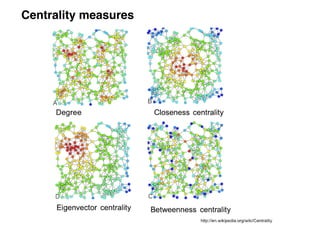
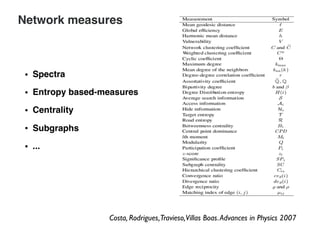
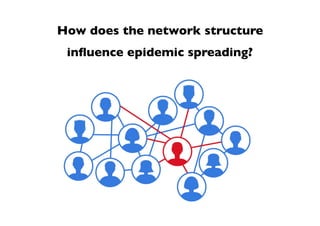
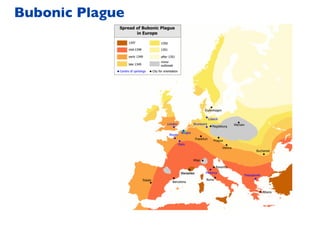
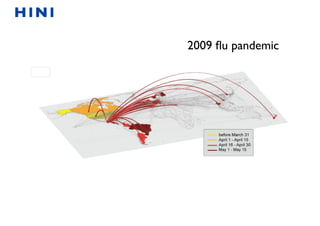
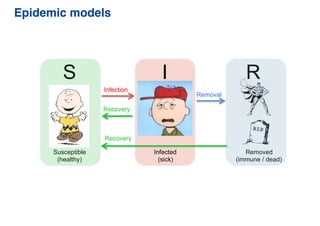
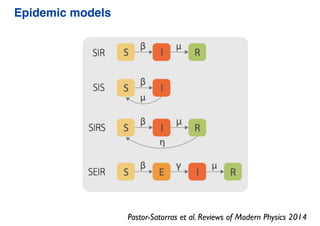
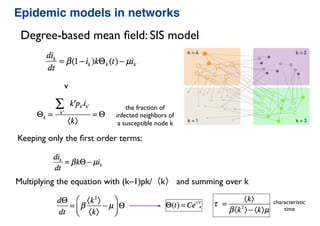
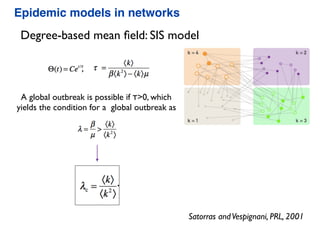
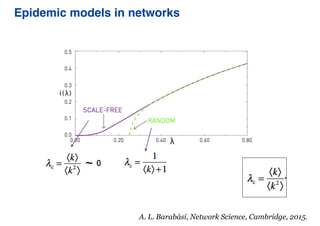
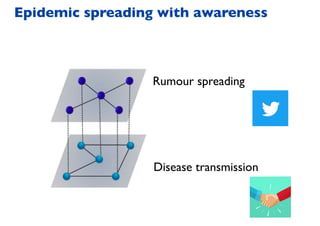
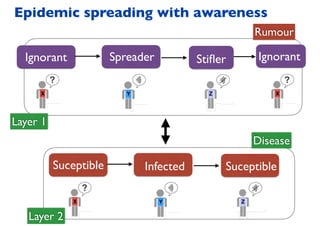
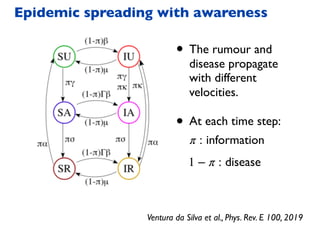
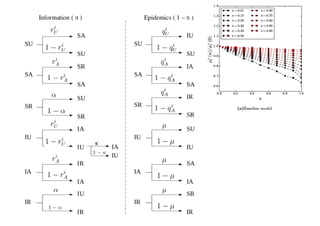
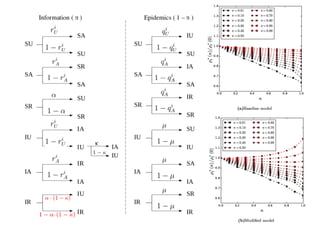
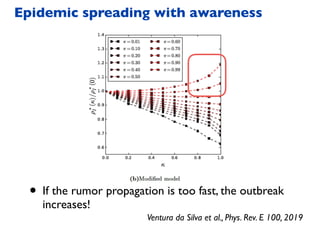
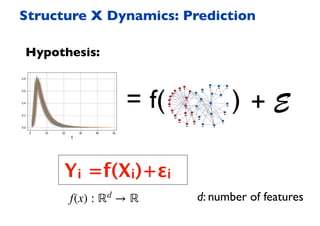
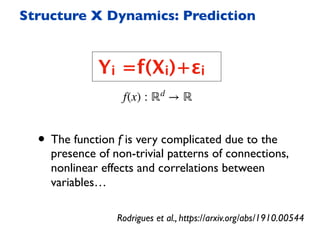
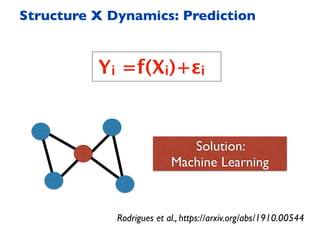
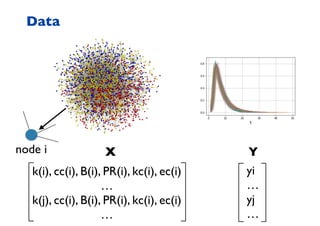
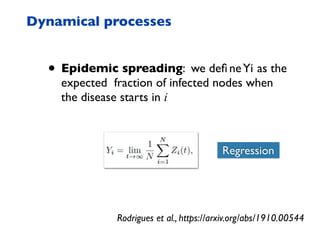
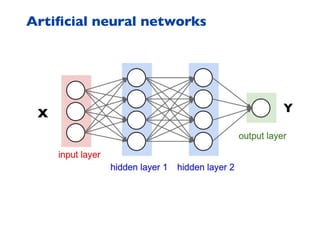
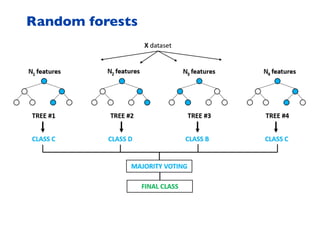
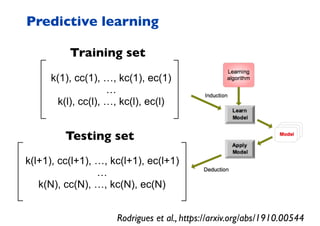
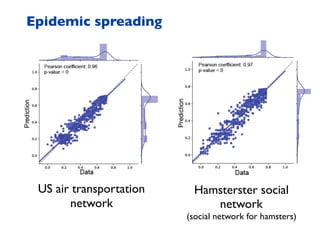
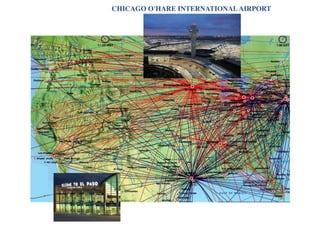
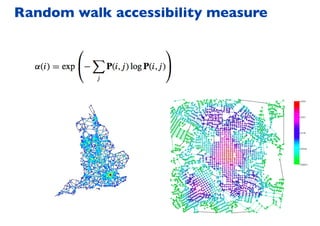
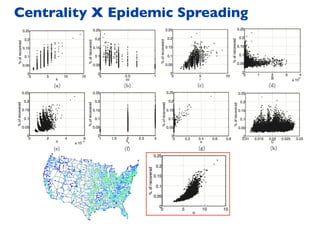
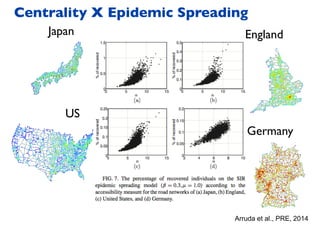
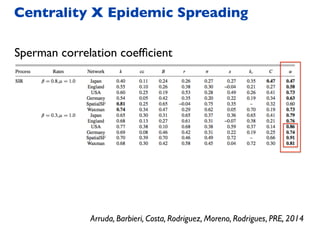
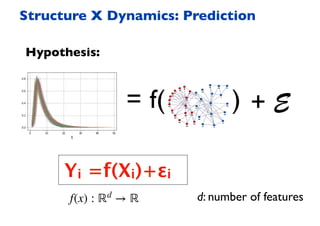
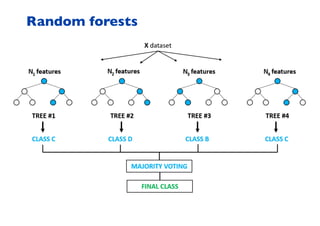
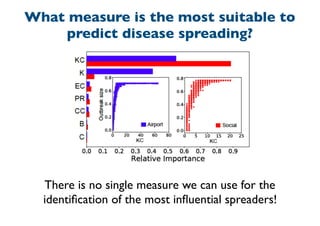
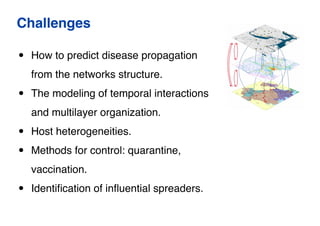
This document summarizes a presentation on machine learning of epidemic processes in networks. It discusses using machine learning to predict epidemic spreading from network structure. Specifically, it covers using features like degree, clustering, and centrality measures as inputs to algorithms like random forests and neural networks to predict the fraction of infected nodes. The best approach uses a combination of network measures, not a single measure. This allows machine learning to help identify influential spreaders and understand how network structure influences epidemic dynamics.



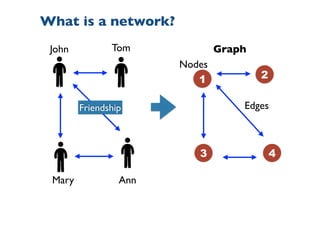

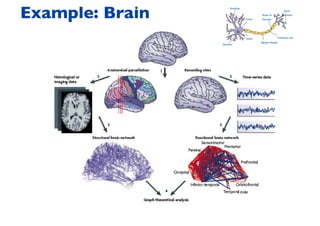
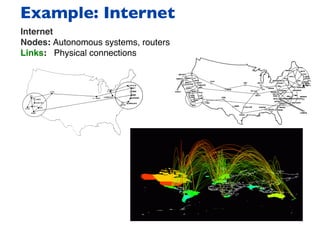
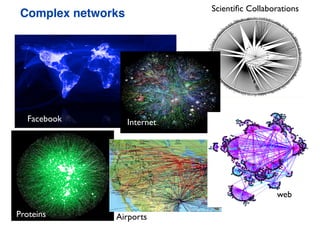

![To describe the network topology,
we need networks measures.
x = [x1, x2,…]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-sp-2020-ictp-200304030944/85/Machine-Learning-of-Epidemic-Processes-in-Networks-10-320.jpg)