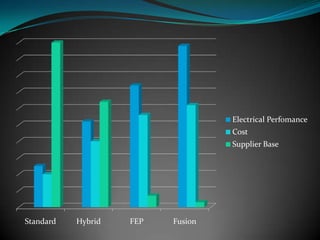
The document discusses various multilayer PCB lamination methods and their impact on performance and cost, highlighting four key types: standard, hybrid, fep, and fusion bonding. It emphasizes the benefits of advanced lamination techniques, particularly fusion bonding with PTFE, which offers superior electrical performance and durability. Transline Technology asserts its expertise in manufacturing fusion bonded PCBs and its success in increasing product performance for major clients like Lockheed Martin.