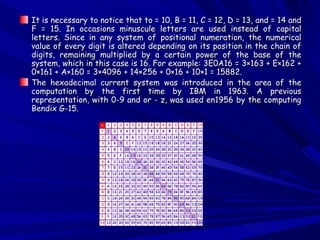
The hexadecimal system is a base-16 numeral system that uses 16 symbols to represent numbers. It is commonly used in computer science because each hexadecimal digit can represent 4 binary digits, allowing a byte of data to be easily represented with two hexadecimal characters. The symbols used are the numbers 0-9 and the letters A-F, with the letters representing the values 10-15. Values in hexadecimal notation are represented by a string of hexadecimal digits, with each digit multiplied by a power of 16 depending on its position.