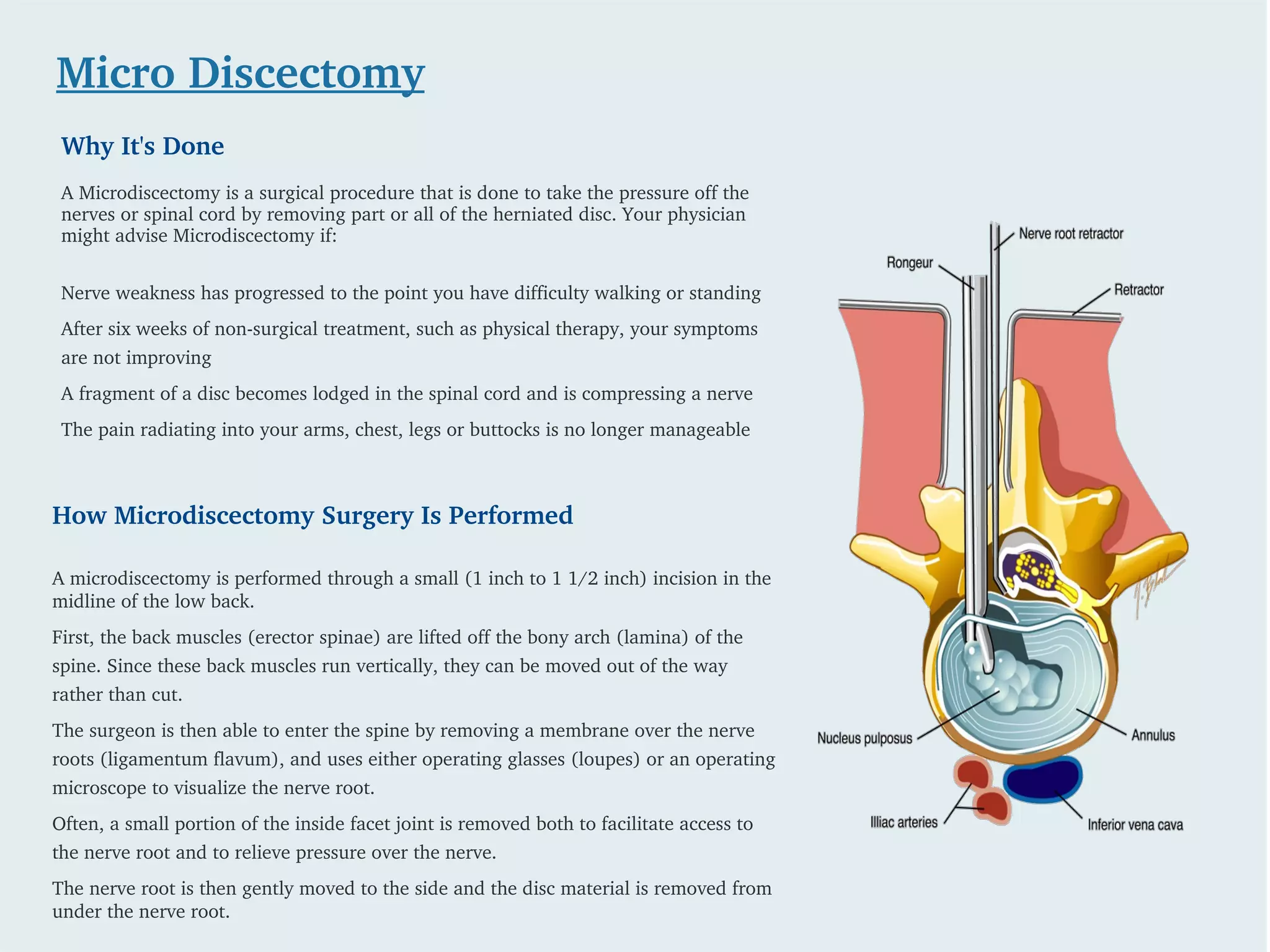
Herniated disc surgery is typically recommended when conservative treatments fail and symptoms such as muscle weakness or bowel control issues persist. Procedures like microdiscectomy involve removing part or all of the herniated disc through a small incision to relieve nerve pressure, while laminotomy and laminectomy involve removing portions of the lamina to alleviate nerve compression. Although these surgeries can provide symptom relief, they do not address the underlying causes of herniation, and preventative measures are advised post-surgery.