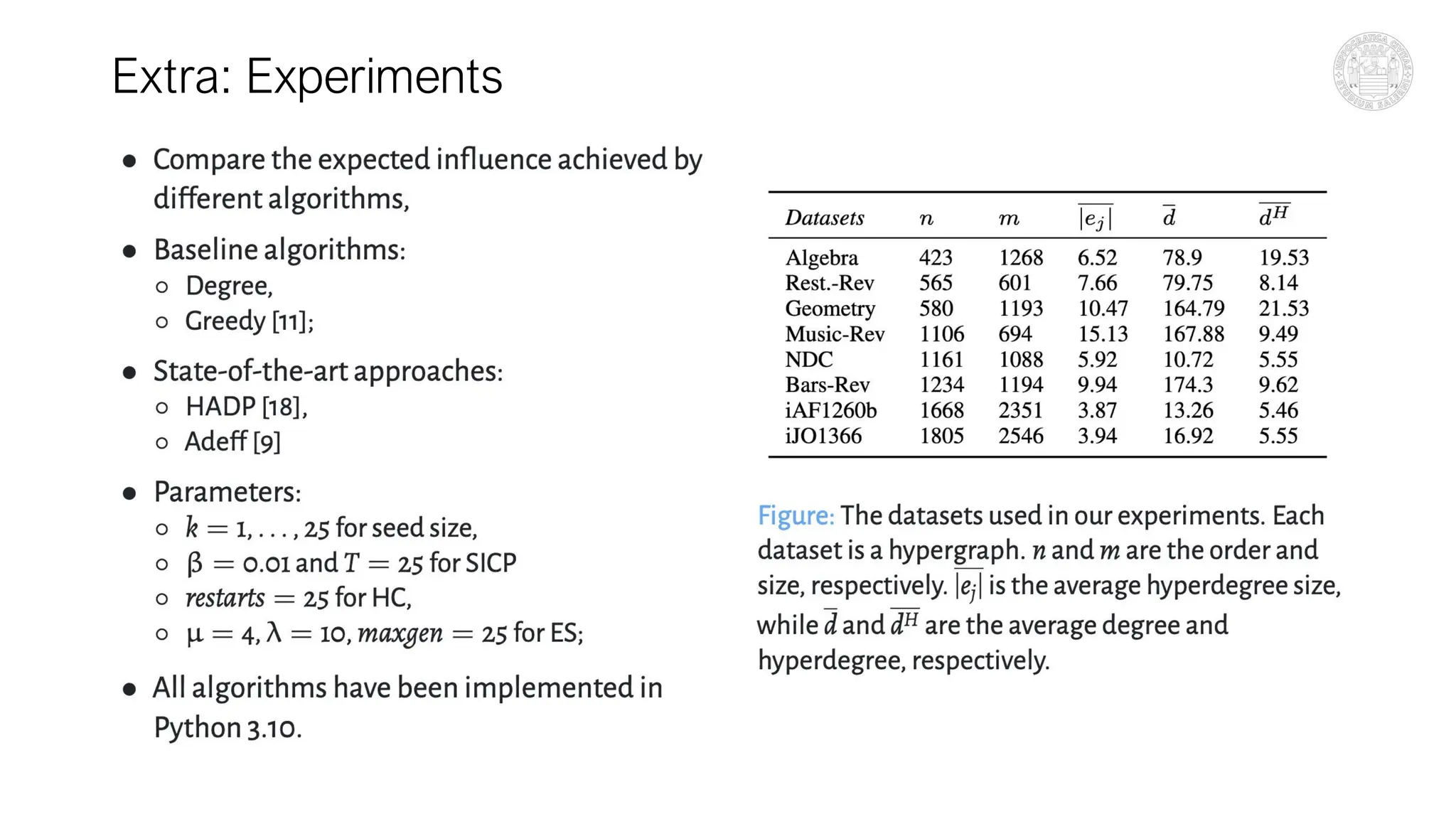
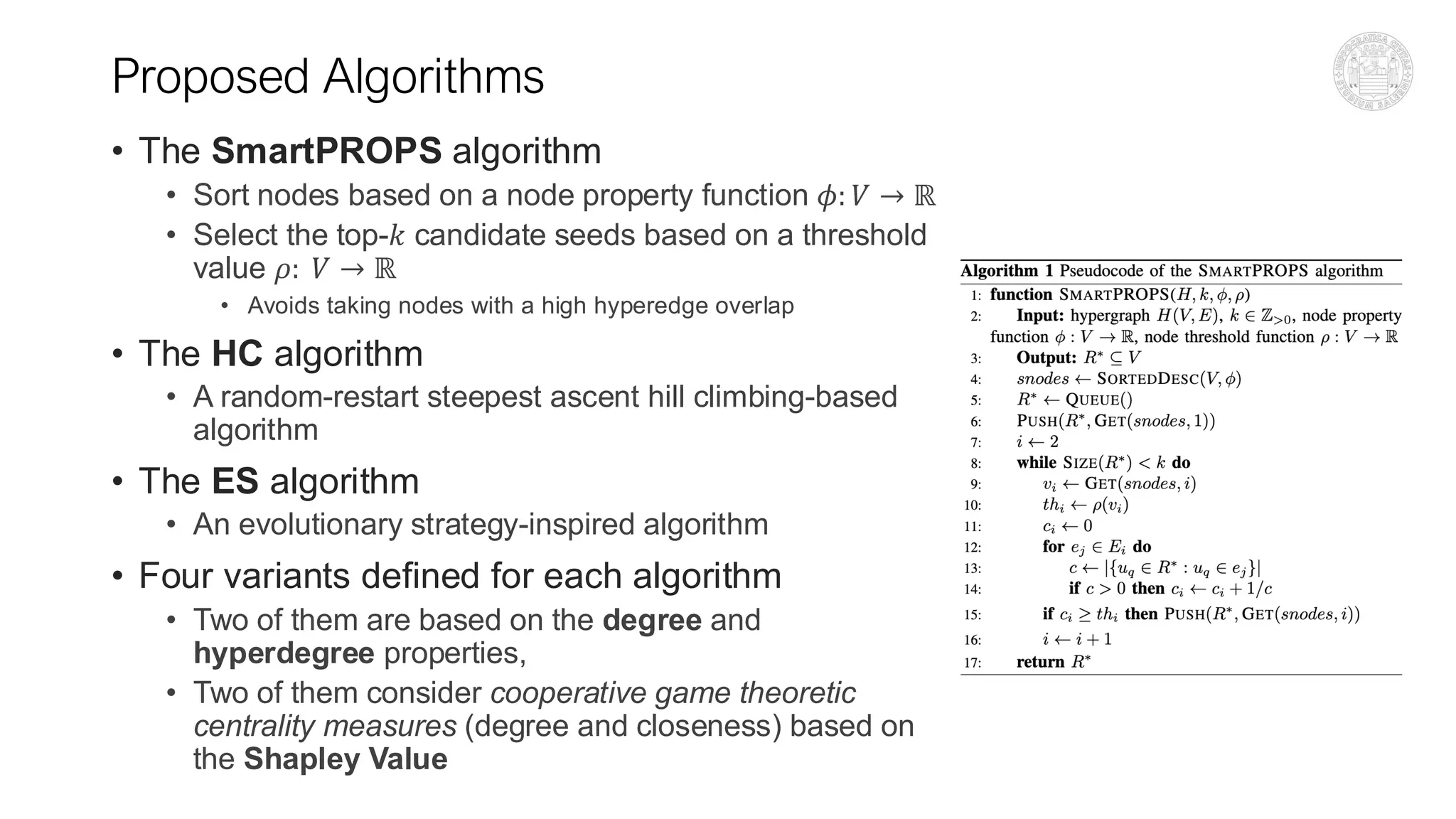
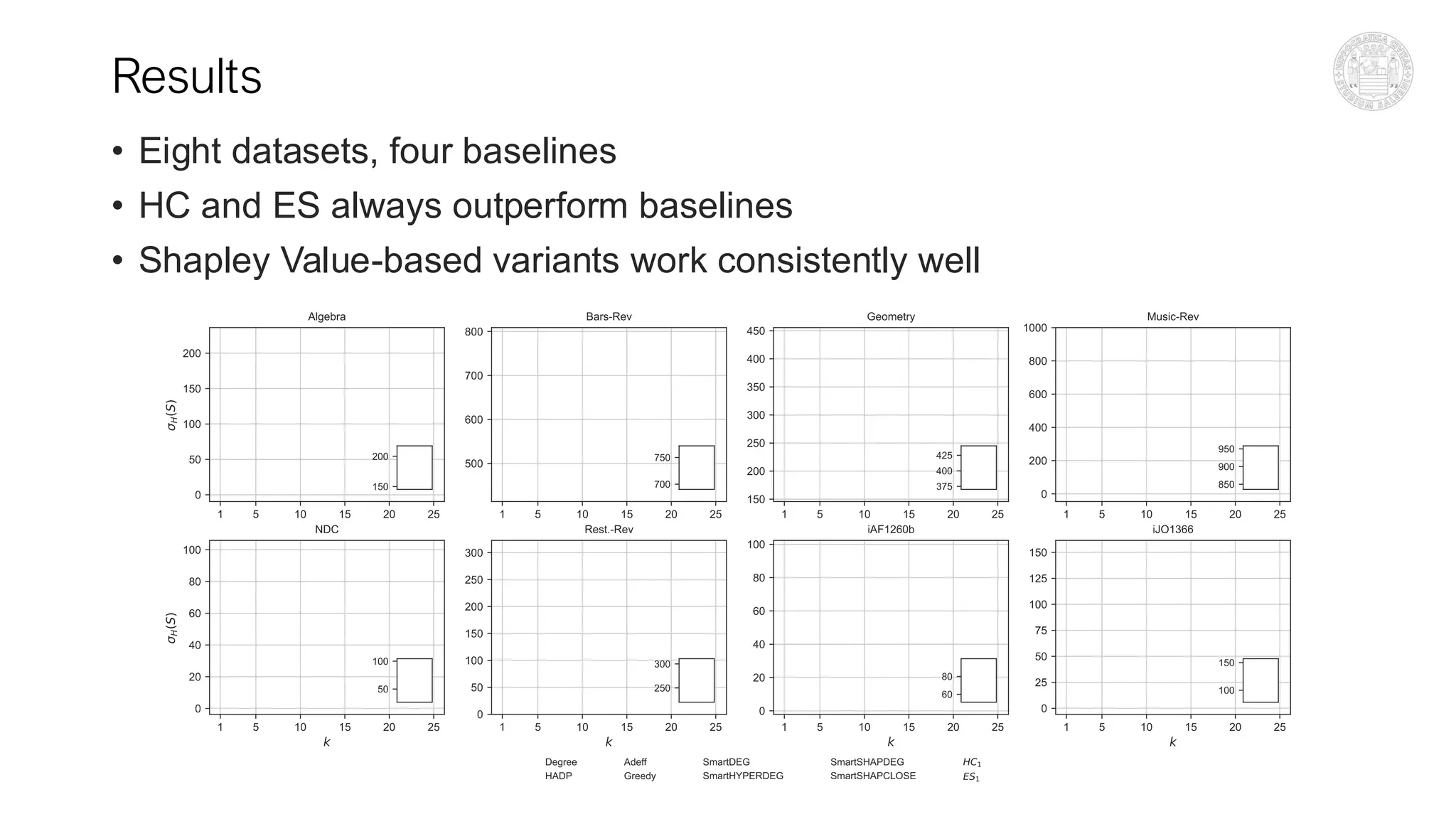
The document discusses algorithms for influence maximization (IM) in hypergraphs, which model higher-order interactions important for fields like marketing and social systems. Three main algorithms are proposed: SmartProps, HC (hill climbing), and ES (evolutionary strategies), with variations that utilize node properties and game-theoretic measures for improved performance. The proposed methods consistently outperform baseline approaches in simulations conducted on eight datasets, highlighting the significance of game-theoretic centrality in IM problems on hypergraphs.

![Context and Motivation
• Influence Maximization (IM)
• The aim is to find a set of nodes (seeds) in a given
network (e.g., a graph) that can maximize the spread of
information through the network under certain diffusion
processes
• Crucial for viral marketing, opinion formation, etc. [1,2]
• Higher-order Interactions
• Interactions that involve three or more entities
simultaneously
• Social systems, neuroscience, ecology, biology, etc. [3]
• Best modeled via hypergraphs [4]
• A hypergraph consists of nodes and hyperedges
• Hyperedge = subset of nodes
• What about IM on hypergraphs?
• Only a bunch of approaches in the last years [5,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aulettacauteruccioferraioli-aixia24-slide-241126135655-11f67dff/75/Heuristics-Approaches-for-the-Influence-Maximization-Problem-on-Hypergraphs-2-2048.jpg)
![Influence Maximization on Hypergraphs
• Given a hypergraph 𝐻 = 𝑉, 𝐸 , a value 𝑘 ∈ ℤ>0, and a diffusion process 𝜎𝐻
• Find a subset 𝑆∗
⊆ 𝑉 of 𝑘 nodes such that the expected number of infected
nodes is maximized:
𝑆∗
= 𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑆⊆𝑉, 𝑆 =𝑘𝜎𝐻(𝑆)
• Expected influence 𝜎𝐻 𝑆
• The number of reached nodes at the end of the process 𝜎𝐻 starting from the seed set 𝑆
• We consider the Suceptible-Infected (SI) model with Contact Process (CP) [6]
• A node can be either in a susceptible (S) or infected (I) state,
• An S-node can be infected by each of its neighbors in I-state with probability 𝛽
• The process iterates for 𝑇 > 0 steps](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aulettacauteruccioferraioli-aixia24-slide-241126135655-11f67dff/75/Heuristics-Approaches-for-the-Influence-Maximization-Problem-on-Hypergraphs-3-2048.jpg)


![Bibliography
[1] Kempe, D., Kleinberg, J., Tardos, E., 2003. Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network, in: KDD,
pp. 137–146
[2] Amoruso, M., Anello, D., Auletta, V., Cerulli, R., Ferraioli, D., Raiconi, A., 2020. Contrasting the spread of
misinformation in online social networks. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 69, 847–879. AI Access Foundation
[3] Battiston, F., Cencetti, G., Iacopini, I., Latora, V., Lucas, M., Patania, A., Young, J.G., Petri, G., 2020. Networks
beyond pairwise interactions: Structure and dynamics. Physics Reports 874, 1–92. Elsevier.
[4] Aksoy, S.G., Joslyn, C., Marrero, C.O., Praggastis, B., Purvine, E., 2020. Hypernetwork science via high-order
hypergraph walks. EPJ Data Science 9, 16. Springer.
[5] Xie, M., Zhan, X.X., Liu, C., Zhang, Z.K., 2023. An efficient adaptive degree-based heuristic algorithm for influence
maximization in hypergraphs. Information Processing & Management 60, 103161. Elsevier
[6] Gong, X., X., H.W., Wang, Chen, C., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., 2024. Influence maximization on hypergraphs via multi-
hop influence estimation. Information Processing & Management 61, 103683. Elsevier](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aulettacauteruccioferraioli-aixia24-slide-241126135655-11f67dff/75/Heuristics-Approaches-for-the-Influence-Maximization-Problem-on-Hypergraphs-8-2048.jpg)